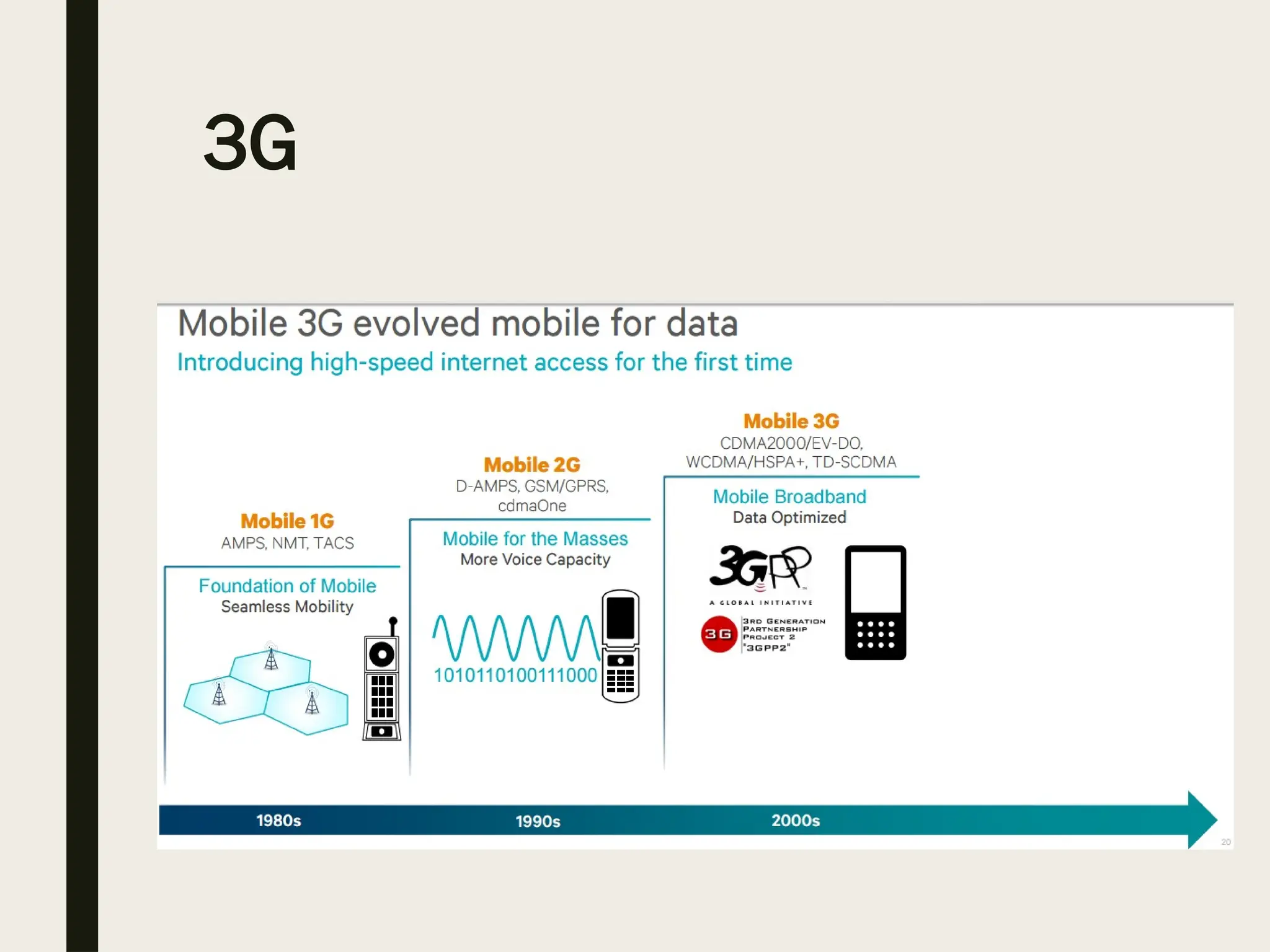
The document compares 3G and Wi-Fi technologies, outlining their definitions, functionalities, applications, and differences. 3G is designed for mobile telecommunications, offering various services and higher data rates, while Wi-Fi provides high-speed internet within a limited range, primarily for stationary devices. Both technologies are wireless and support broadband data services but differ in deployment models, spectrum usage, and primary markets.