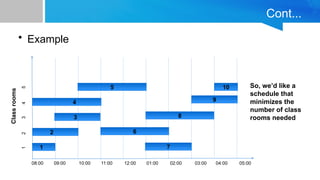
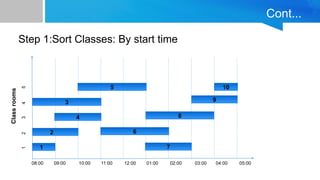
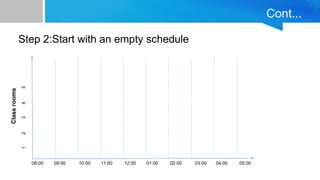
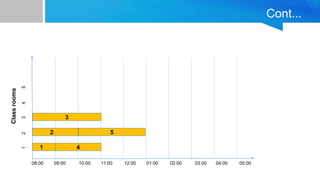
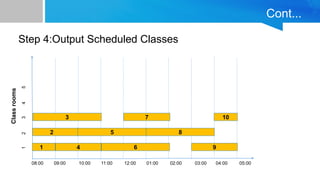
The document outlines a greedy algorithm for solving class scheduling problems, emphasizing its characteristics such as making locally optimal choices and its efficiency. It provides a structured approach for maximizing the number of non-overlapping classes while minimizing classroom usage, including steps, pseudocode, and examples. Limitations of the greedy algorithm are also discussed, highlighting its potential shortcomings in complex scenarios.







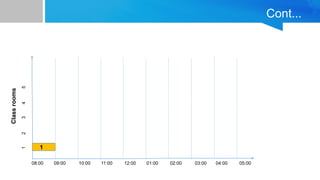
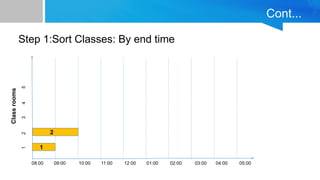
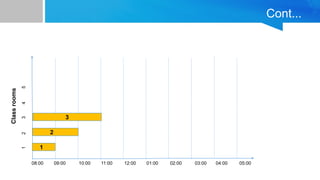
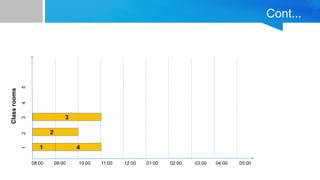
![Pseudocode implementation of the greedy scheduling algorithm
class Class:
int startTime
int endTime
function scheduleClasses(classes, numClassrooms):
sort(classes)
classrooms = array of size numClassrooms with all elements set to 0
schedule = empty list
for each class in classes:
for i from 0 to numClassrooms - 1:
if classrooms[i] <= class.startTime: // Check if classroom is free
schedule.append((class, i))
classrooms[i] = class.endTime
break
return schedule](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agreedyalgorithmforclassschedulingproblems-250112185152-0c500d2f/85/A-greedy-algorithm-for-class-scheduling-problems-pptx-17-320.jpg)