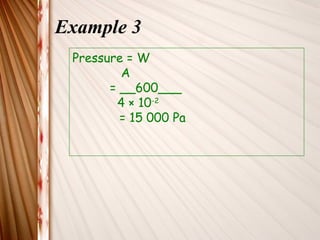
This chapter discusses pressure and its relationship to force and area. Pressure is defined as force per unit area, with the formula P=F/A. Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating pressure given the force and contact area. Quizzes throughout assess understanding of key concepts like how elephants and ladies exert different pressures due to differences in their contact areas.