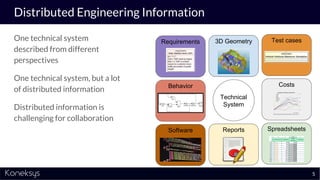
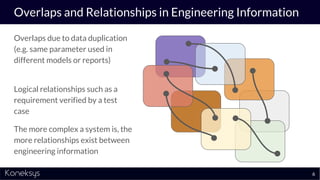
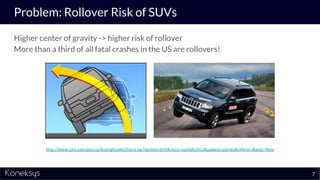
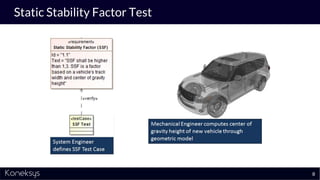
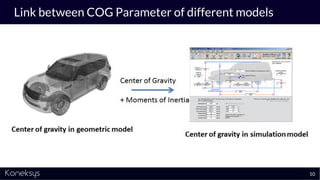
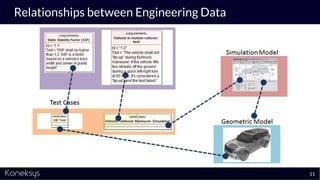
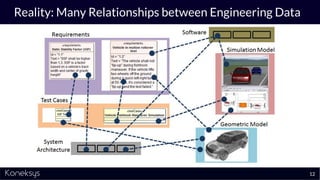
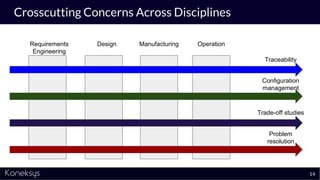
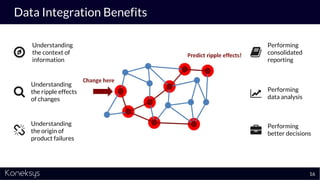
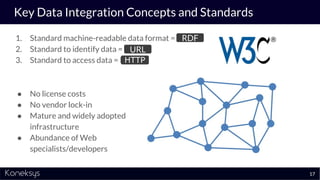
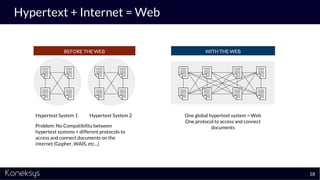
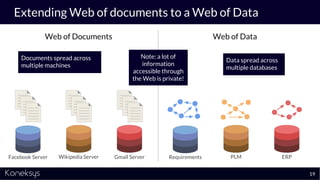
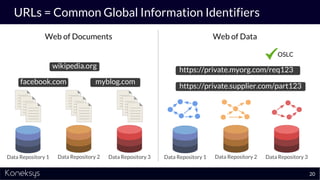
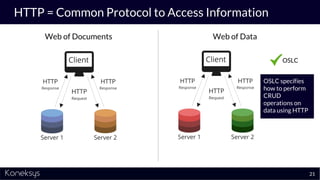
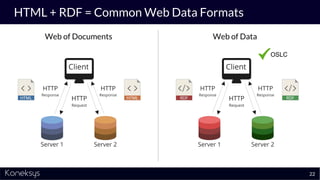
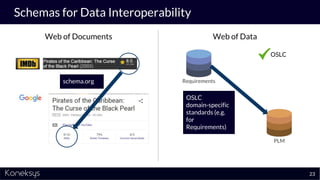
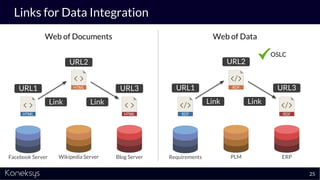
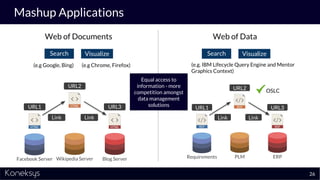
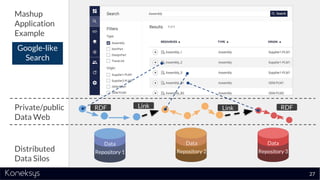
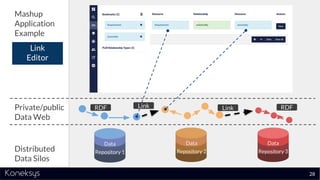
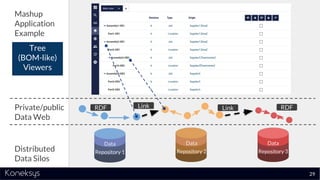
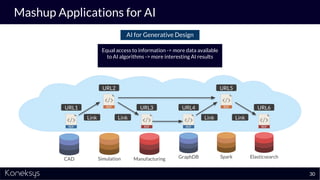
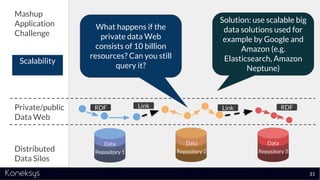
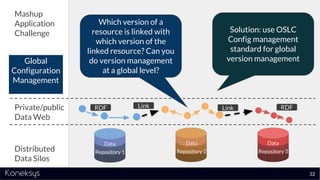
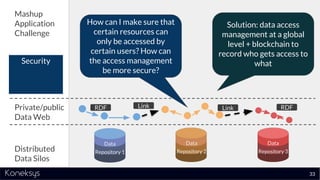
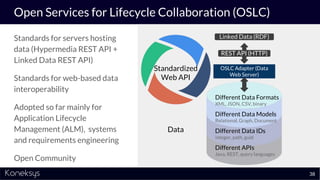
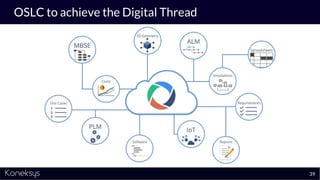
The document discusses the importance of achieving a digital thread through the integration of Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) and Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) using the Open Services for Lifecycle Collaboration (OSLC) framework. It highlights current challenges in engineering collaboration, the complexities of managing distributed information, and the advantages of data integration for better decision-making. Konekys, the organization behind the presentation, focuses on creating data integration solutions and promoting OSLC standards to enhance collaboration across various engineering disciplines.