This document discusses backups in Linux systems. It covers various tools for backing up files and directories like tar, rsync, burning software and tape drives. It explains how to create, view, extract tar archives and compress them using gzip or bzip2 to reduce file sizes. Key areas covered include what to backup, local and remote backup locations, and how backups are different for small and large systems. The document also provides a brief overview of zip files and their role in backups.


![CoreLinuxforRedHatandFedoralearningunderGNUFreeDocumentationLicense-Copyleft(c)AcácioOliveira2012
Everyoneispermittedtocopyanddistributeverbatimcopiesofthislicensedocument,changingisallowed
What to backup
3
Backup for:
•Hardware failures
•Software failures
•[Epic] User failures
•Disasters
Backups
What to backup:
•At minimum, all user data and intellectual property
•At maximum, entire systems, OS and all
Factors for what gets backed up:
•budget
•time
•resources
•need](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tjlkdt00q32wtre684g1-signature-b02a6c073768d8536fdd50c0a47af6292b168fbd705c8180447bb0b754b59738-poli-141223132216-conversion-gate02/75/4-8-apend-backups-3-2048.jpg)
![CoreLinuxforRedHatandFedoralearningunderGNUFreeDocumentationLicense-Copyleft(c)AcácioOliveira2012
Everyoneispermittedtocopyanddistributeverbatimcopiesofthislicensedocument,changingisallowed
Create and view tar archives
5
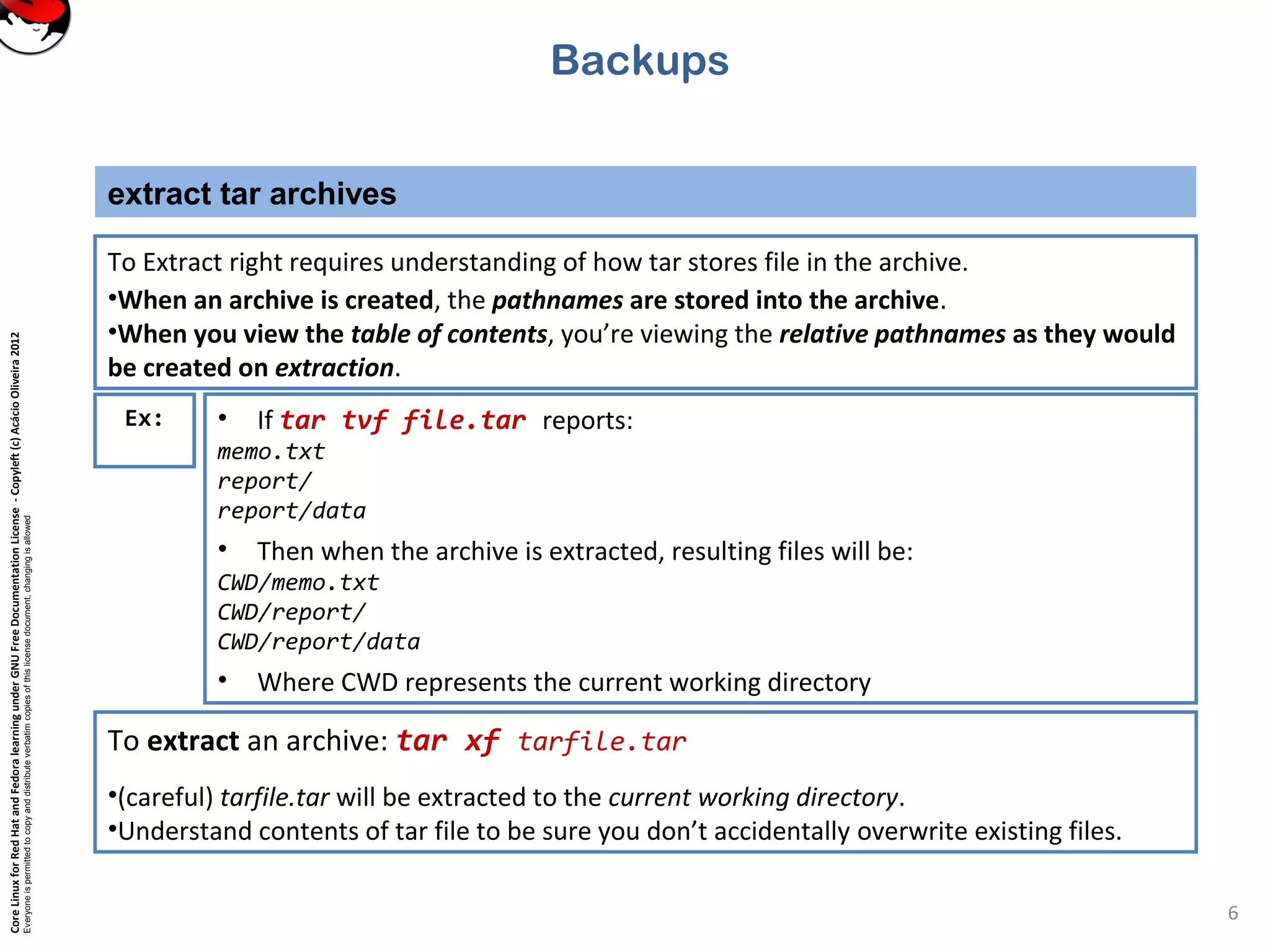
To create a tar archive: tar cf <tarfile.tar> <file> [file]...
•The c option tells tar to create an archive.
•The f option is critical - tells tar to put archive in a file on disk, rather than on tape device.
•You can add the v option (tar cvf) to get verbose output.
Tar will report every file added to the archive.
Backups
To view a tar archive (a table of contents): tar tf tarfile.tar
•The t option asks tar to print a table of contents of the archive.
•add the verbose flag (tvf), tar will report detailed info on each file, similar to ls –l cmd.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tjlkdt00q32wtre684g1-signature-b02a6c073768d8536fdd50c0a47af6292b168fbd705c8180447bb0b754b59738-poli-141223132216-conversion-gate02/75/4-8-apend-backups-5-2048.jpg)