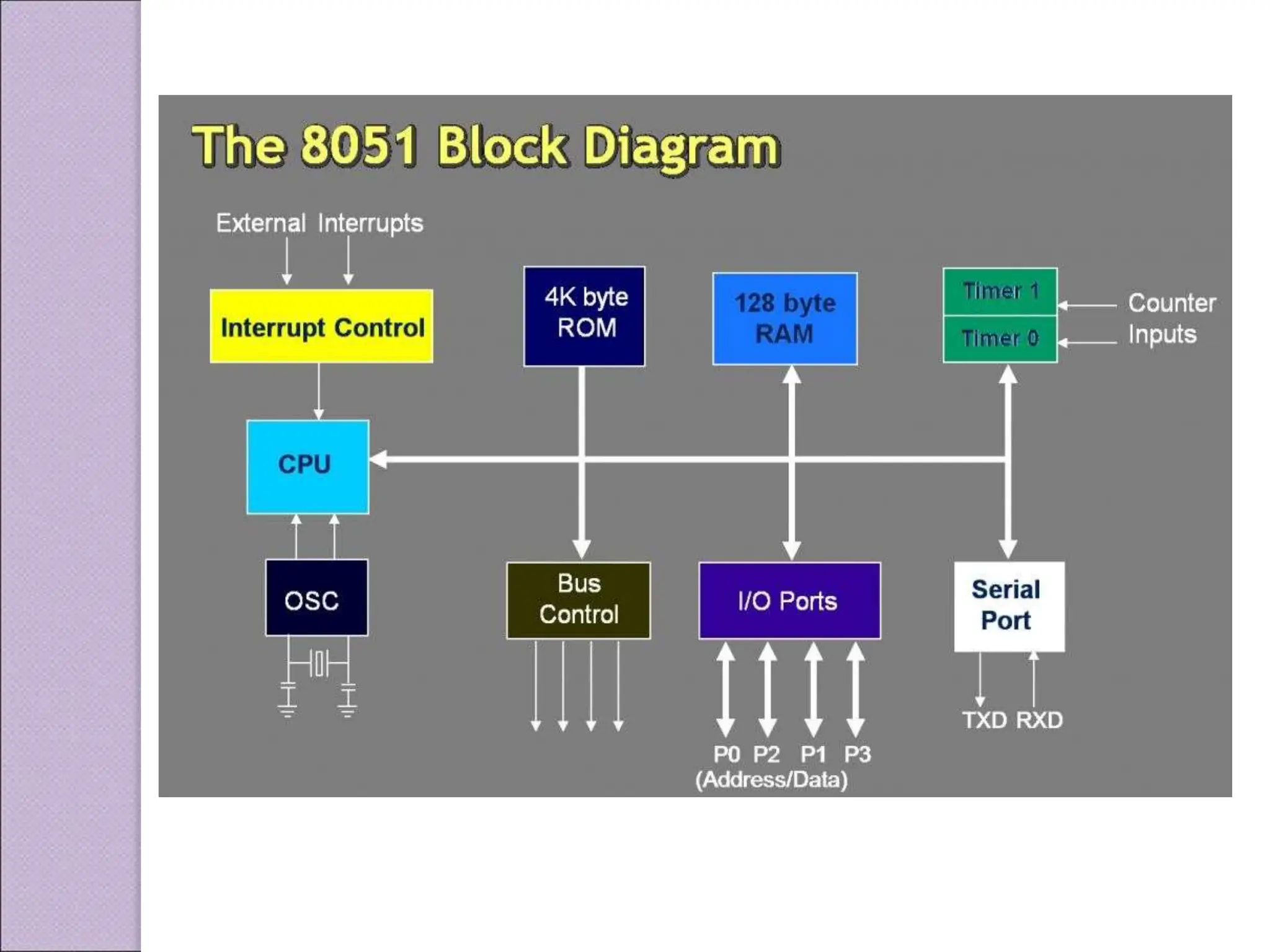
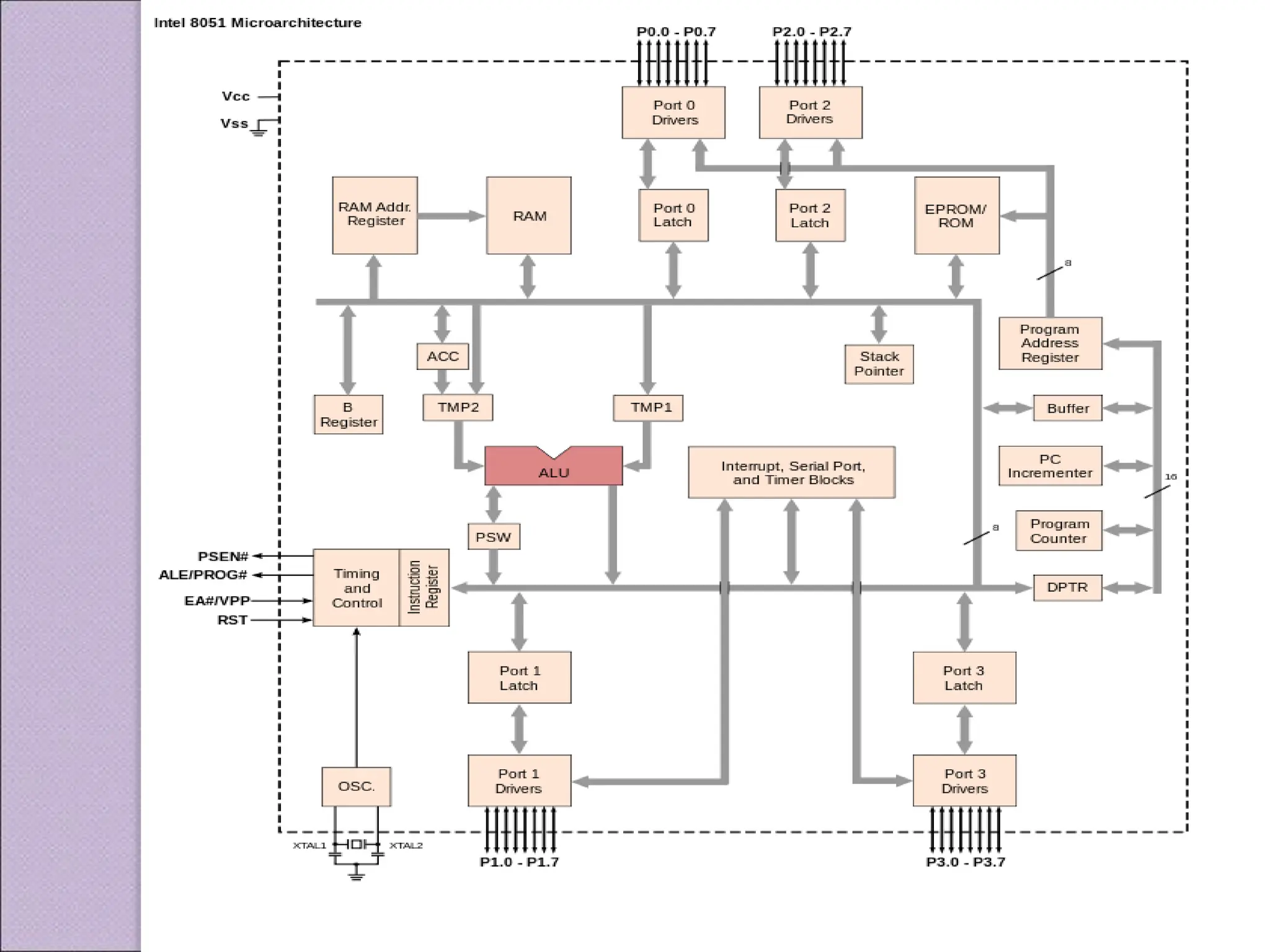
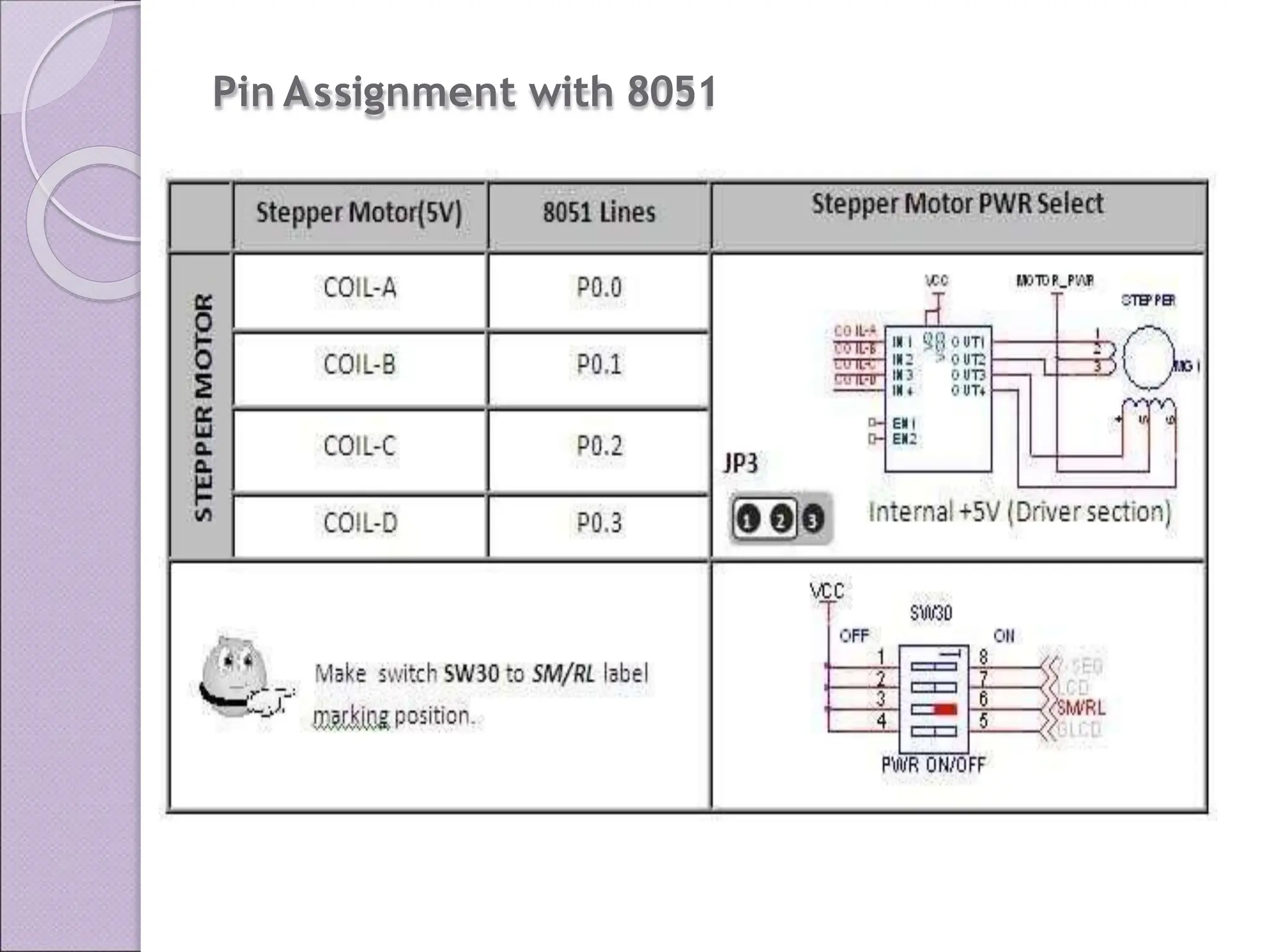
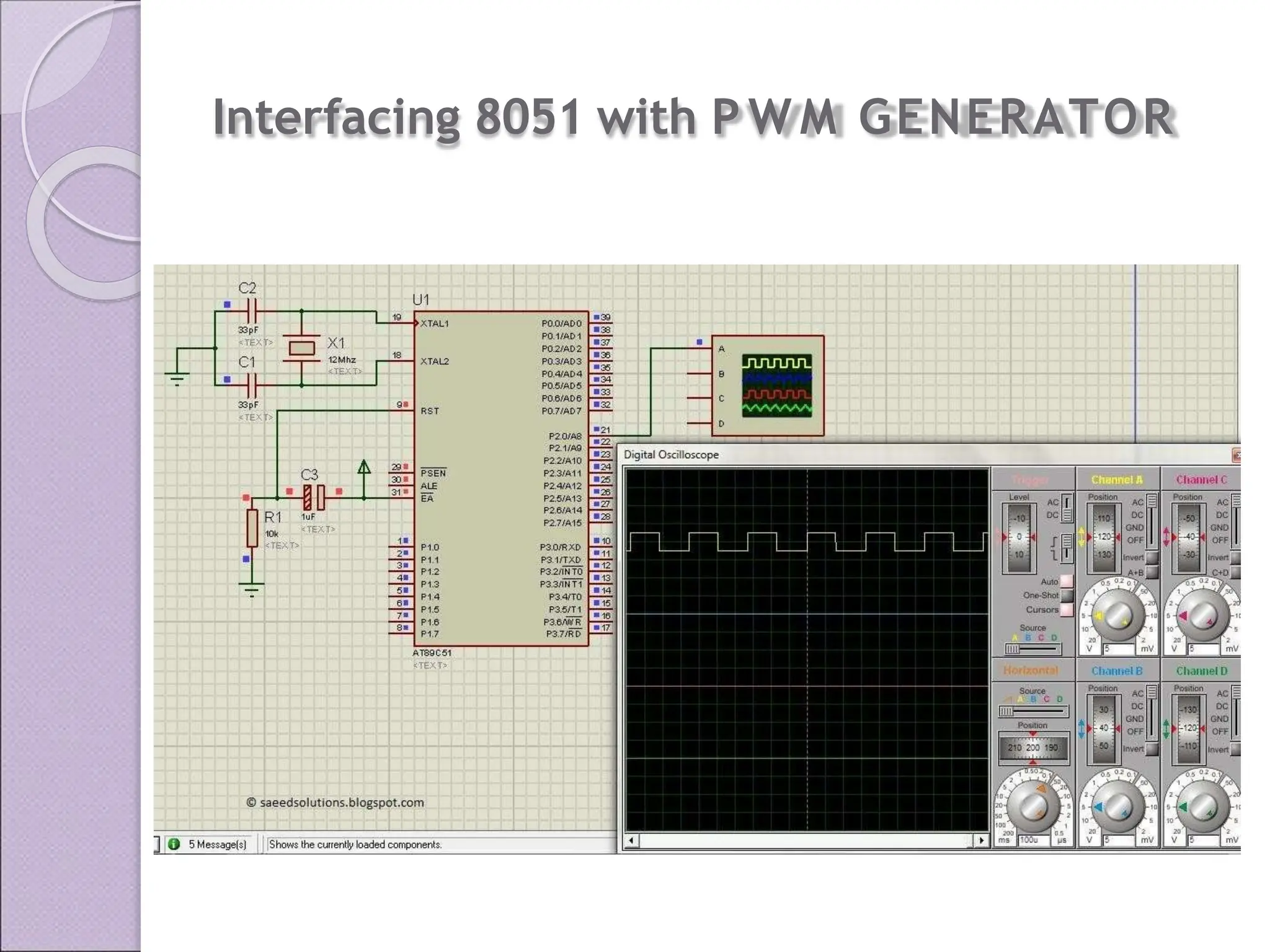
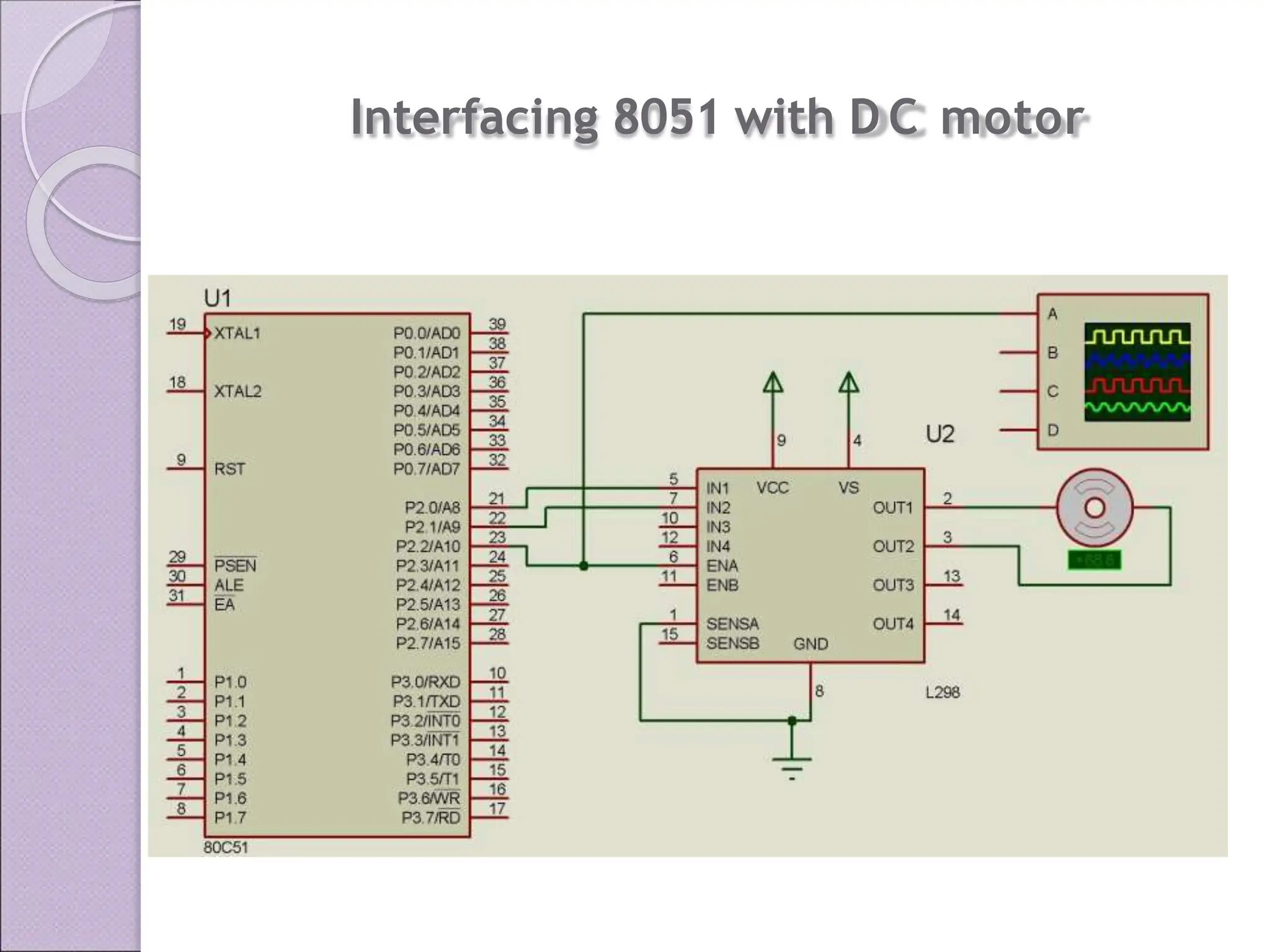
