Recommended
PPT
Unit One - Solved problems on error analysis .ppt
PPT
PDF
Chapter assignment character assignemetb
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
Engineering Numerical Analysis Lecture-1
PDF
Introduction-Accuracy-and-Errors.pdf
PPTX
LEC01.wararAWQWWRwrrwqRQRWQWQqqrwq1.pptx
PPTX
Engineering analysisPart1=Ch1+Ch2+Ch3+Ch4.pptx
PDF
Dr.Shoeb_ME212_Lec-2-NUMERICAL METHODS_g
PPTX
PPTX
Numerical Analysis and Its application to Boundary Value Problems
PDF
PPTX
NUMERICAL METHOD CHAPTE 1 numerical solution part 1.pptx
PDF
Errors in Numerical Analysis
PPTX
PDF
NM Note 01 dhfehfihieahfiheifhihdifhi8hifdiafh
PPTX
numerical chapter 2 numerical method and analysis.pptx
PDF
Numerical Analysis_Approximation Error & Operator.pdf
PPT
Lesson 1 Measuring Errors.ppt the material regards errors in measuring a
PPTX
Numerical Analysis Class1 Introduction to numerical analysis
PPTX
PPT
PPT
PPTX
PDF
Numerical analysis using Scilab: Error analysis and propagation
PPTX
PPTX
