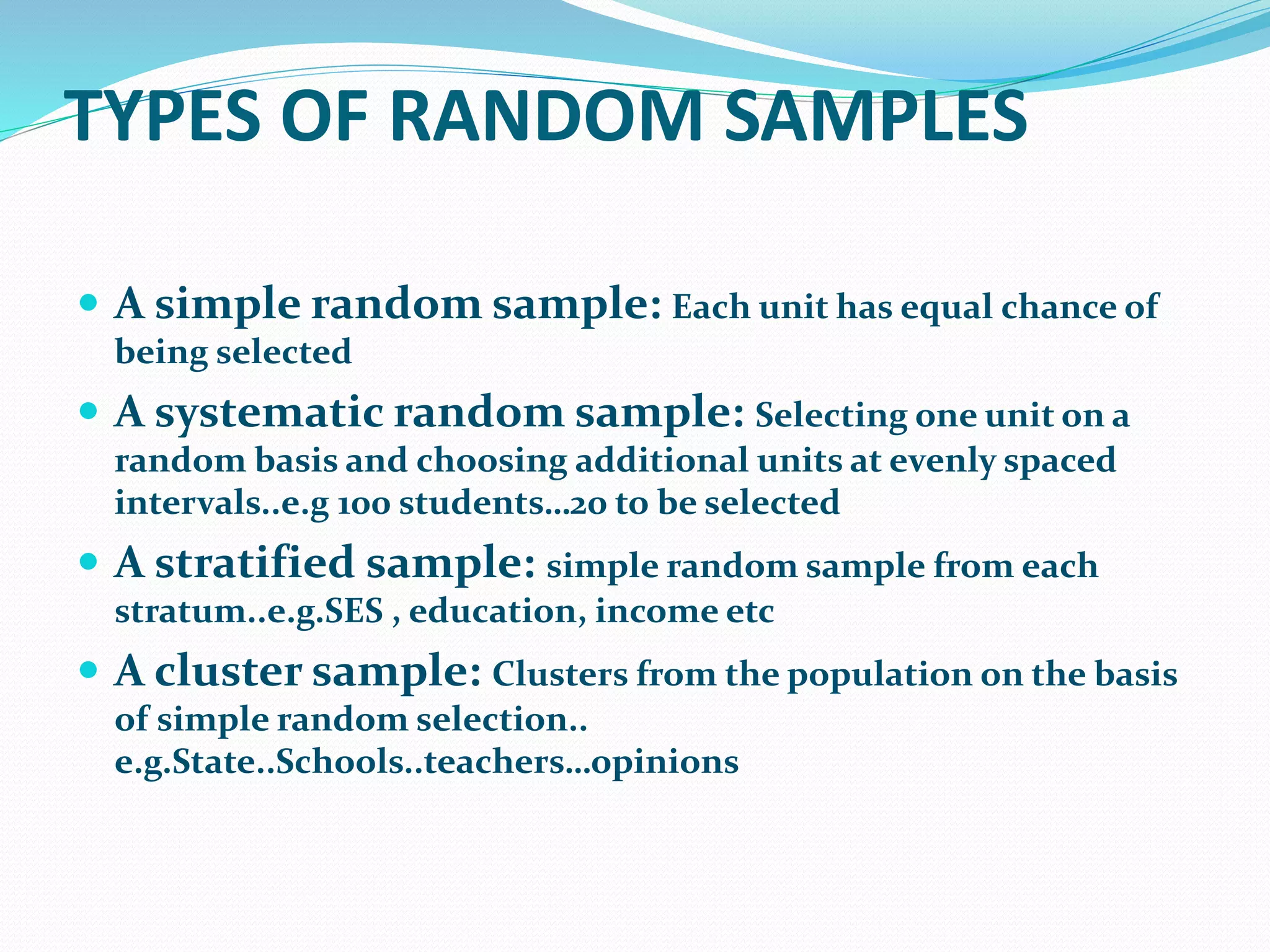
A sample is a subset of a population that is used to gain information about the whole population. A population is the complete set of individuals or objects under consideration. Sampling involves selecting a sample in order to make inferences about the population. The main reasons for sampling instead of a complete census are that it is more economical, timely, and sometimes populations are too large or inaccessible. However, samples can contain errors and biases that mean results may not accurately represent the true population.