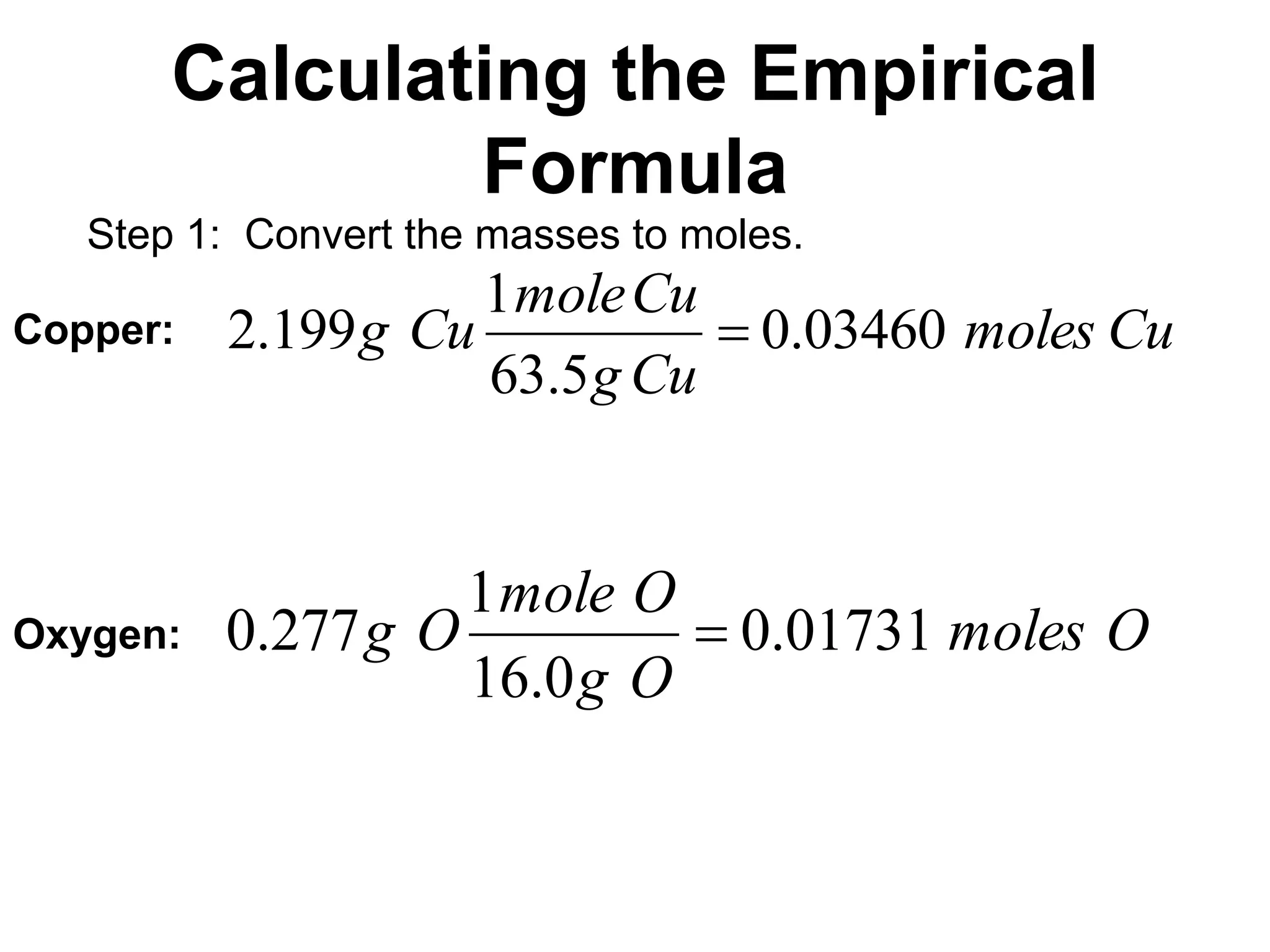
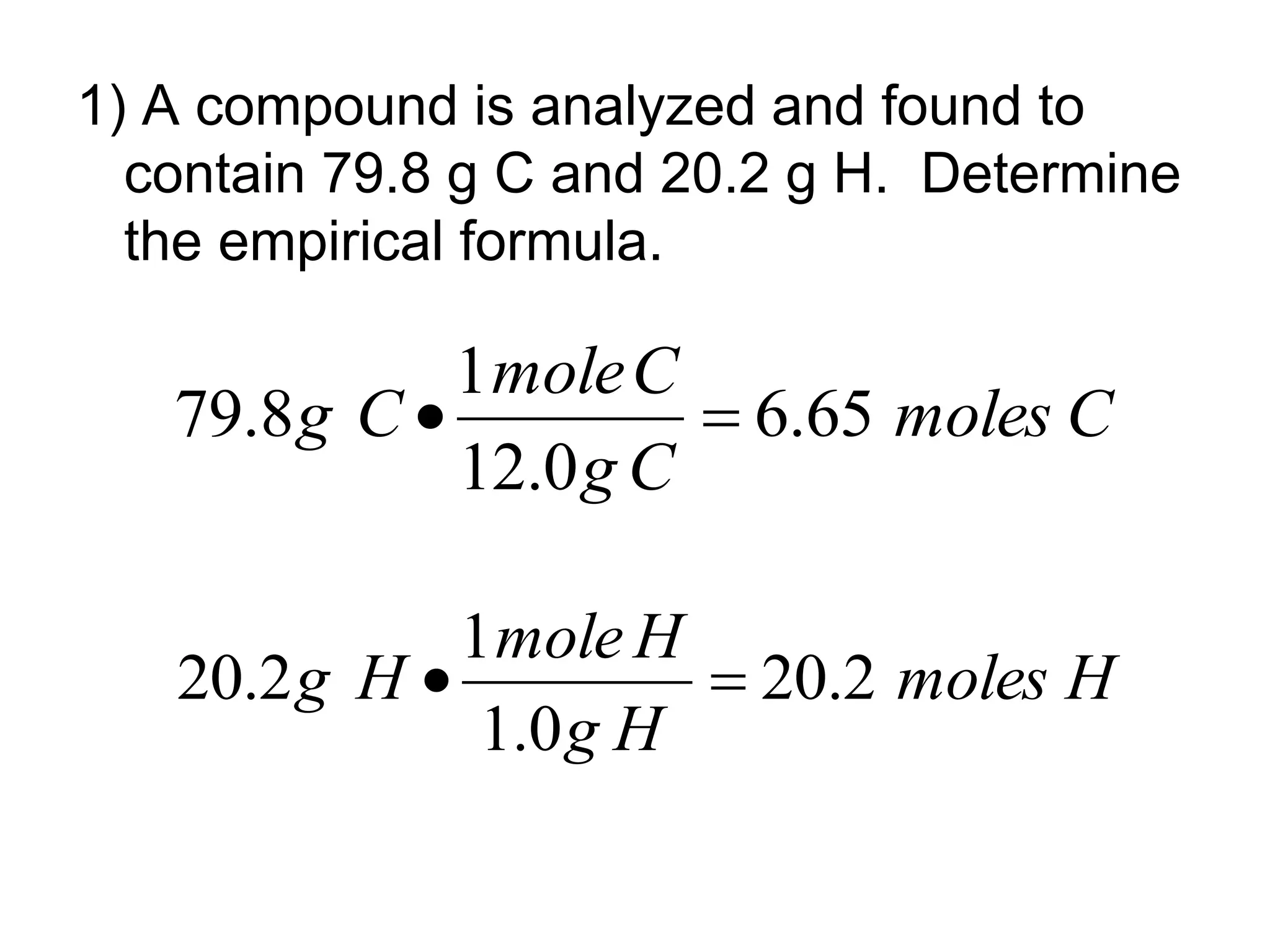
