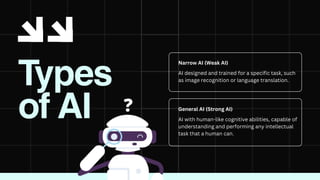
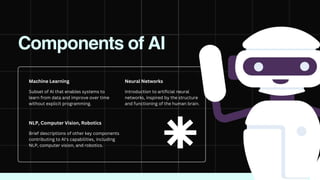
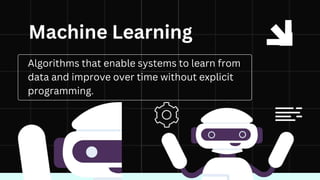
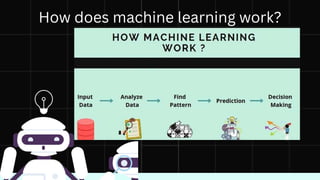
The document discusses artificial intelligence (AI) as the development of systems that perform tasks requiring human intelligence, categorized into narrow AI and general AI. It covers key components like machine learning, neural networks, and applications in various sectors including healthcare, automotive, gaming, and finance. Additionally, it explains how machine learning enables systems to learn and improve over time, providing insights into its operation and examples.