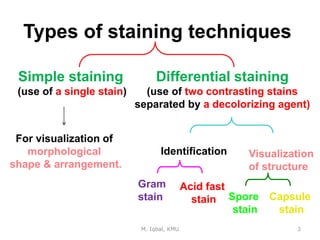
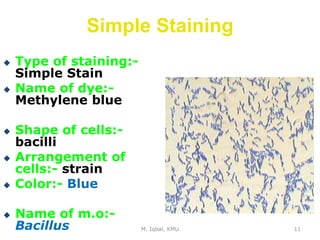
This document discusses staining techniques used to visualize bacterial cells under a microscope. It describes simple staining, which uses a single dye to color all bacterial cells, and differential staining techniques like Gram staining that classify bacteria into groups. Gram staining involves staining cells with crystal violet dye, adding iodine as a mordant, washing with alcohol as a decolorizer, and counterstaining with safranin. This causes Gram-positive bacteria to appear violet and Gram-negative bacteria to appear pink based on differences in their cell wall structure. The document provides examples of staining Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis and E. coli to demonstrate the staining results.