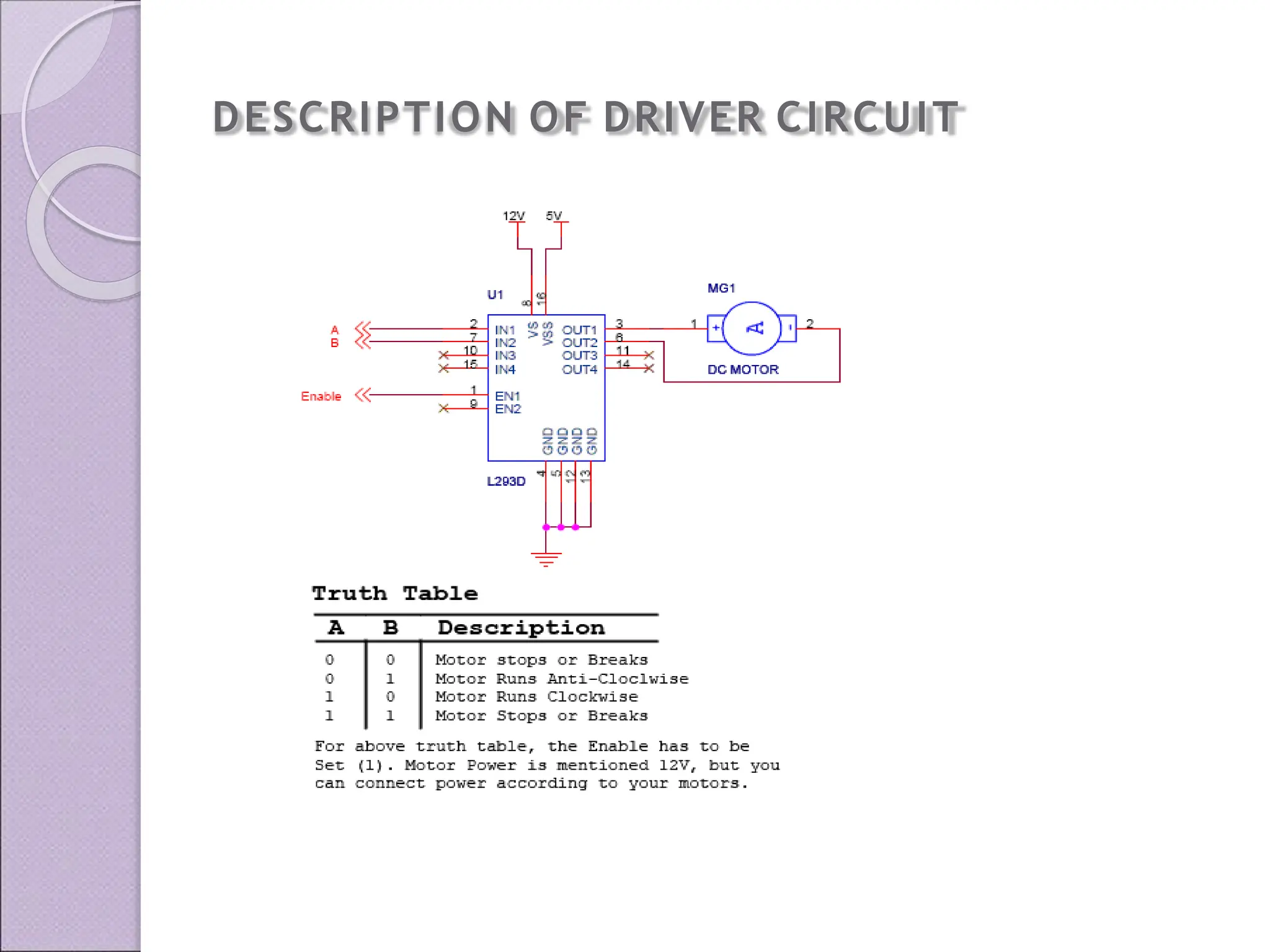
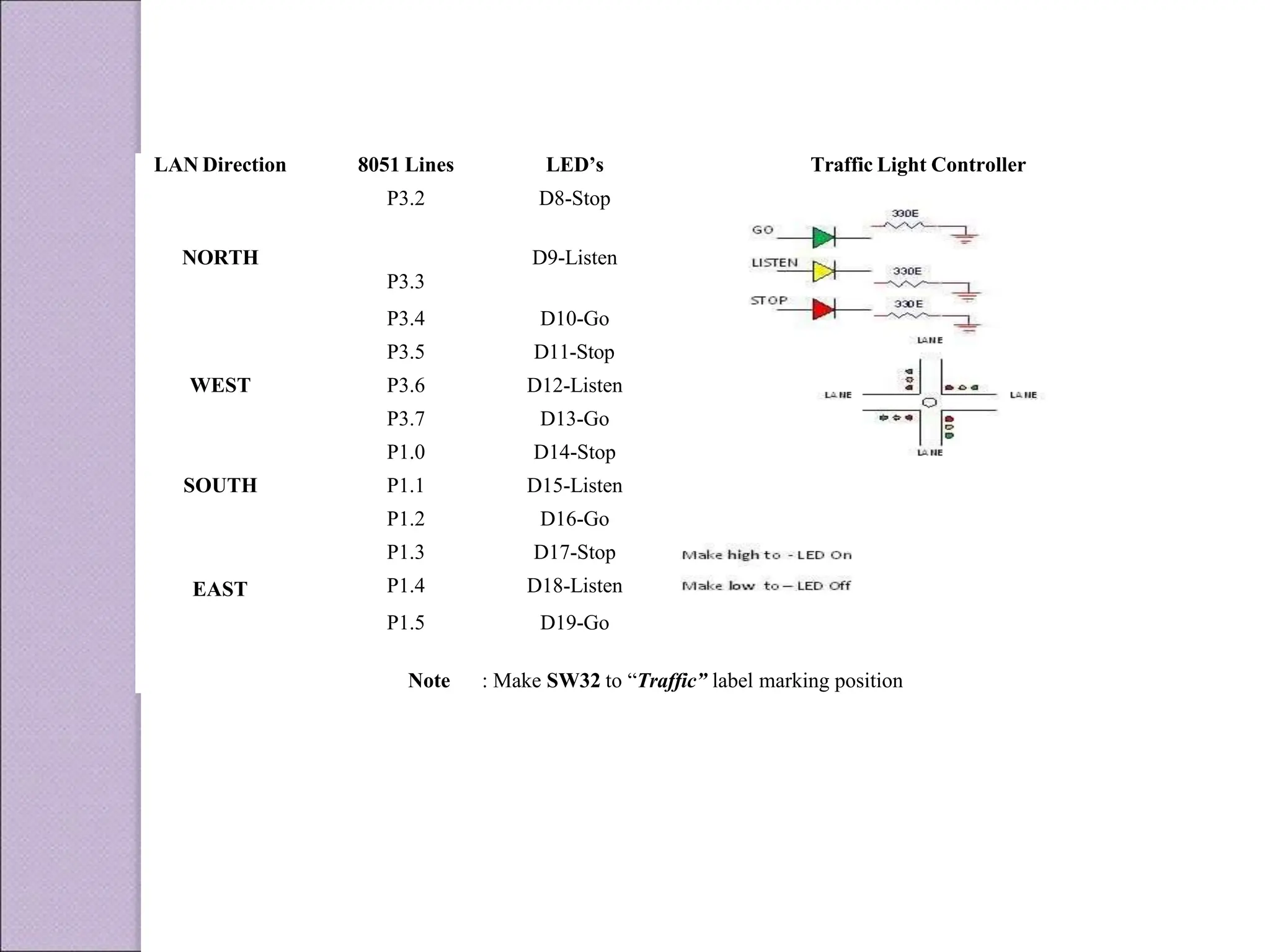
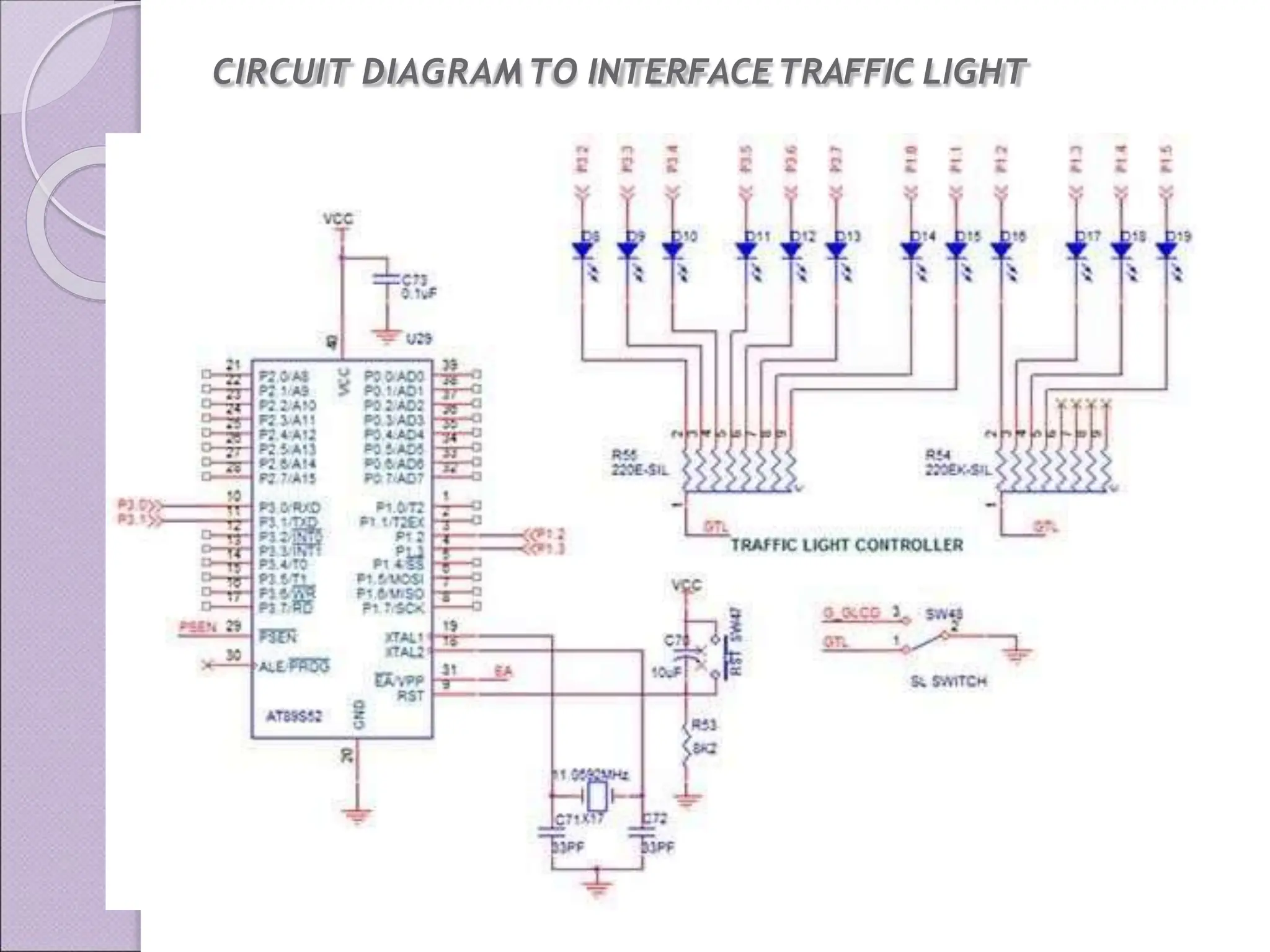
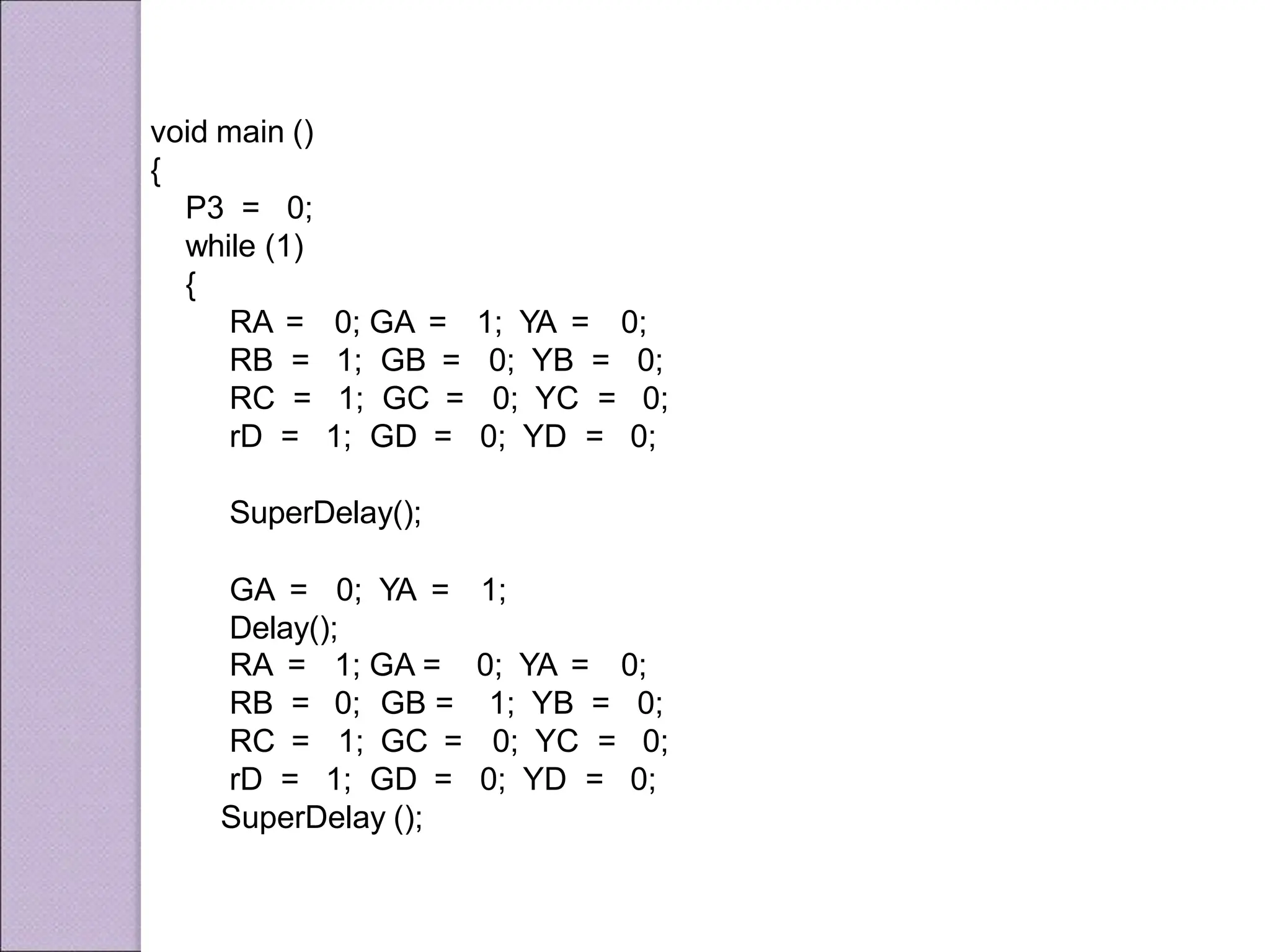
