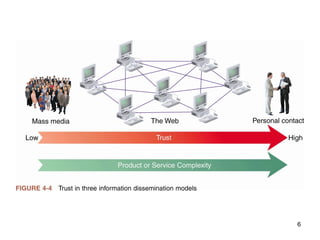
Product-based marketing strategies focus on physical products sold while customers think in terms of product categories. Web presence must integrate with a company's image and brand. Examples include web-based office supply stores that organize products into categories. Effective online communications require selecting appropriate media to reach different market segments. While physical stores have limitations, websites can present separate virtual spaces for various segments.