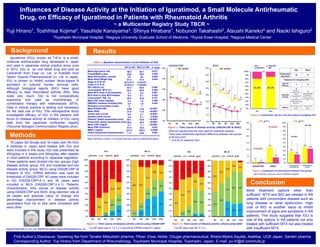
This study investigated the efficacy of iguratimod (IGU) in treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients based on their disease activity at the start of IGU treatment. 78 RA patients were divided into two groups based on their DAS28-CRP scores: a high disease activity group (HG) and a moderate/low disease activity group (MLG). Patients in the HG had significantly higher disease activity scores and worse symptoms at baseline compared to the MLG. While both groups saw improvements in their disease activity scores over 24 weeks of IGU treatment, the HG saw significantly greater decreases in their scores and percentages of improvement compared to the MLG. The results suggest that IGU can be an effective treatment for RA