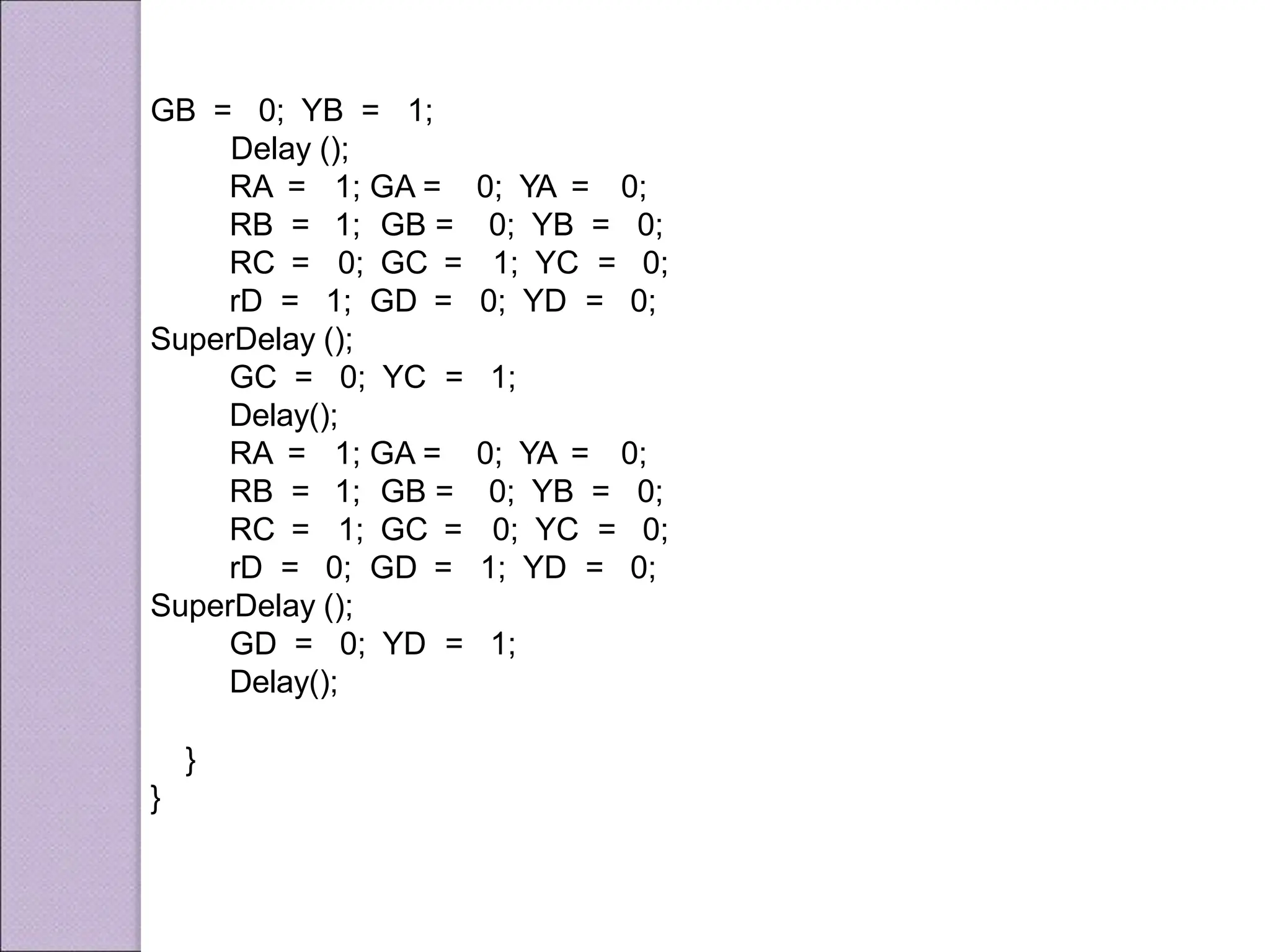
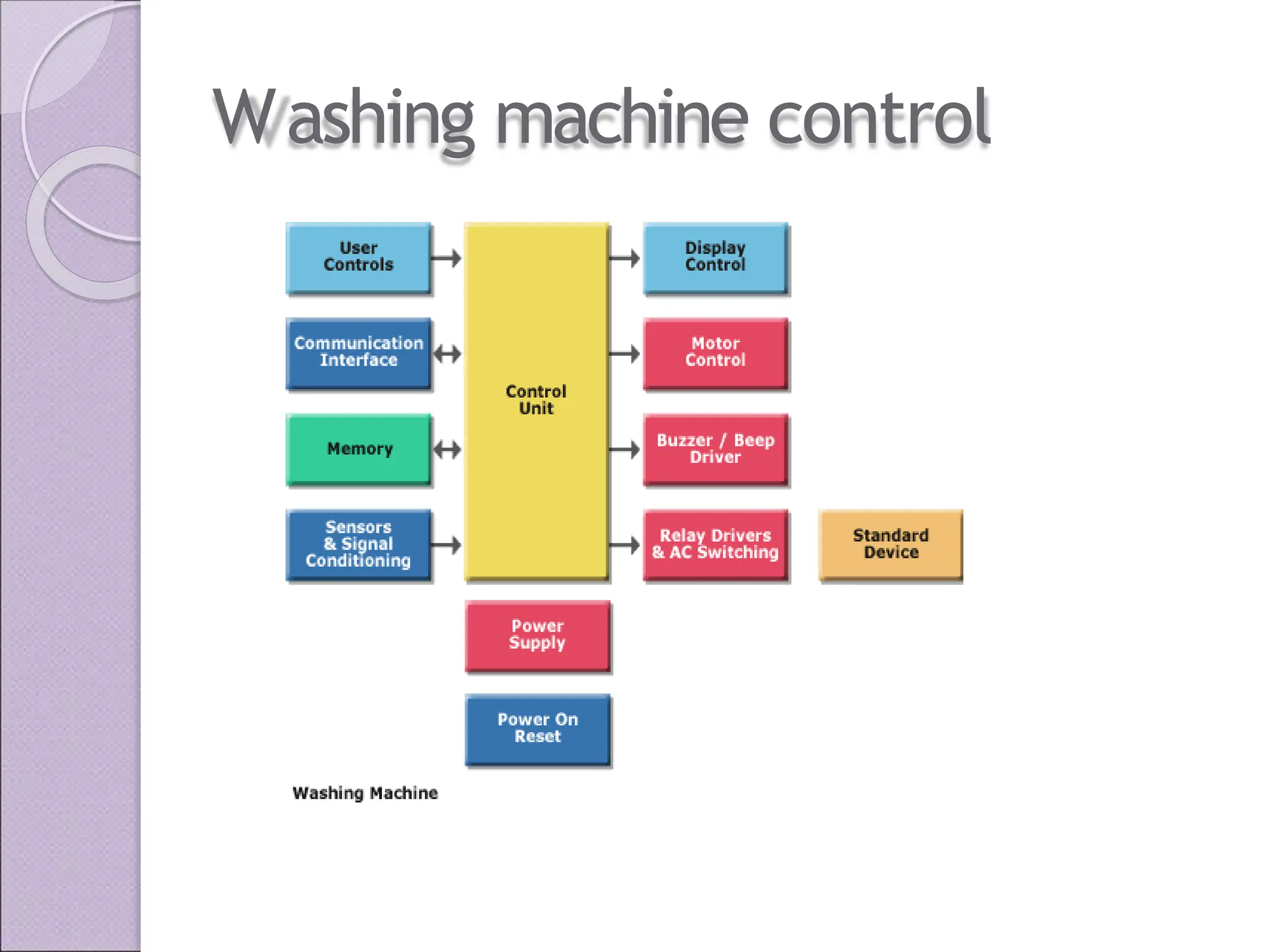
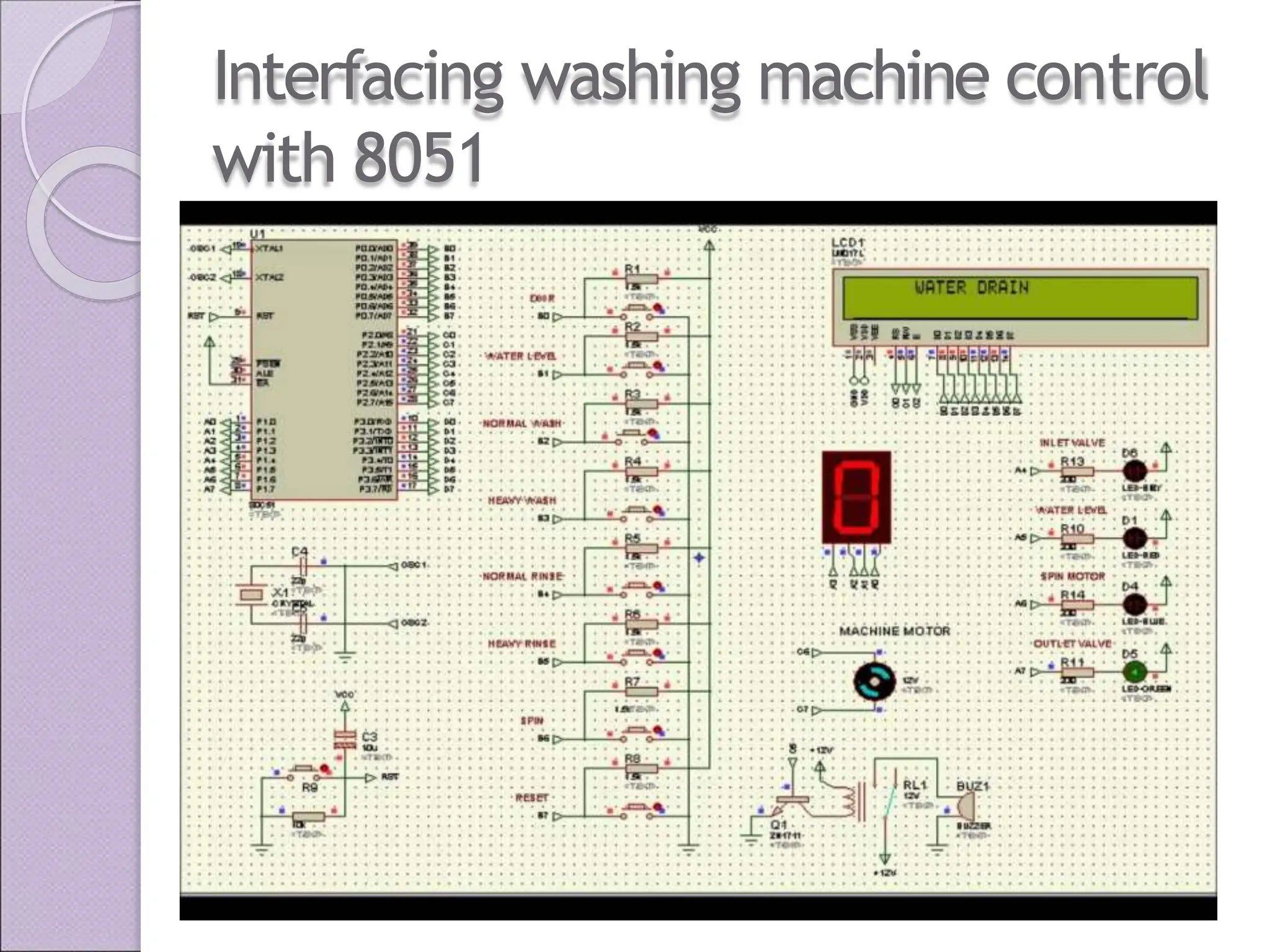
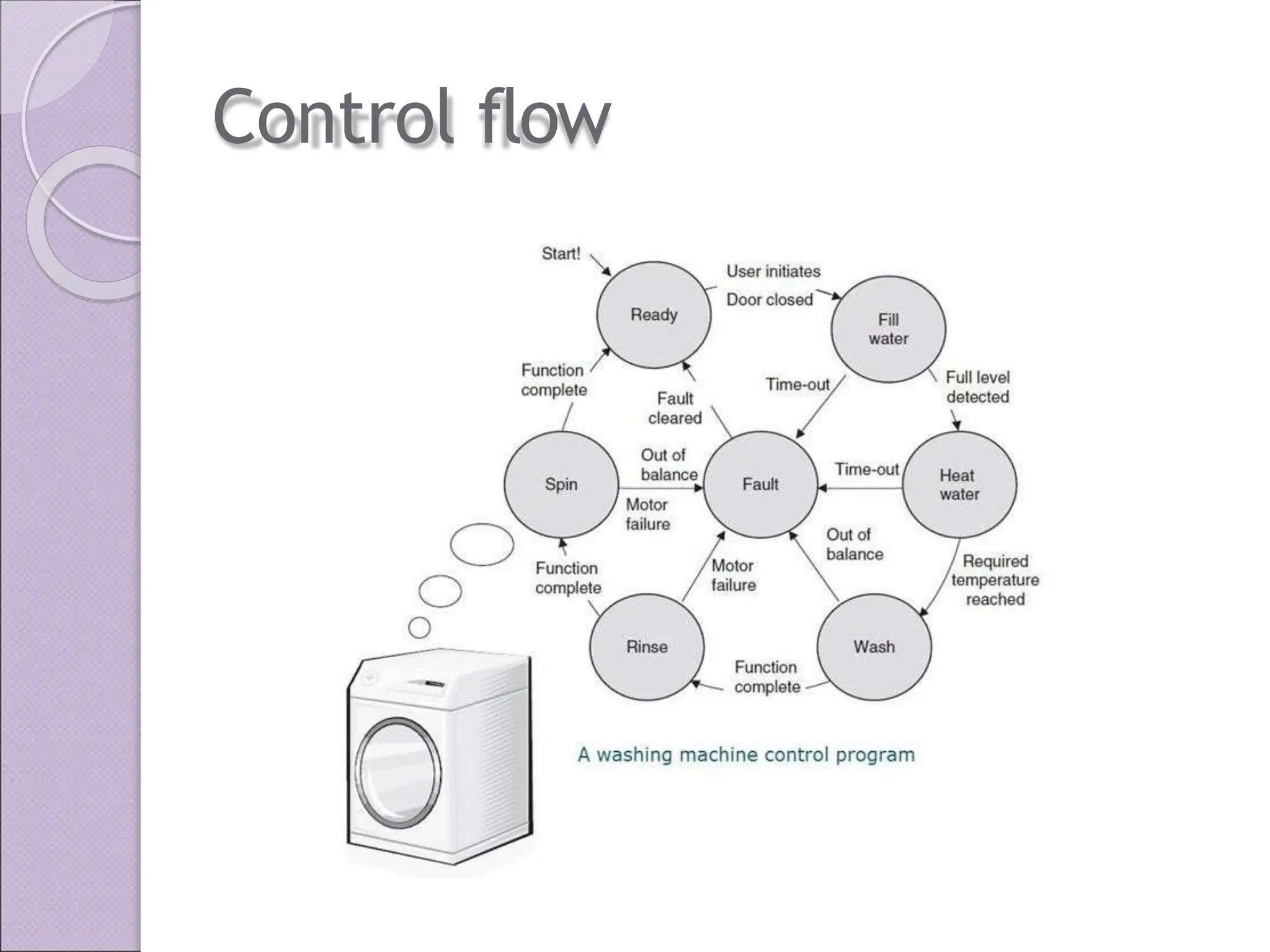
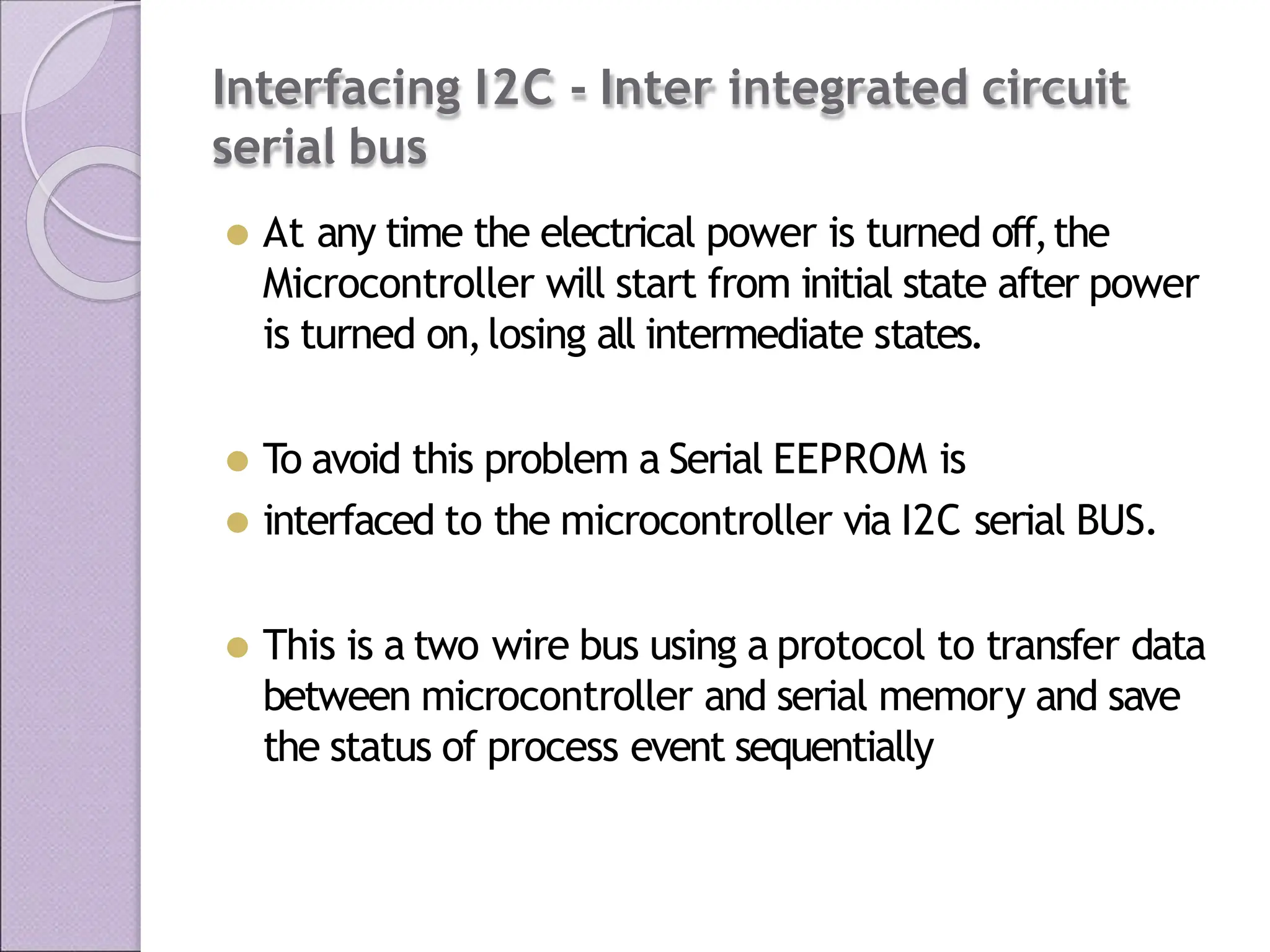
