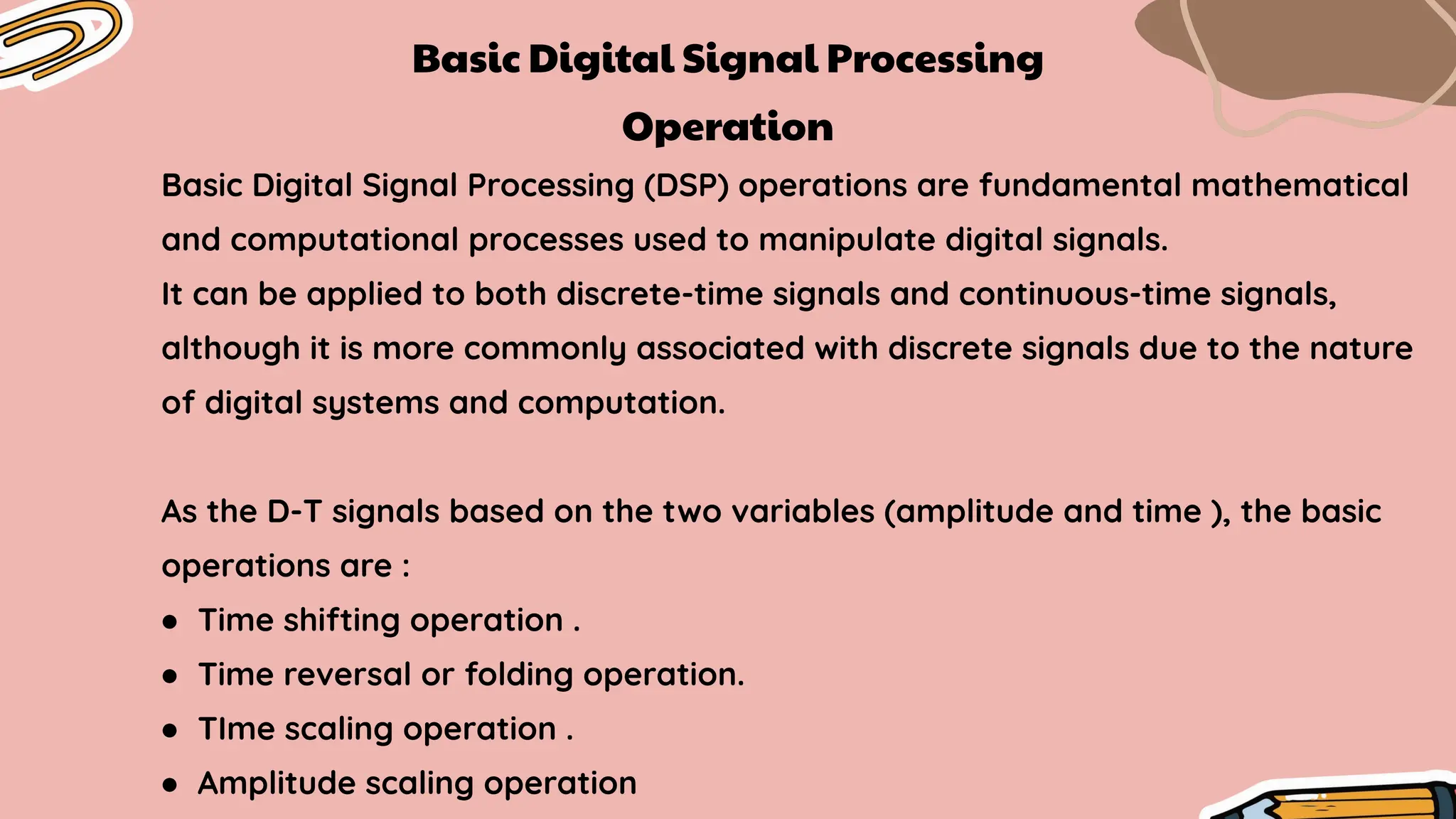
The document presents an overview of basic digital signal processing (DSP) operations, including time shifting, time reversal, time scaling, and amplitude scaling. It details how these operations manipulate digital signals and provides examples and mathematical representations for each operation. Various applications of these operations, such as filtering and signal reconstruction, are also discussed.