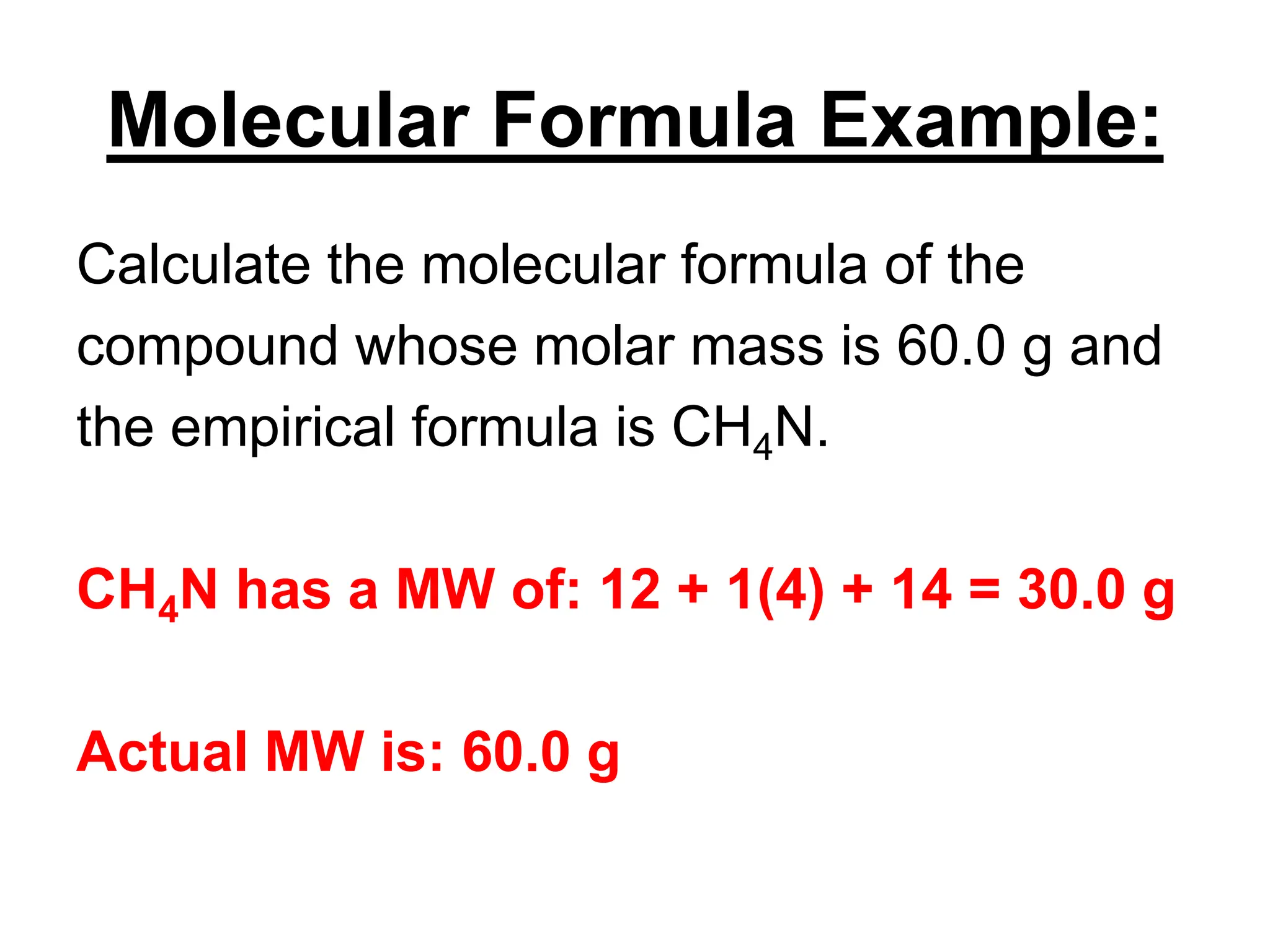
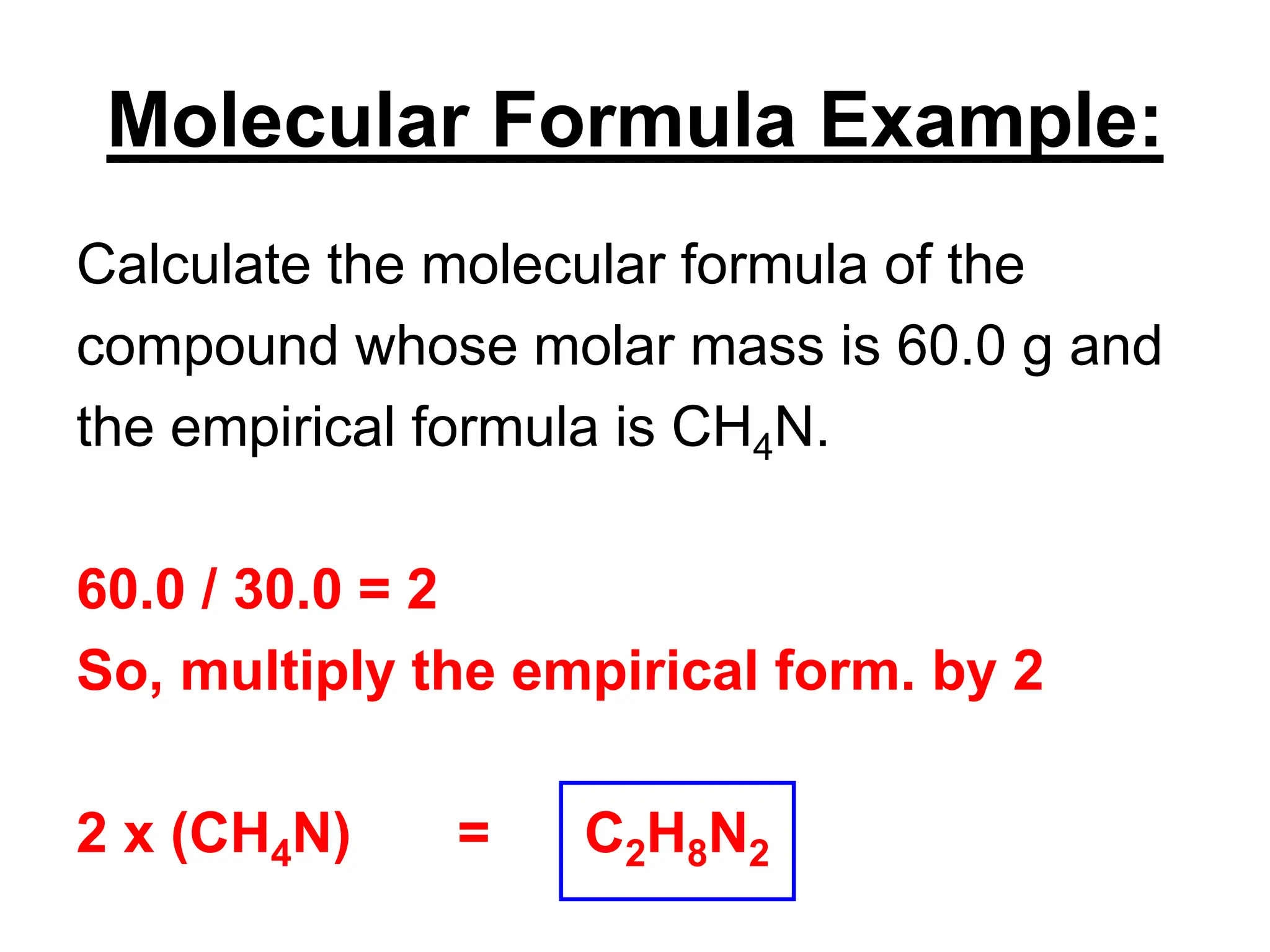
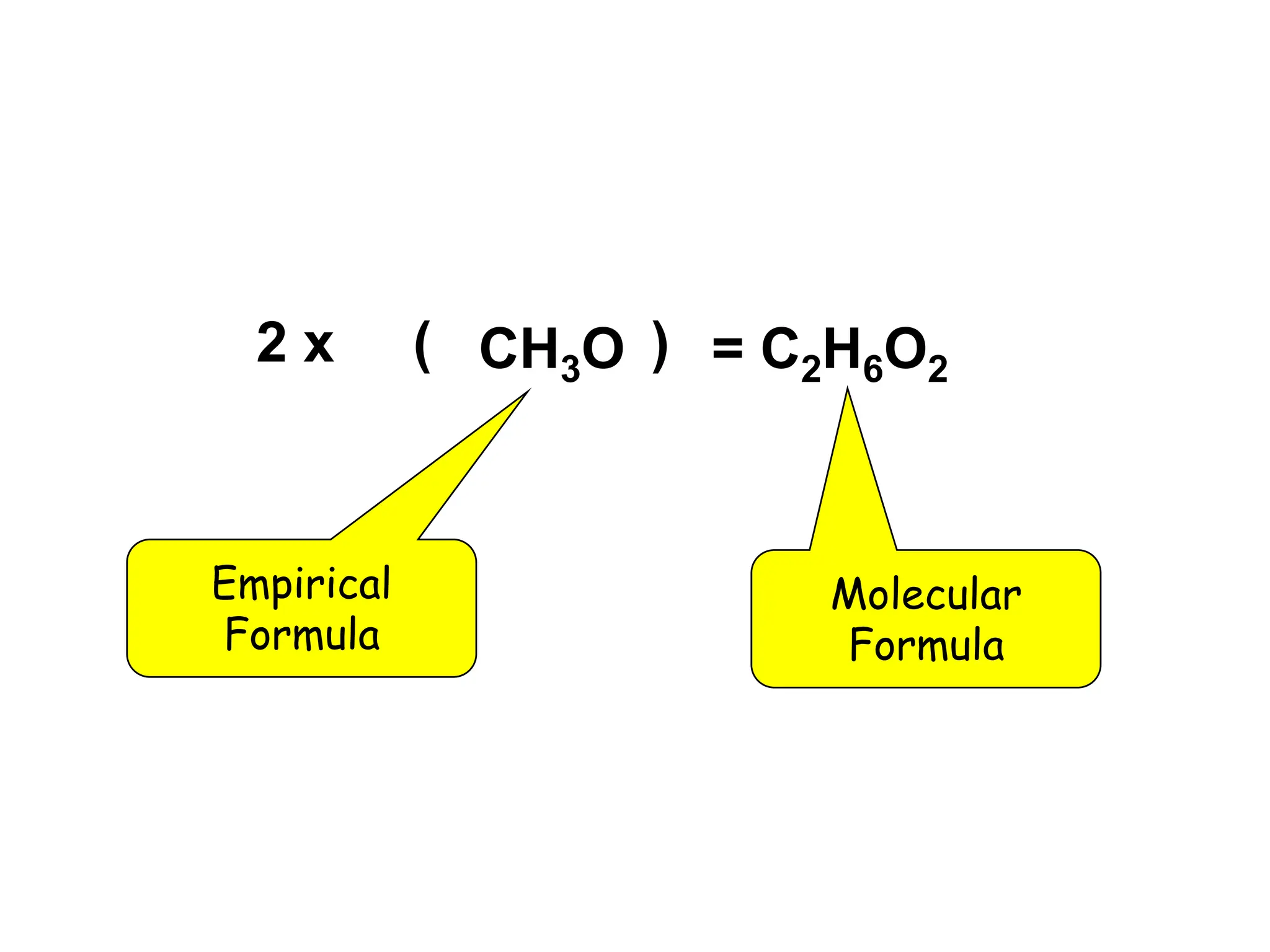
