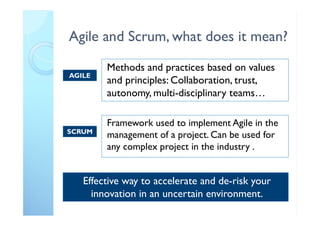
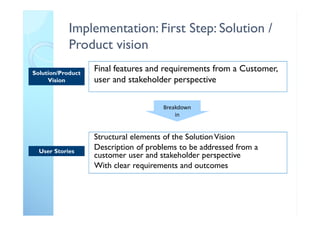
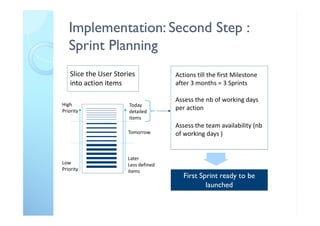
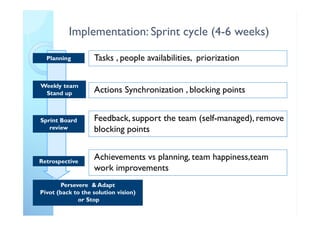
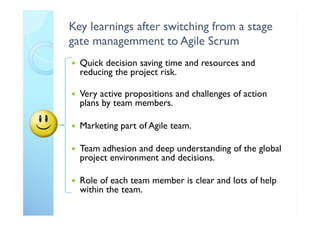
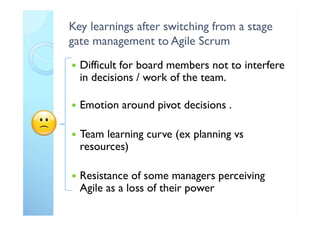
The document outlines the principles and practical implementation of Agile and Scrum methodologies to enhance project delivery and innovation management. It highlights the importance of customer-centric approaches, self-managed teams, and the need for a cultural shift within organizations for successful Agile adaptation. Key learnings emphasize quick decision-making, team clarity, and the necessity of an Agile coach to guide the transition.