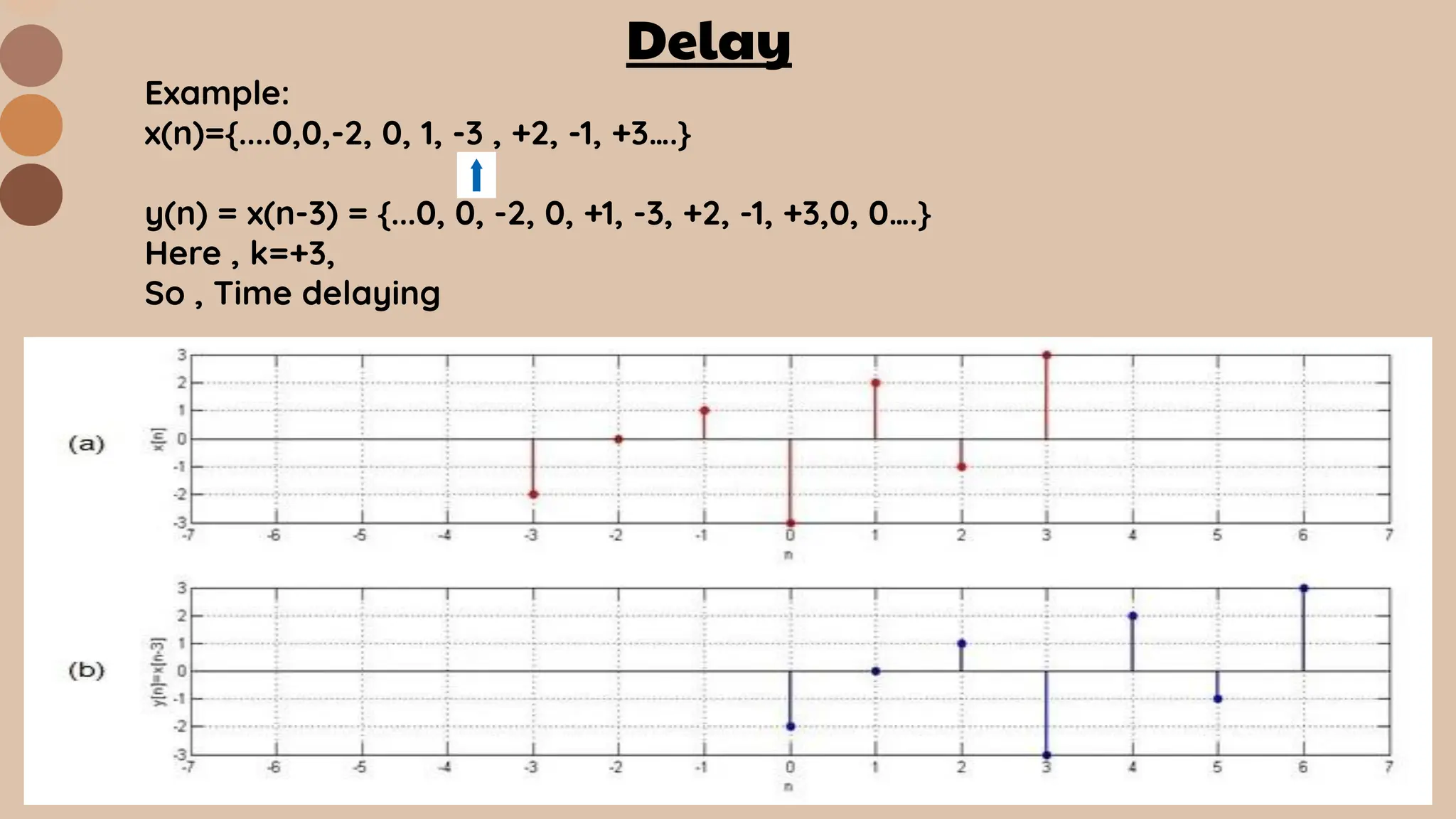
![TIME SHIFTING
Time shifting refers to the operation of shifting a signal along the time axis by a certain
amount. Time shifting modifies the temporal alignment of a signal without altering its
amplitude or shape.