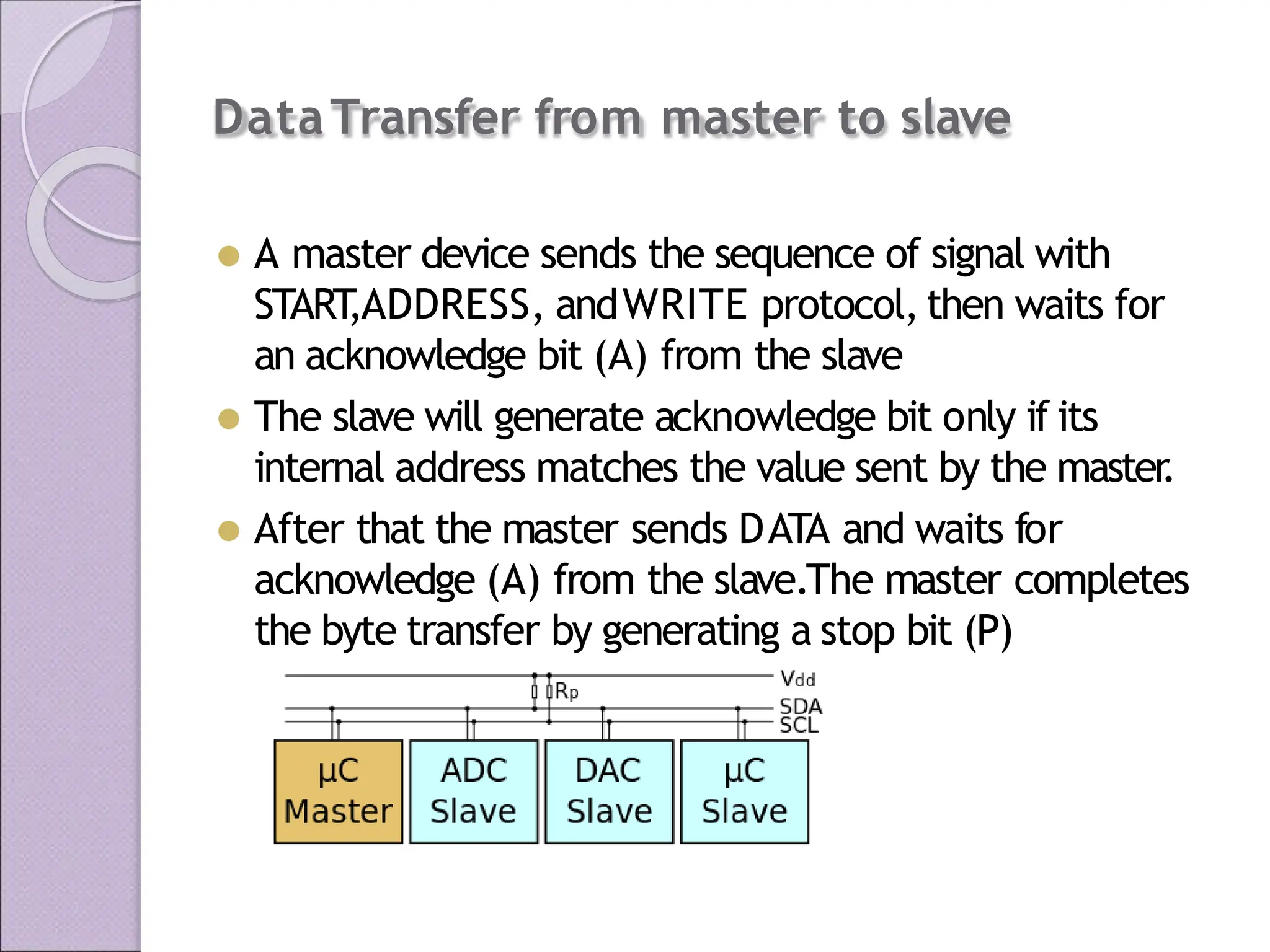
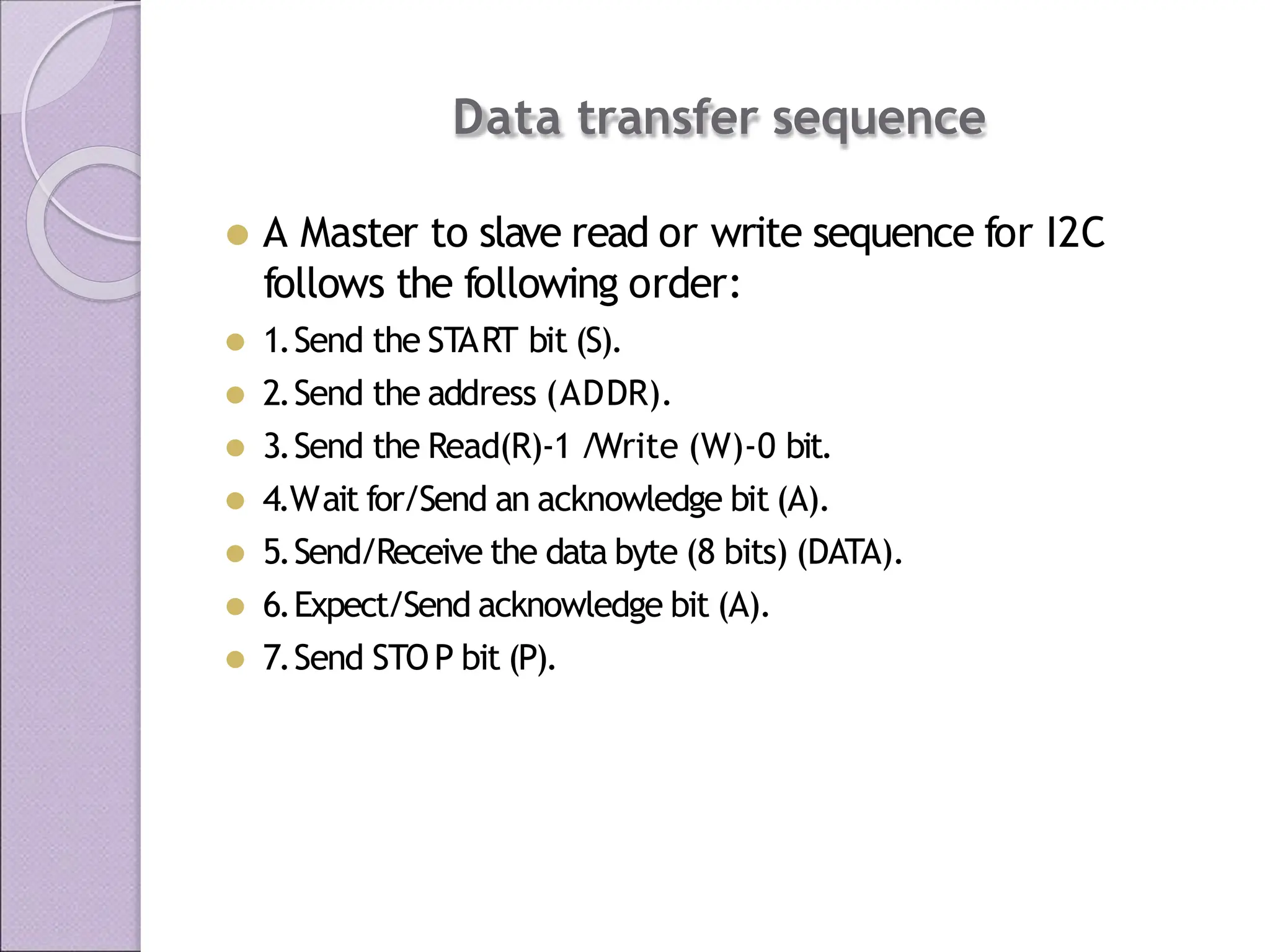
This document discusses various applications of the 8051 microcontroller. It begins by explaining the differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers, with microcontrollers being designed for special purposes with all peripherals built-in. Embedded systems are then introduced as using exclusively written software embedded in custom hardware. Common microcontrollers for embedded systems include PIC and 8051. The architecture and applications of the 8051 microcontroller are then outlined, followed by descriptions of interfacing 8051 with devices like relays, stepper motors, DC motors, and PWM generators. Programming examples are provided for some applications. Other applications discussed include traffic light controllers and washing machine controls. Interfacing the 8051 with I2C is also summarized.