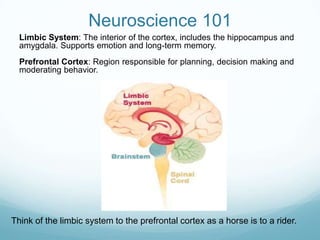
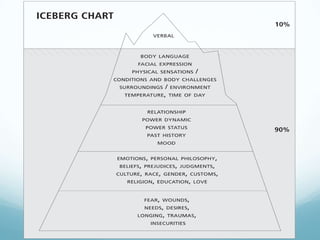
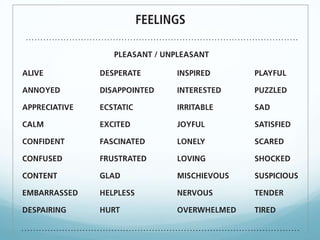
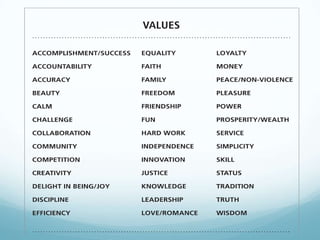
The document discusses a new model for enhancing organizational security through peacebuilding, emphasizing the importance of emotional intelligence and understanding user behavior in the context of security practices. It highlights the limitations of traditional security approaches, the influence of stress on decision-making, and the role of empathy in fostering effective communication. Ultimately, it advocates for a collaborative partnership with users to achieve mutual security goals, framed within the concept of 'cyber peace'.