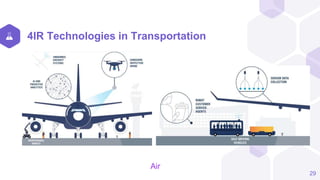
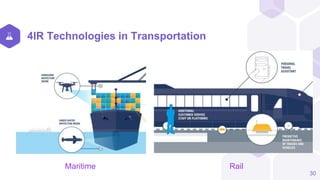
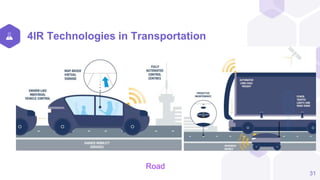
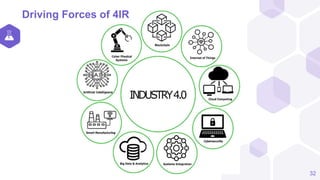
The document discusses the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) and its implications for Bangladesh, detailing its characteristics, driving forces, and benefits across various sectors such as agriculture, health, and transportation. It emphasizes the transformative potential of 4IR technologies, including AI, IoT, and blockchain, while also highlighting challenges like job disruption and the need for proper infrastructure and workforce readiness. Recommendations for leveraging 4IR opportunities in Bangladesh include enhancing technological infrastructure, focusing on education and training, and implementing cybersecurity measures.