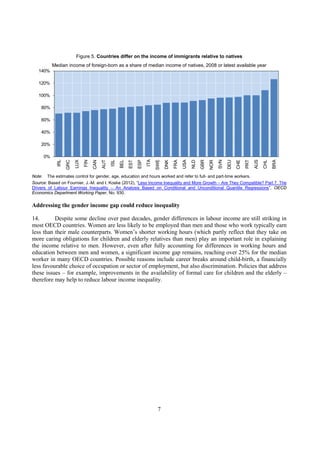
This document analyzes drivers of inequality in labor income and policies that can reduce it. Technological change and globalization contribute to wider income dispersion among full-time workers, though unions and employment protections can moderate these effects. Higher education attainment is generally associated with narrower income distribution. Temporary contracts, gender gaps, and immigrant underperformance also impact inequality. Policy options like more equitable education, moderate job protections, higher minimum wages, and stronger unions can help compress labor income differences across countries.