PDF
Using Charts and Tables in Presenting Data
PDF
Analyzing the data of your initial survey
More Related Content
PPT
Unit One - Solved problems on error analysis .ppt
PPT
PDF
Chapter assignment character assignemetb
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
Engineering Numerical Analysis Lecture-1
PDF
Introduction-Accuracy-and-Errors.pdf
PPTX
LEC01.wararAWQWWRwrrwqRQRWQWQqqrwq1.pptx
Similar to 3_Sources of error_numerical methods.pptx
PPTX
Engineering analysisPart1=Ch1+Ch2+Ch3+Ch4.pptx
PDF
Dr.Shoeb_ME212_Lec-2-NUMERICAL METHODS_g
PPTX
PPTX
Numerical Analysis and Its application to Boundary Value Problems
PDF
PPTX
NUMERICAL METHOD CHAPTE 1 numerical solution part 1.pptx
PDF
Errors in Numerical Analysis
PPTX
PDF
NM Note 01 dhfehfihieahfiheifhihdifhi8hifdiafh
PPTX
numerical chapter 2 numerical method and analysis.pptx
PDF
Numerical Analysis_Approximation Error & Operator.pdf
PPT
Lesson 1 Measuring Errors.ppt the material regards errors in measuring a
PPTX
Numerical Analysis Class1 Introduction to numerical analysis
PPTX
PPT
PPT
PPTX
PDF
Numerical analysis using Scilab: Error analysis and propagation
PPTX
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PDF
Using Charts and Tables in Presenting Data
PDF
Analyzing the data of your initial survey
PDF
The Tale of Melon City poem ppt by Sahasra
PPTX
Multiple Linear Regression - Least Square Method X₁ on X₂ and X₃
PDF
Most Imp Chapters & Weightage for Boards 2025.pdf
PPTX
10-12-2025 Francois Staring How can Researchers and Initial Teacher Educators...
PDF
Micro Economics for class 12 and class 11
PPTX
Pig- piggy bank in Big Data Analytics.ppt.pptx
PDF
DHA/HAAD/MOH/DOH OPTOMETRY MCQ PYQ. .pdf
PPTX
Growth & Development MILESTONES (ADOLESCENTS ).pptx
PPTX
Partial Correlation - Values of r₁₂.₃, r₂₃.₁ & r₁₃.₂ r₁₂, r₁₃ and r₂₃
PDF
Types of eggs and Egg membranes (Developmental Zoology)
PPTX
The Cell & Cell Cycle-detailed structure and function of organelles.pptx
PPTX