Mathematically, time shifting can be represented as :
Input Output
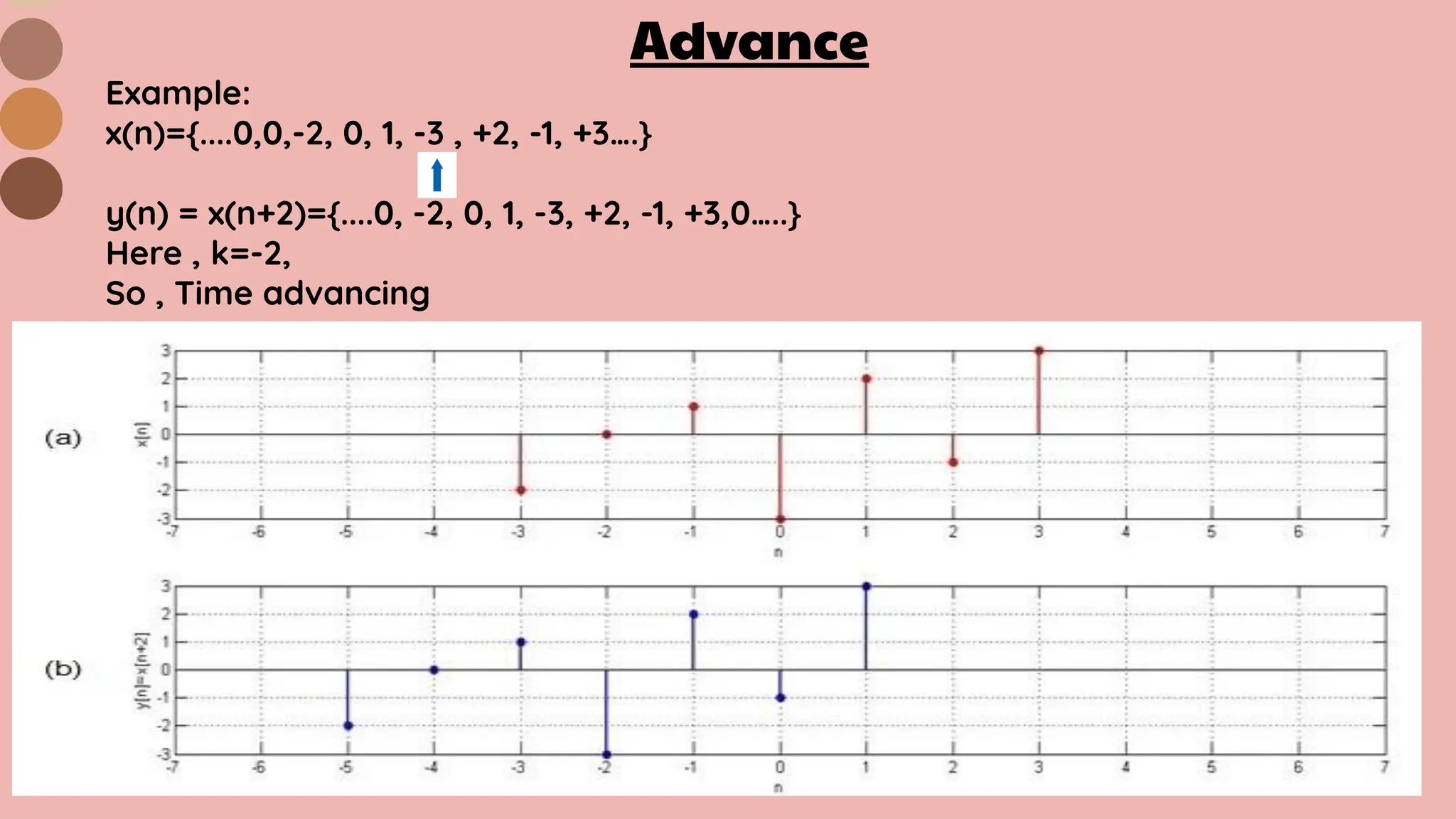
x[n] y[n]= x[n-k]
Where k=Integer = +ve or -ve
Types of Time Shifting :
1. Delay (when k= +ve)
2. Advance (when k= -ve)
Time Shifting Operation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group-9-240608191101-3dd18c6a/75/About_dsp_convolution_correlations_andPorperties-7-2048.jpg)
![TIME REVERSING
Time-reversing is a fundamental operation that involves reversing the order of samples in a
signal with respect to time. This operation can be applied to both discrete-time signals and
continuous-time signals, although in DSP, it's primarily discussed in the context of discrete-time
signals.
