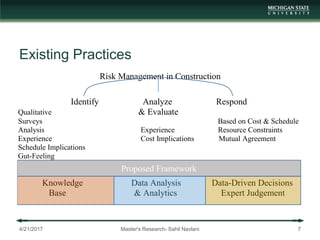
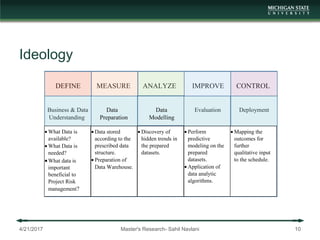
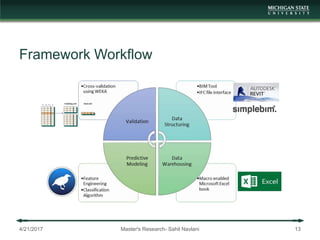
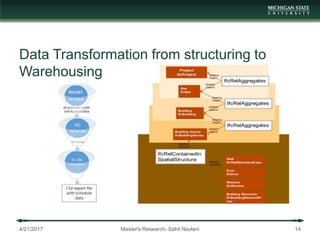
The document presents a framework for integrating building information modeling (BIM) with data analytics to predict schedule delays in modular and manufactured construction. It aims to develop a data-driven framework to assist construction schedule decision making. The framework is based on lean six sigma techniques and employs data analytics on BIM data structured according to a defined data model. A case study demonstrates applying the framework to predict delays on a modular housing project. The research contributes an exploratory conjunction of construction and data analytics and proposes a functional framework for implementation.