PURPOSIVE SAMPLING IN EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH RACHITHRA RK.pptx
PDF
Multiple Myeloma , definition, etiology, PP, CM , DE and management
PPTX
How to Manage Package Reservation in Odoo 18 Inventory
PPTX
3 G8_Q3_L3_ (Cartoon as Representation in Opinion Editorial Article).pptx
PPTX
How to Create Lead_Opportunity From Odoo 18 Website
PDF
Blood Group Incompatibility: Rh Factor and Erythroblastosis Fetalis
PPTX
PARENTAL ROUTES OF DRUGS ADMINISTRATION .pptx
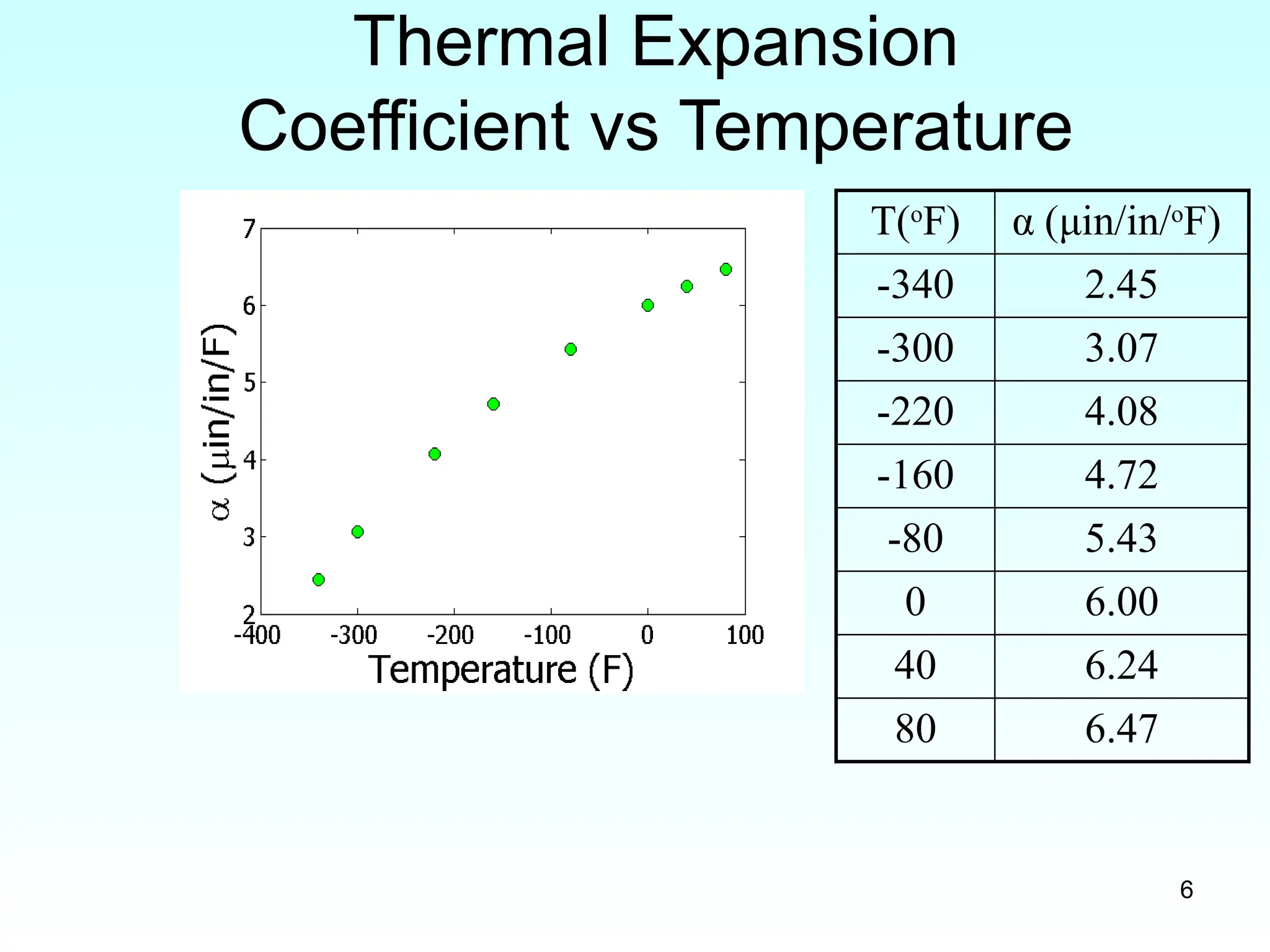
3_Sources of error_numerical methods.pptx 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 8
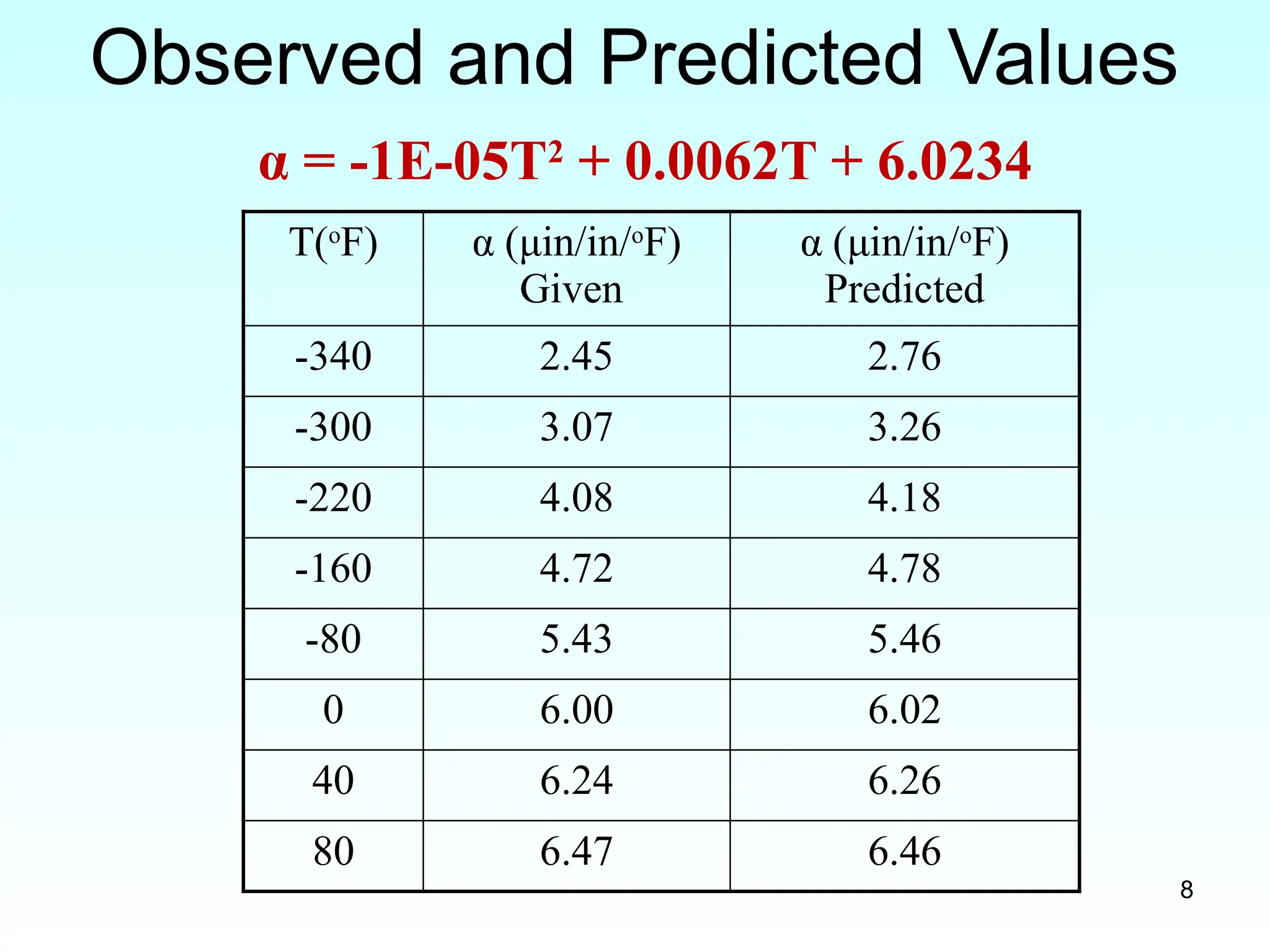
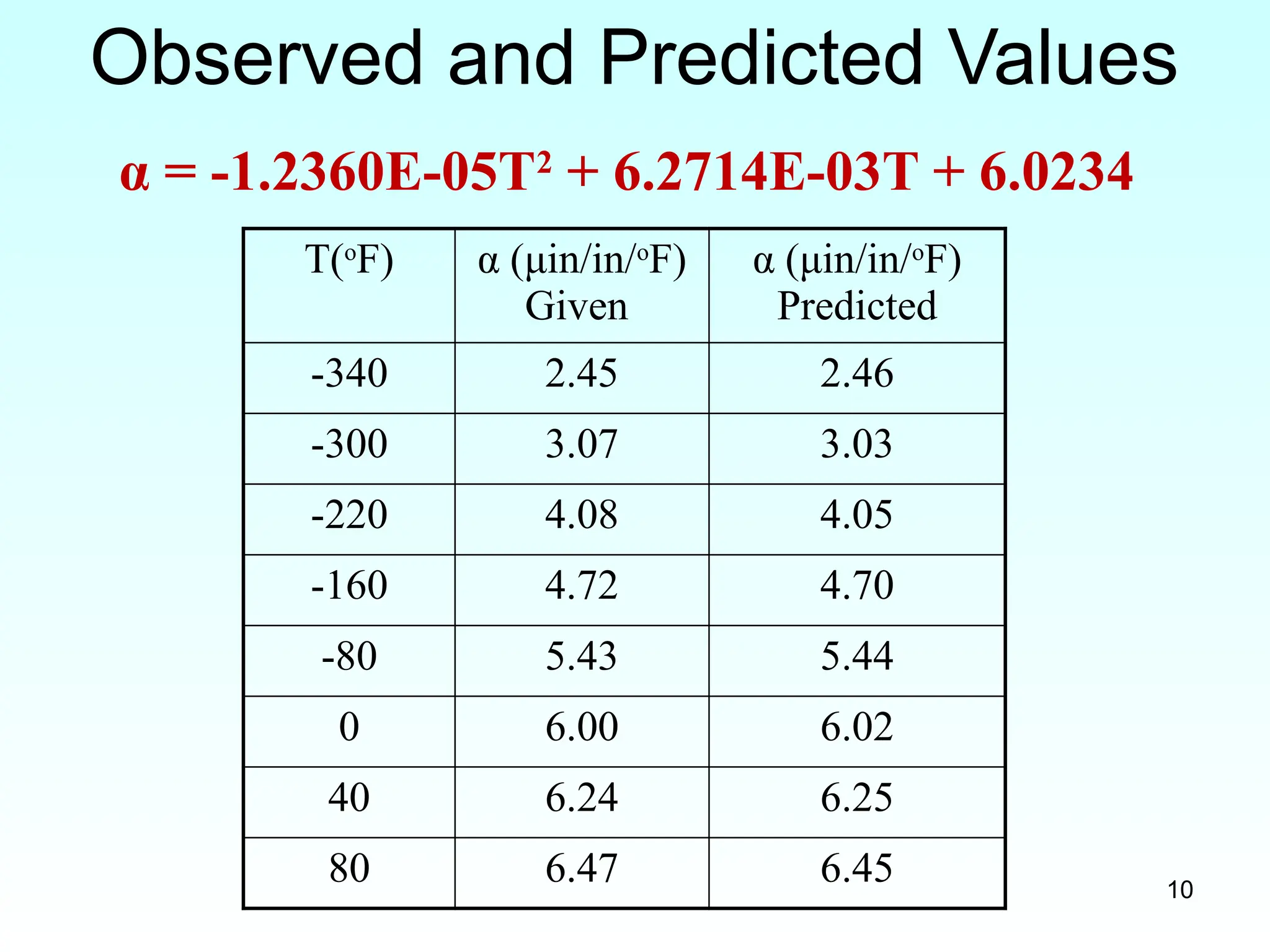
Observed and Predicted Values
T(o
F) α (μin/in/o
F)
Given
α (μin/in/o
F)
Predicted
-340 2.45 2.76
-300 3.07 3.26
-220 4.08 4.18
-160 4.72 4.78
-80 5.43 5.46
0 6.00 6.02
40 6.24 6.26
80 6.47 6.46
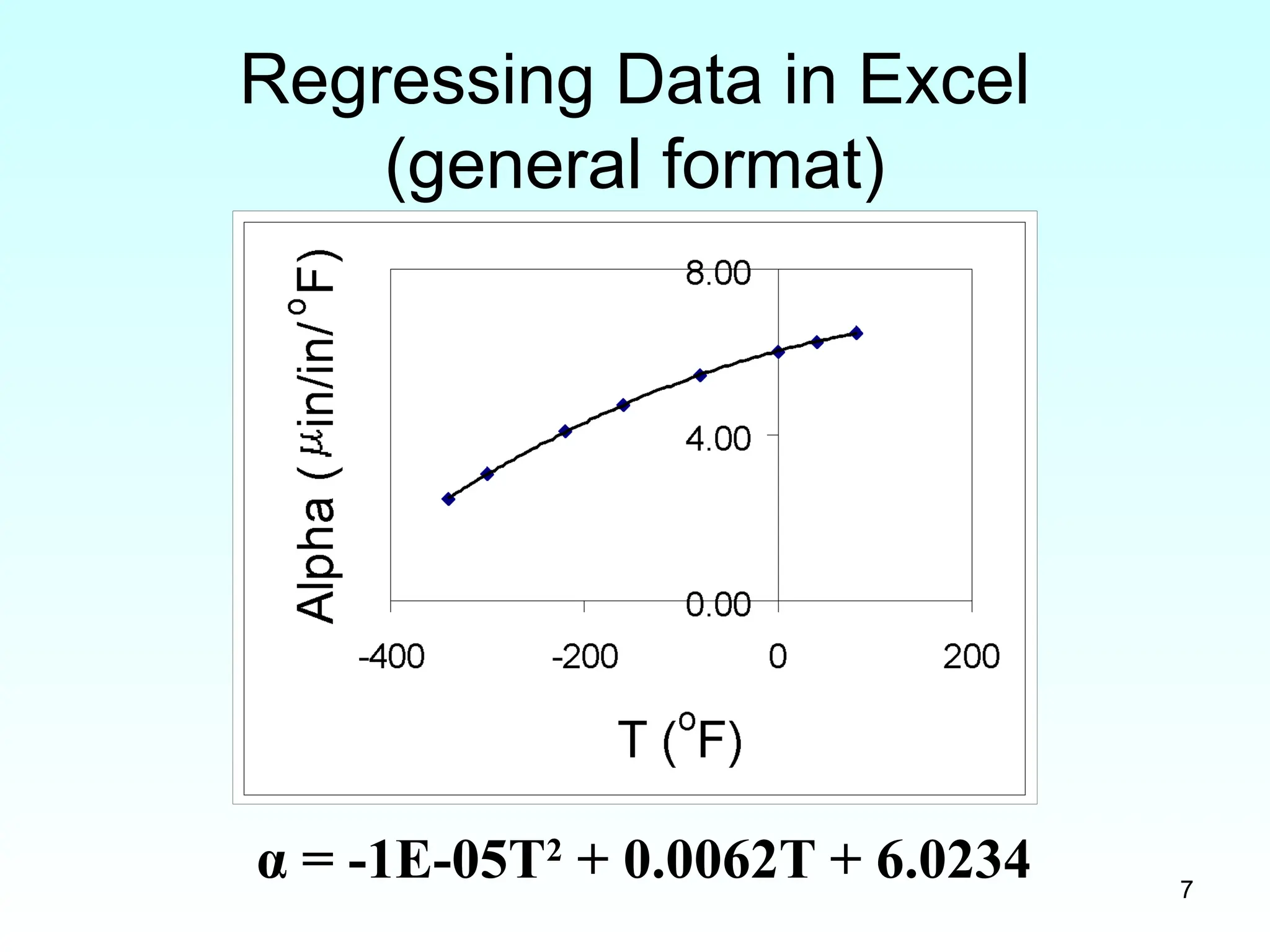
α = -1E-05T2
+ 0.0062T + 6.0234
9. 10. 10