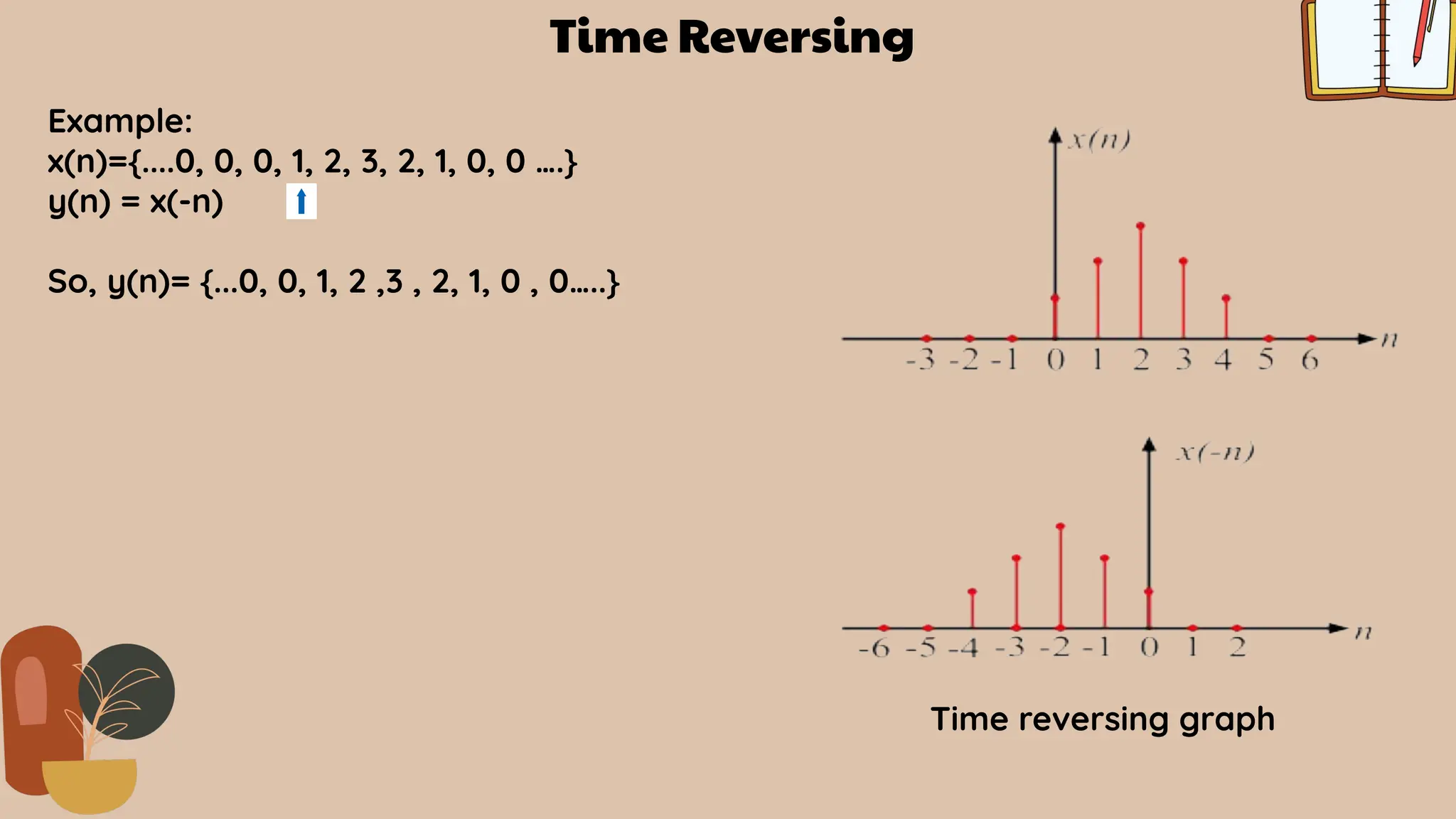
Mathematically, time reversing can be represented as :
Input Output
x[n] y[n]= x[-n]
The output function resulting from time-reversal as being a mirrored version of the input
function with respect to time.It effectively flips the signal around a vertical axis located at
the midpoint of the signal's duration.