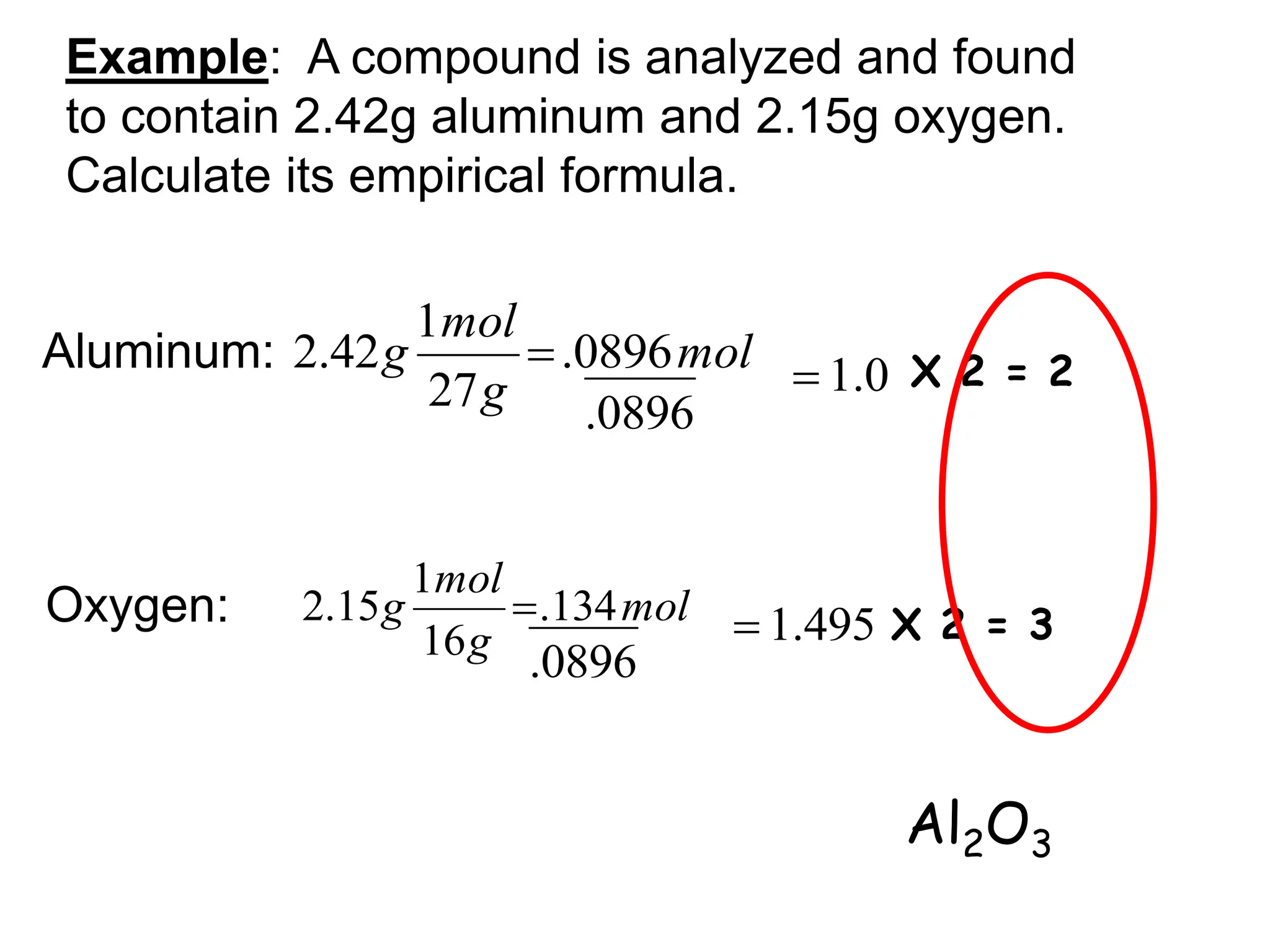
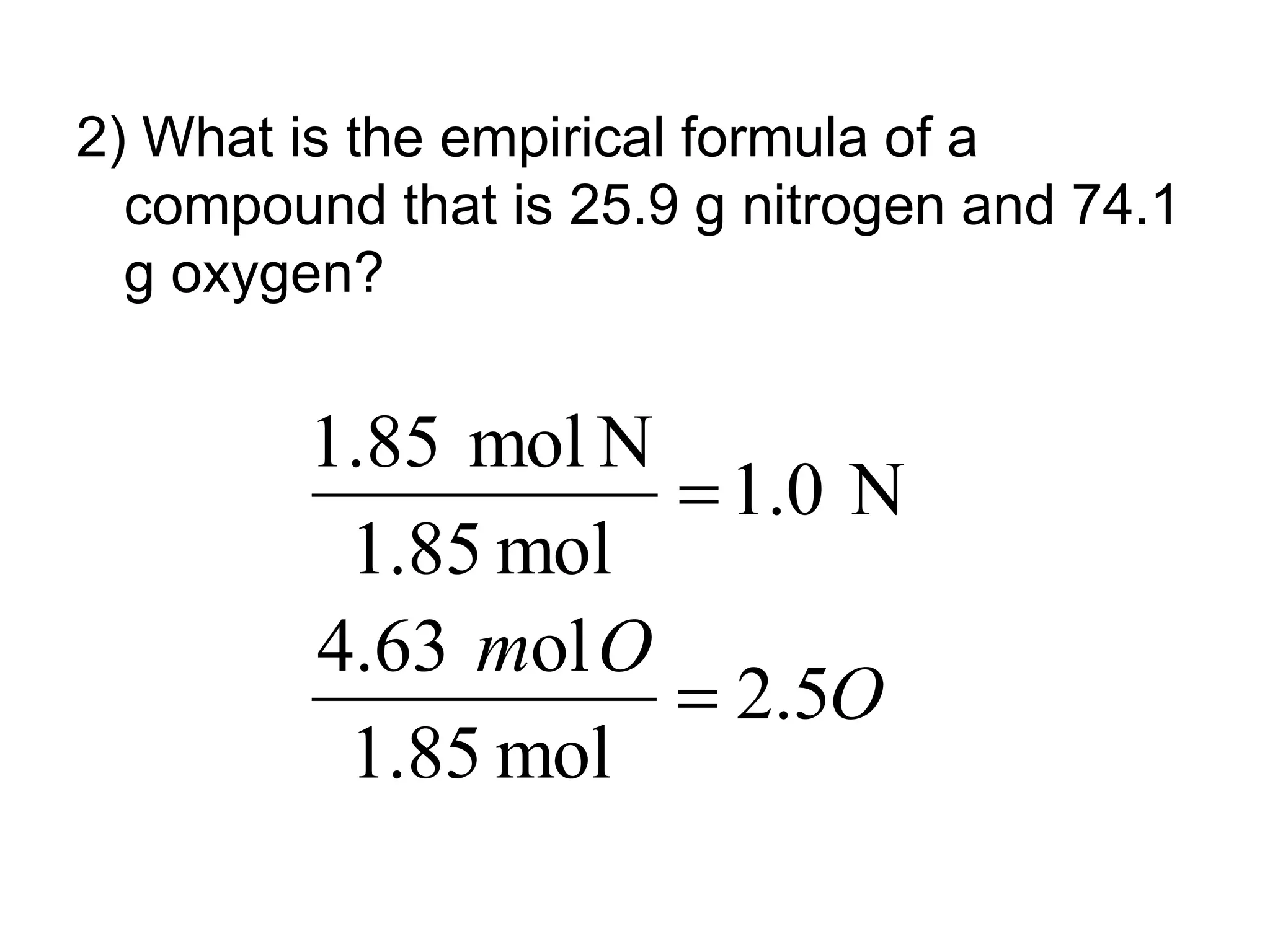The document explains how to calculate empirical and molecular formulas from the composition of compounds. It outlines three main steps for determining empirical formulas: converting masses to moles, finding mole ratios, and rounding to obtain whole numbers. Examples illustrate the calculation process for different compounds and emphasize that the molecular formula is a multiple of the empirical formula.