Observed and Predicted Values
T(o
F) α (μin/in/o
F)
Given
α (μin/in/o
F)
Predicted
-340 2.45 2.46
-300 3.07 3.03
-220 4.08 4.05
-160 4.72 4.70
-80 5.43 5.44
0 6.00 6.02
40 6.24 6.25
80 6.47 6.45
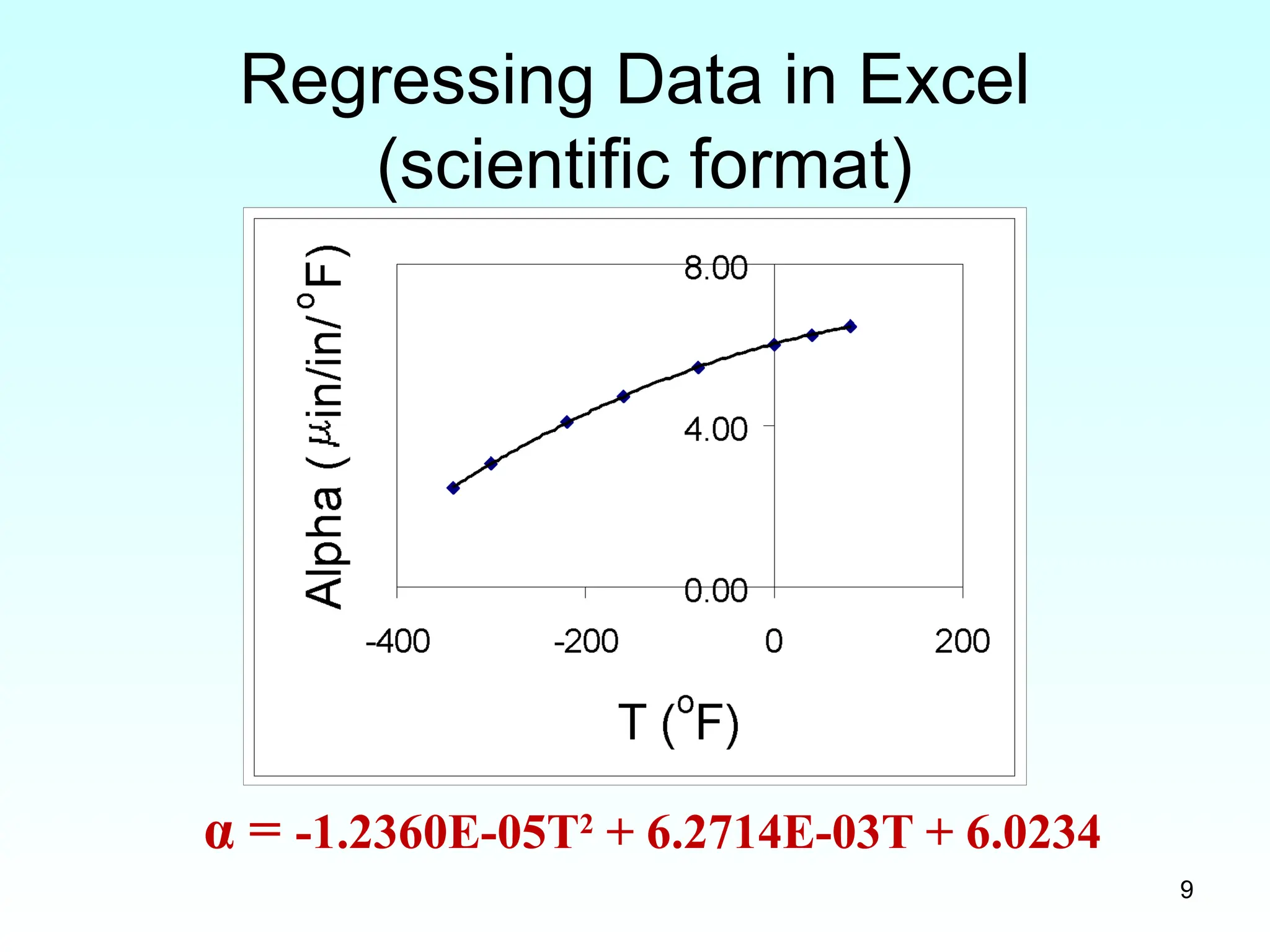
α = -1.2360E-05T2
+ 6.2714E-03T + 6.0234
11. 11
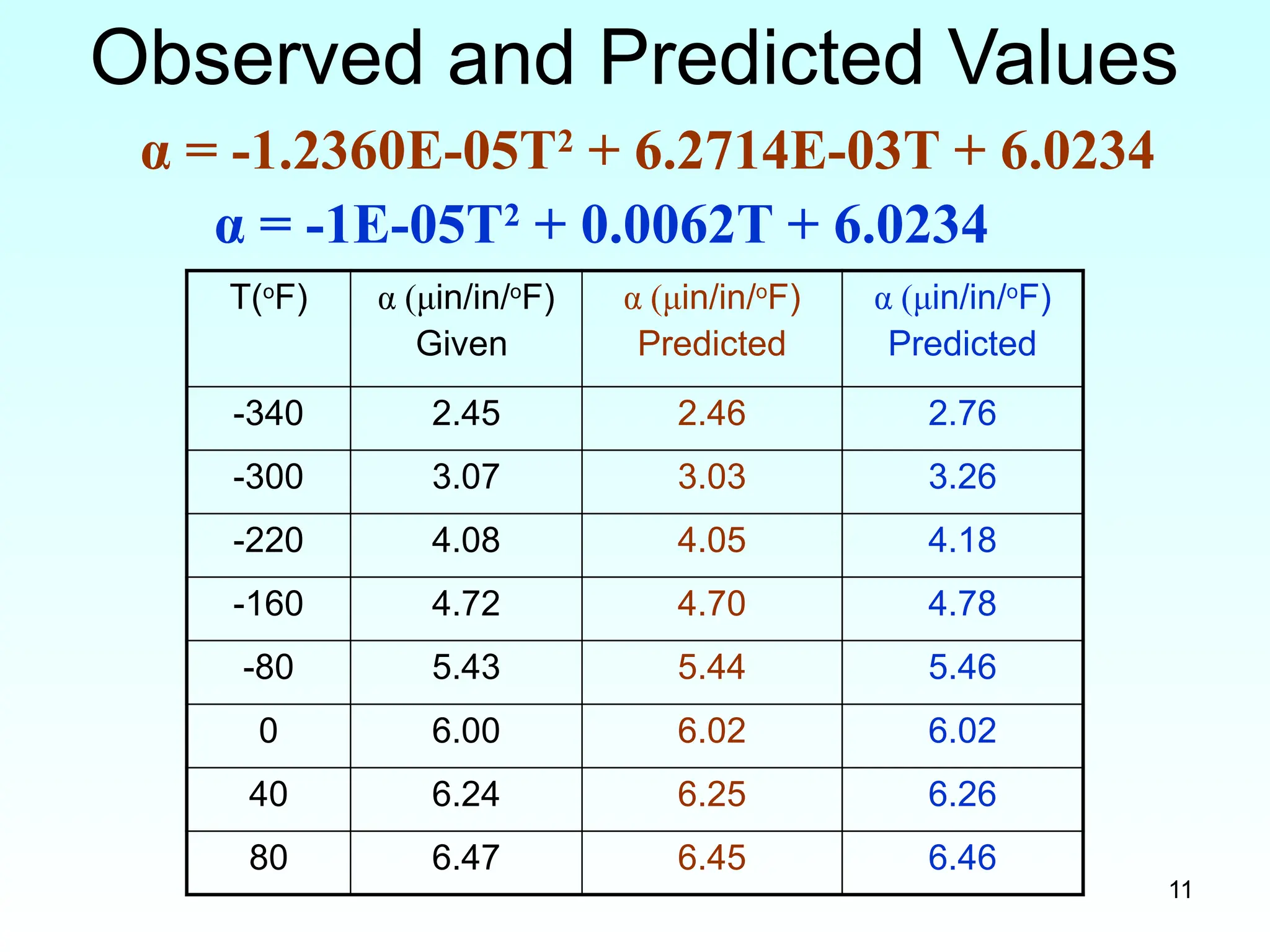
Observed and Predicted Values
T(o
F) α (μin/in/o
F)
Given
α (μin/in/o
F)
Predicted
α (μin/in/o
F)
Predicted
-340 2.45 2.46 2.76
-300 3.07 3.03 3.26
-220 4.08 4.05 4.18
-160 4.72 4.70 4.78
-80 5.43 5.44 5.46
0 6.00 6.02 6.02
40 6.24 6.25 6.26
80 6.47 6.45 6.46
α = -1.2360E-05T2
+ 6.2714E-03T + 6.0234
α = -1E-05T2
+ 0.0062T + 6.0234
12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 16
Example 1 —Maclaurin series
n
1 1 __ ___
2 2.2 1.2 54.545
3 2.92 0.72 24.658
4 3.208 0.288 8.9776
5 3.2944 0.0864 2.6226
6 3.3151 0.020736 0.62550
6 terms are required to get RAE < 1%. How many are required to get at least 1 significant digit
correct in your answer?