Time Reversing Operation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group-9-240608191101-3dd18c6a/75/About_dsp_convolution_correlations_andPorperties-10-2048.jpg)
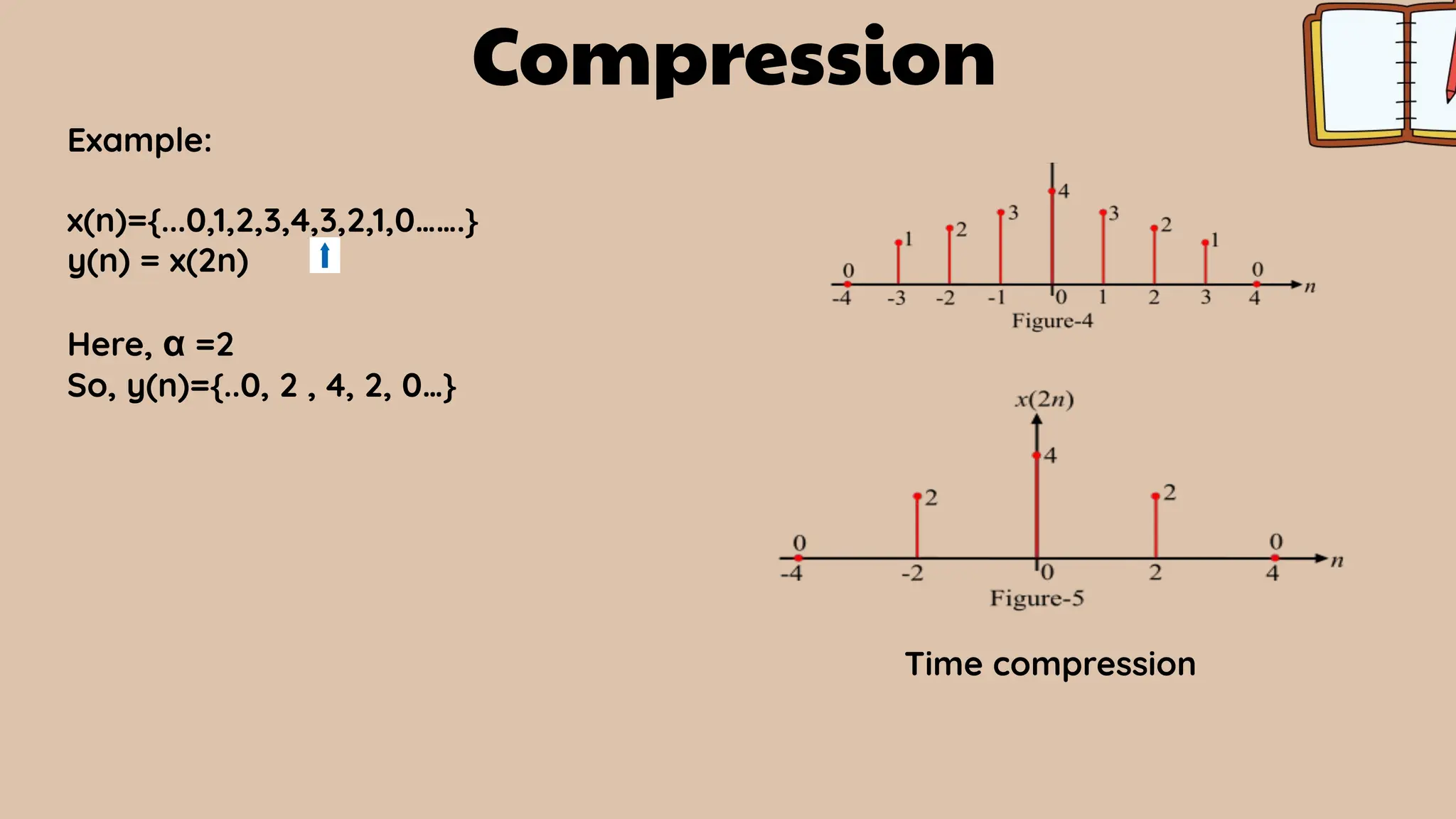
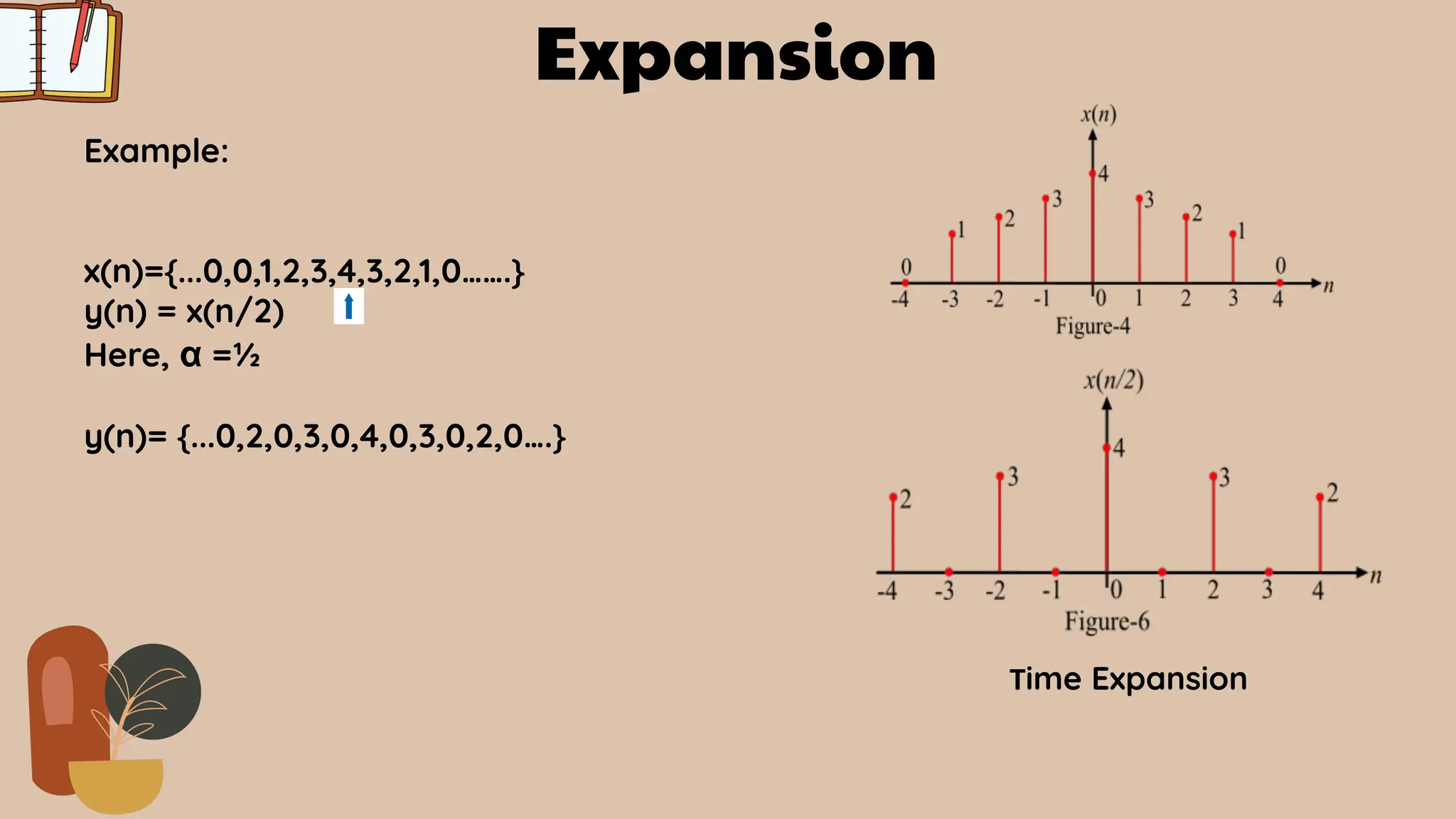
![Time Scaling
Time scaling refers to the process of altering the rate at which a signal progresses
through time without changing its fundamental characteristics. It involves
compressing or expanding the time axis of a signal.
Mathematically, For a discrete-time signal x[n], time scaling by a factor α results in
a new signal y[n] given by:-
y[n] = x[αn]
Types of Time Scaling:
1. Compression (when α>1 )
2. Expansion (when α<1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group-9-240608191101-3dd18c6a/75/About_dsp_convolution_correlations_andPorperties-12-2048.jpg)