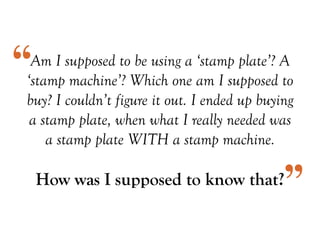
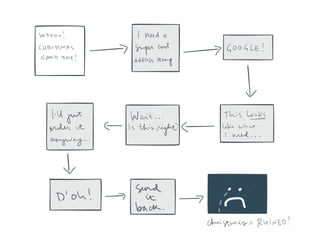
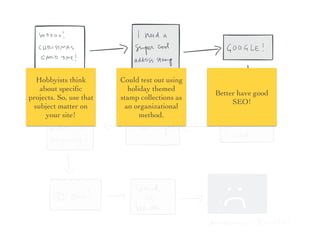
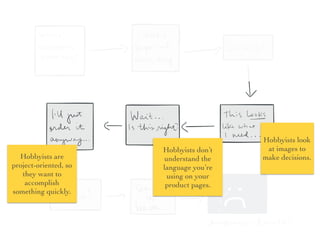
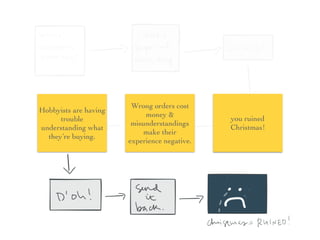
The document discusses the importance of user research in understanding users as human beings and their behaviors. It highlights various user research methods such as interviews, ethnographic studies, and usability testing while emphasizing the need to design user-centric products. It contains a specific case study on improving the experience of novice users ordering stamps, detailing the research goals and insights obtained during the process.