= Approximate
error
= Relative approximate
error
17. 17
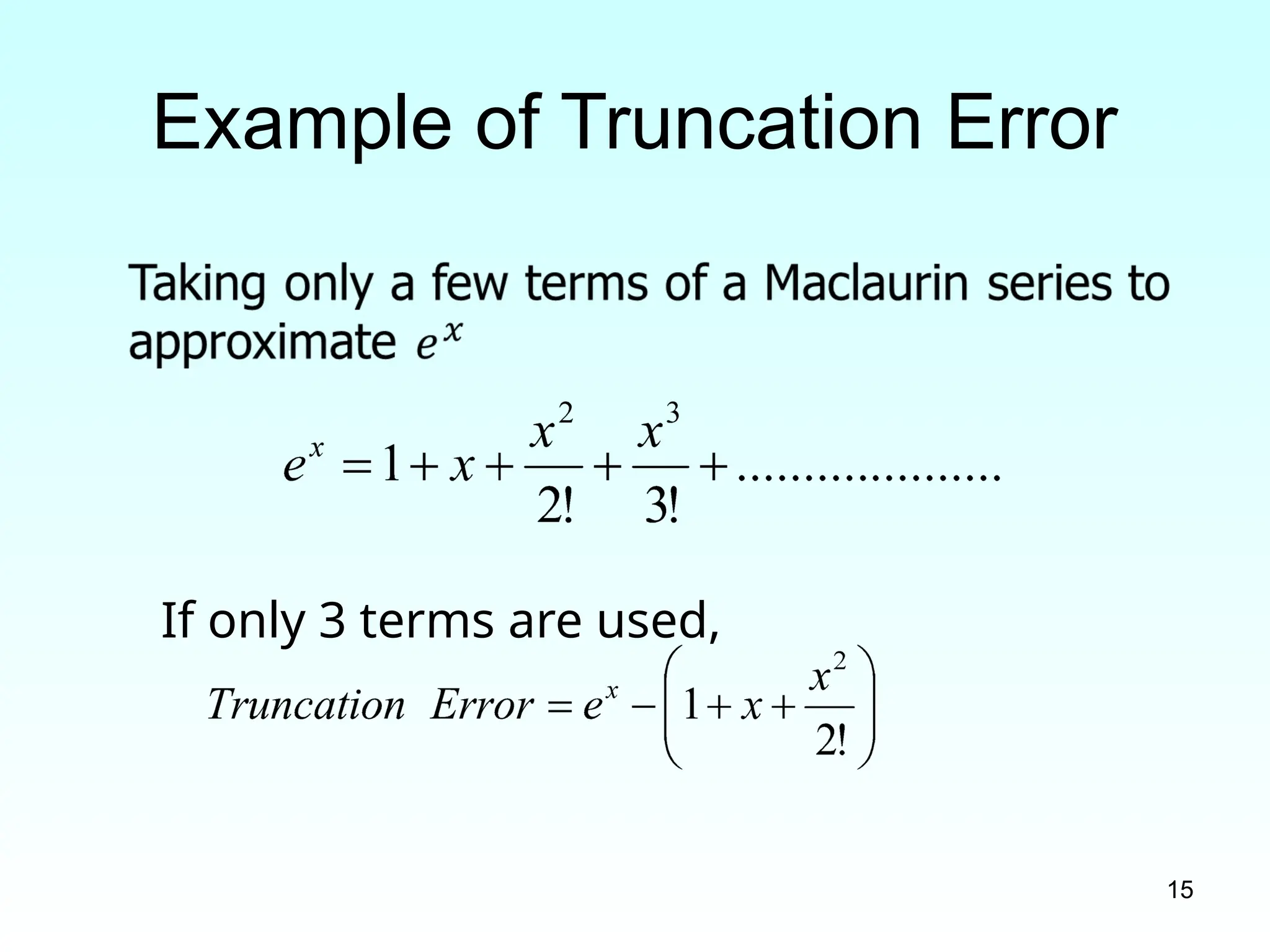
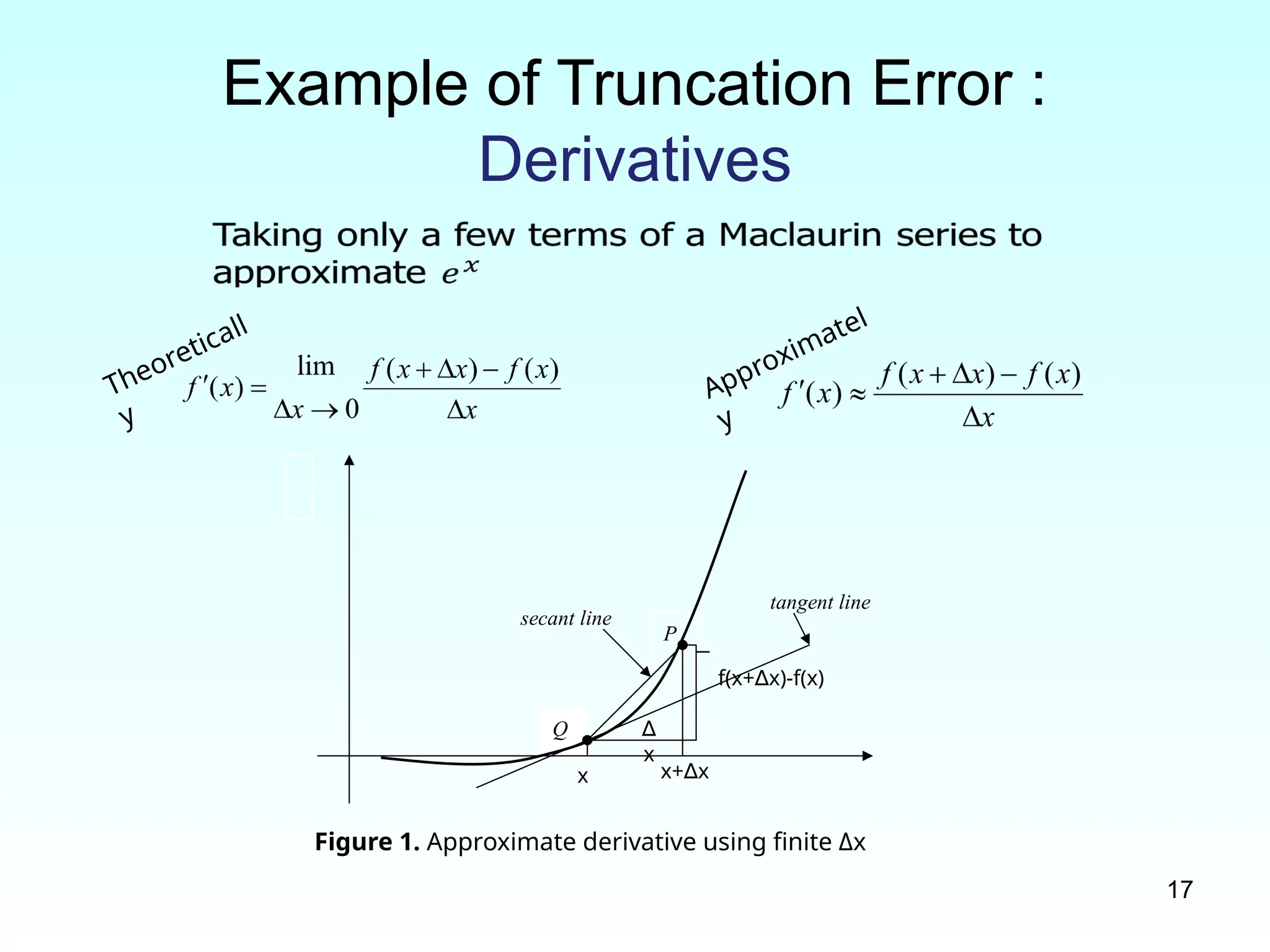
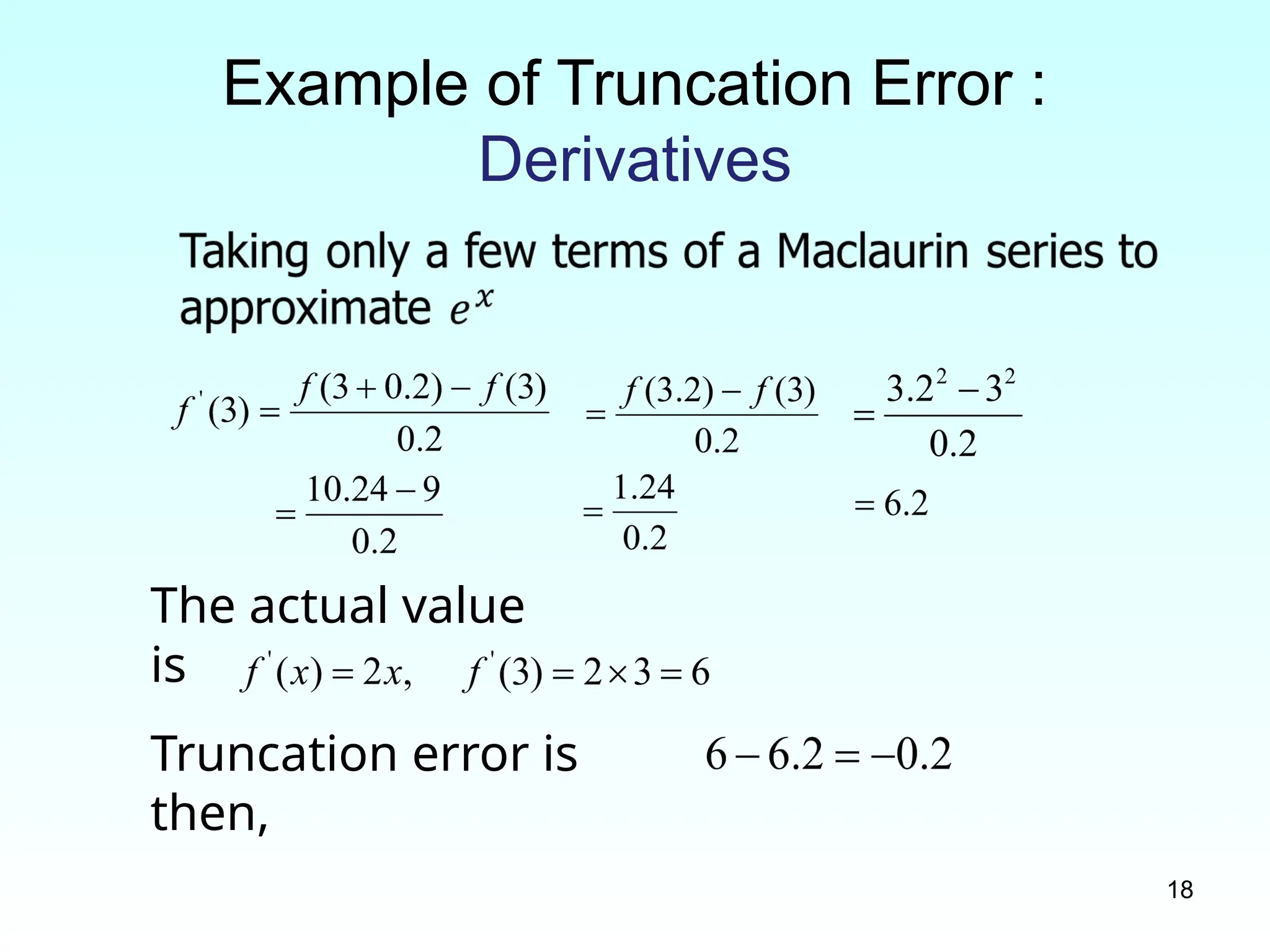
Example of Truncation Error :
