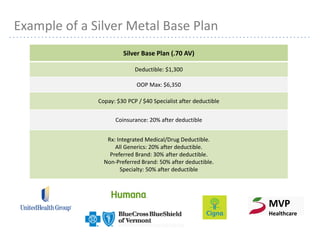
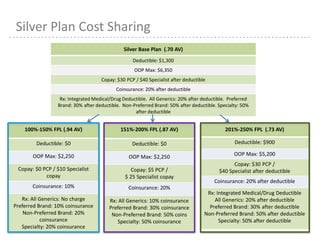
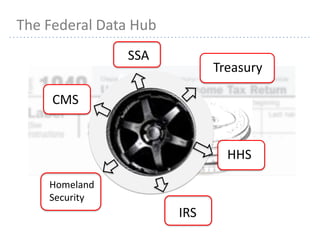
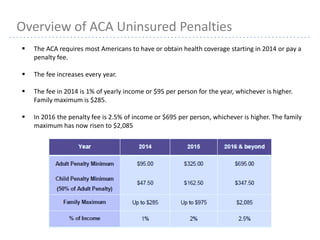
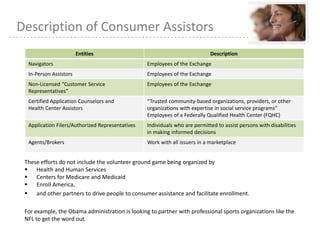
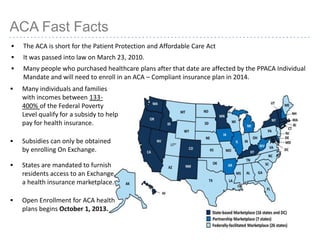
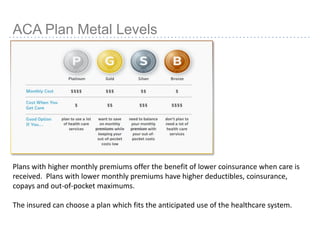
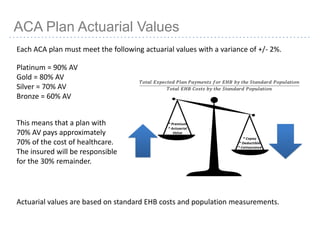
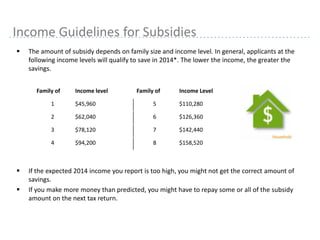
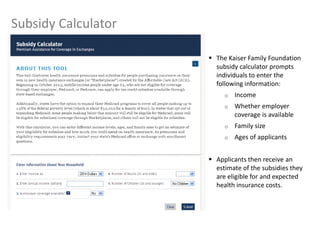
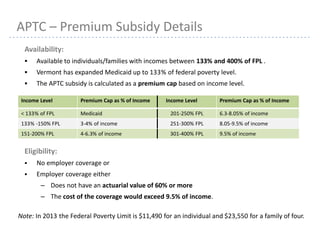
This document provides information about navigating healthcare options under the Affordable Care Act (ACA). It explains that individuals can receive subsidies to help pay for health insurance purchased on exchanges if their income is between 133-400% of the federal poverty level. It also outlines the penalties for not having health insurance ("individual mandate") and details the metal tiers of ACA-compliant health plans (platinum, gold, silver, bronze). Open enrollment begins on October 1, 2013.






![15
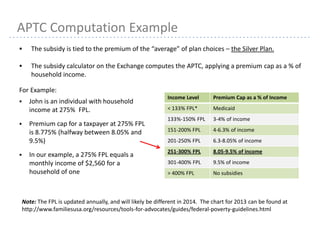
APTC Computation Example continued
If the Silver Plan costs $384/month and John has a monthly income of $2,560 :
– His premium subsidy equals the difference between plan cost and $224.64 [8.775% x $2,560
monthly income]
Individuals may select any plan and still receive the tax credit.
The amount of the tax credit may not exceed the plan premium. Since John is eligible for a
$159.36/month tax credit:
– If he selects a less expensive plan with a cost of $150/month, John can only receive a tax credit of
$150/month
– If he selects a more expensive plan with a cost of $500/month, he will owe $340.64 monthly:
Tax credit: $384 minus $224.64 = $159.36/month
His plan cost: $500 minus $159.36 = $340.64/month](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acapresentationonexchanges-130926095523-phpapp01/85/Aca-presentation-on-exchanges-15-320.jpg)