The document discusses accounting for plant assets, including:
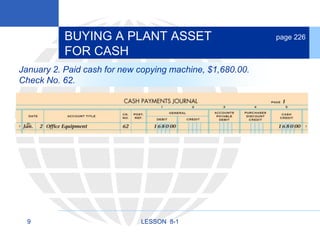
1. Acquiring plant assets through purchase for cash or on account.
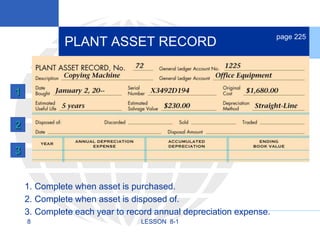
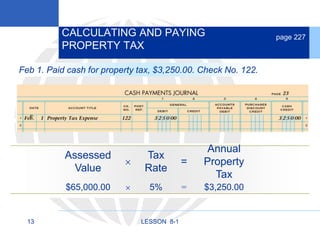
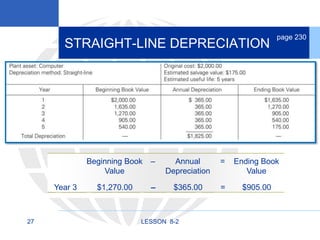
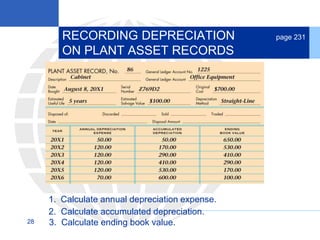
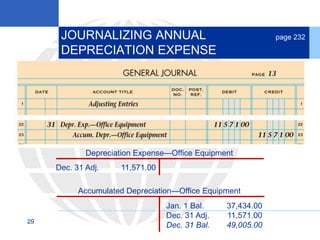
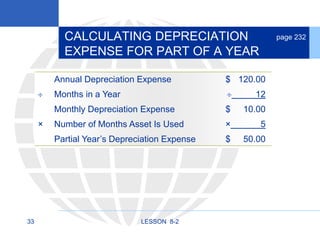
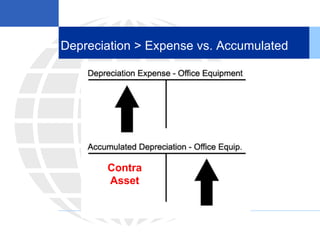
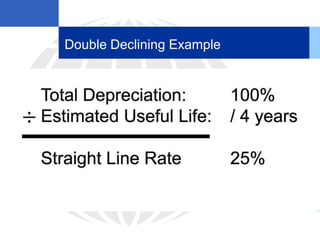
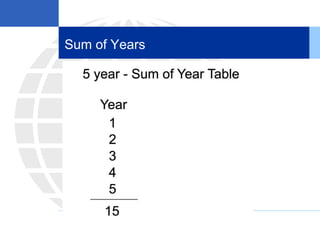
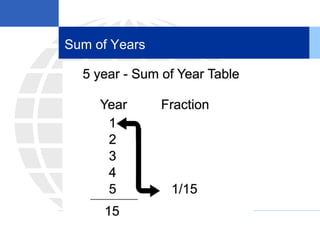
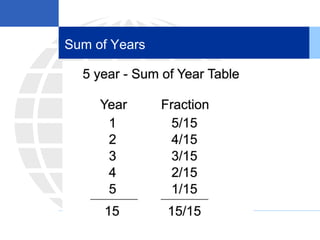
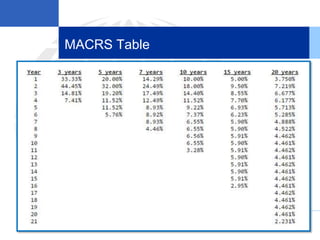
2. Calculating and recording annual depreciation expense using the straight-line method based on original cost, salvage value, and estimated useful life.
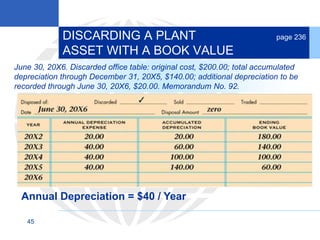
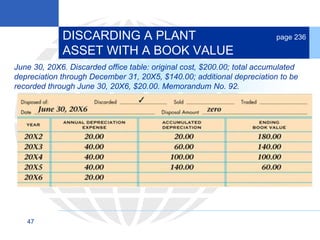
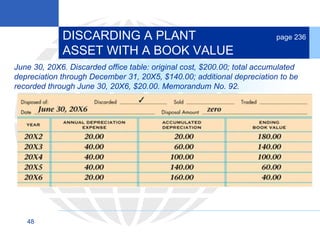
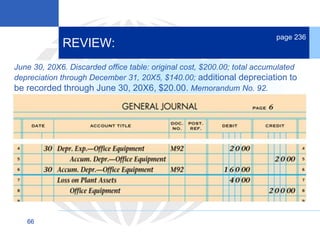
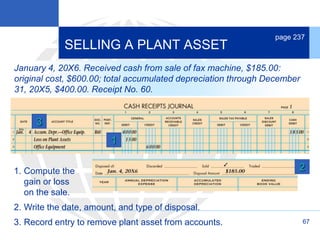
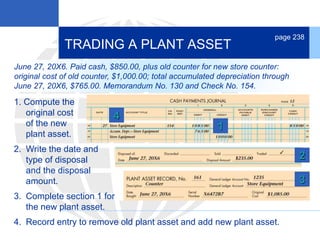
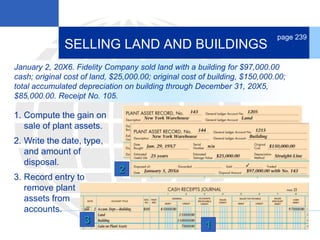
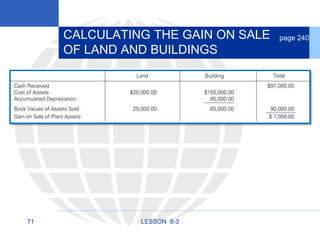
3. Disposing of plant assets by discarding, selling, or trading, which involves recording any additional depreciation, removing the asset, and updating the plant asset record.