4.1 chromosomes, genes, alleles & mutations notes
•Download as DOC, PDF•
0 likes•636 views
Report
Share
Report
Share
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Chapter 19 Heredity Lesson 4 - Examples of Gene and Chromosome Mutations and ...

Chapter 19 Heredity Lesson 4 - Examples of Gene and Chromosome Mutations and ...
Similar to 4.1 chromosomes, genes, alleles & mutations notes
Similar to 4.1 chromosomes, genes, alleles & mutations notes (20)
Effect of mutation on plant at molecular level and their repair mechanism

Effect of mutation on plant at molecular level and their repair mechanism
Genomics epigenetic modifications & epigenomic technologies

Genomics epigenetic modifications & epigenomic technologies
Human variability as property of life & the Genetic phenomena

Human variability as property of life & the Genetic phenomena
More from cartlidge
More from cartlidge (20)
4.1 chromosomes, genes, alleles & mutations notes
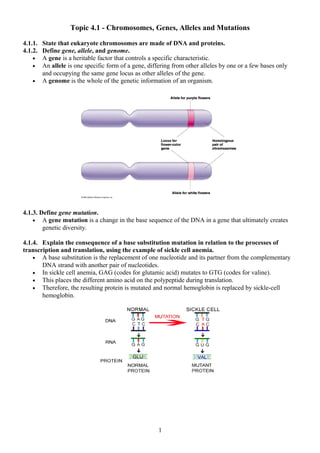
- 1. Topic 4.1 - Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles and Mutations 4.1.1. State that eukaryote chromosomes are made of DNA and proteins. 4.1.2. Define gene, allele, and genome. • A gene is a heritable factor that controls a specific characteristic. • An allele is one specific form of a gene, differing from other alleles by one or a few bases only and occupying the same gene locus as other alleles of the gene. • A genome is the whole of the genetic information of an organism. 4.1.3. Define gene mutation. • A gene mutation is a change in the base sequence of the DNA in a gene that ultimately creates genetic diversity. 4.1.4. Explain the consequence of a base substitution mutation in relation to the processes of transcription and translation, using the example of sickle cell anemia. • A base substitution is the replacement of one nucleotide and its partner from the complementary DNA strand with another pair of nucleotides. • In sickle cell anemia, GAG (codes for glutamic acid) mutates to GTG (codes for valine). • This places the different amino acid on the polypeptide during translation. • Therefore, the resulting protein is mutated and normal hemoglobin is replaced by sickle-cell hemoglobin. 1