Derivatives
P
Q
secant line
tangent line
Figure 1. Approximate derivative using finite Δx
x x+ x
∆
∆
x
f(x+ x)-f(x)
∆
Theoreticall
y
Approximatel
y
18. 19. 19
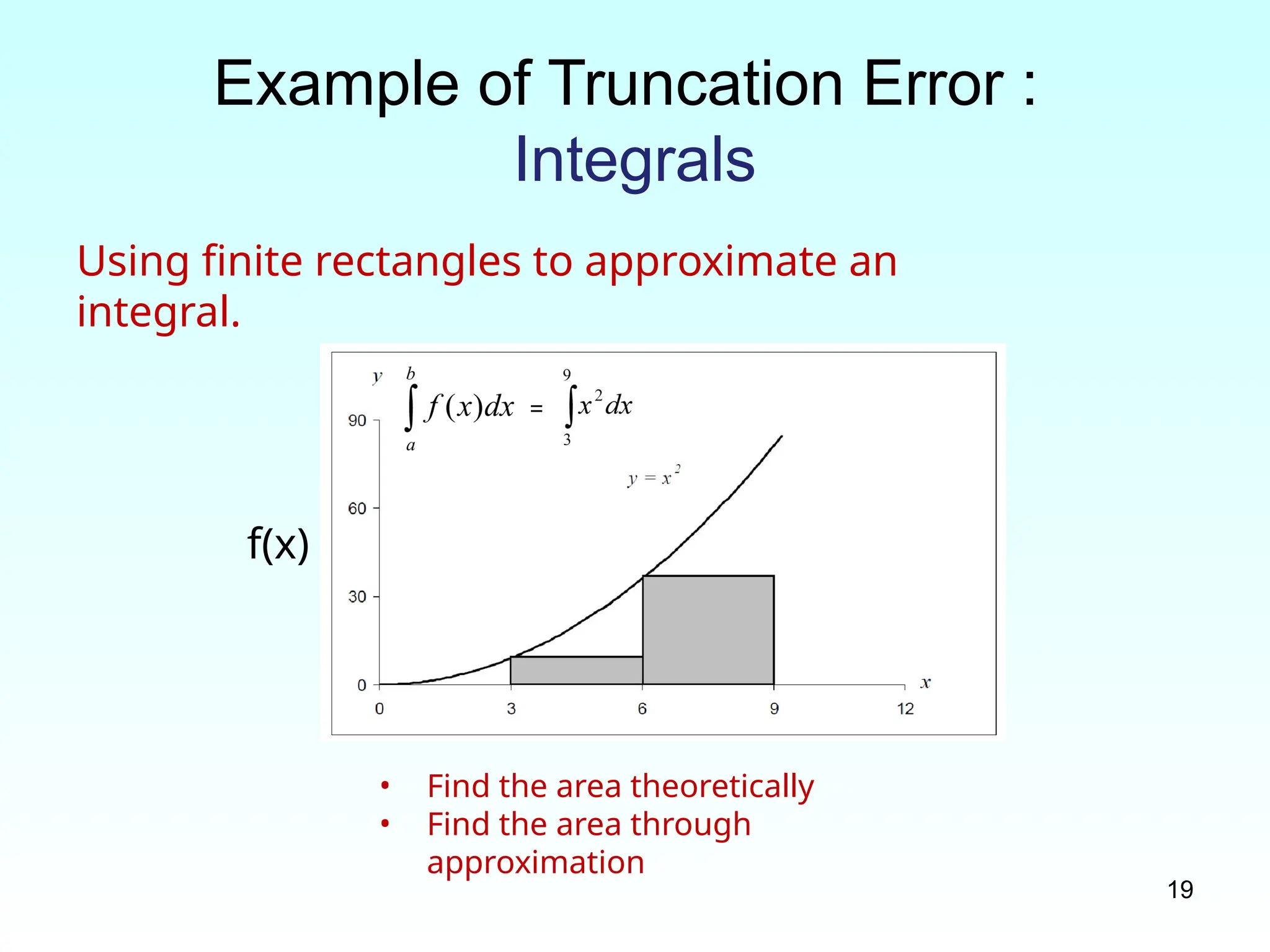
Example of Truncation Error :
Integrals
Using finite rectangles to approximate an
integral.
f(x)
• Find the area theoretically
• Find the area through
approximation
=
20. 20
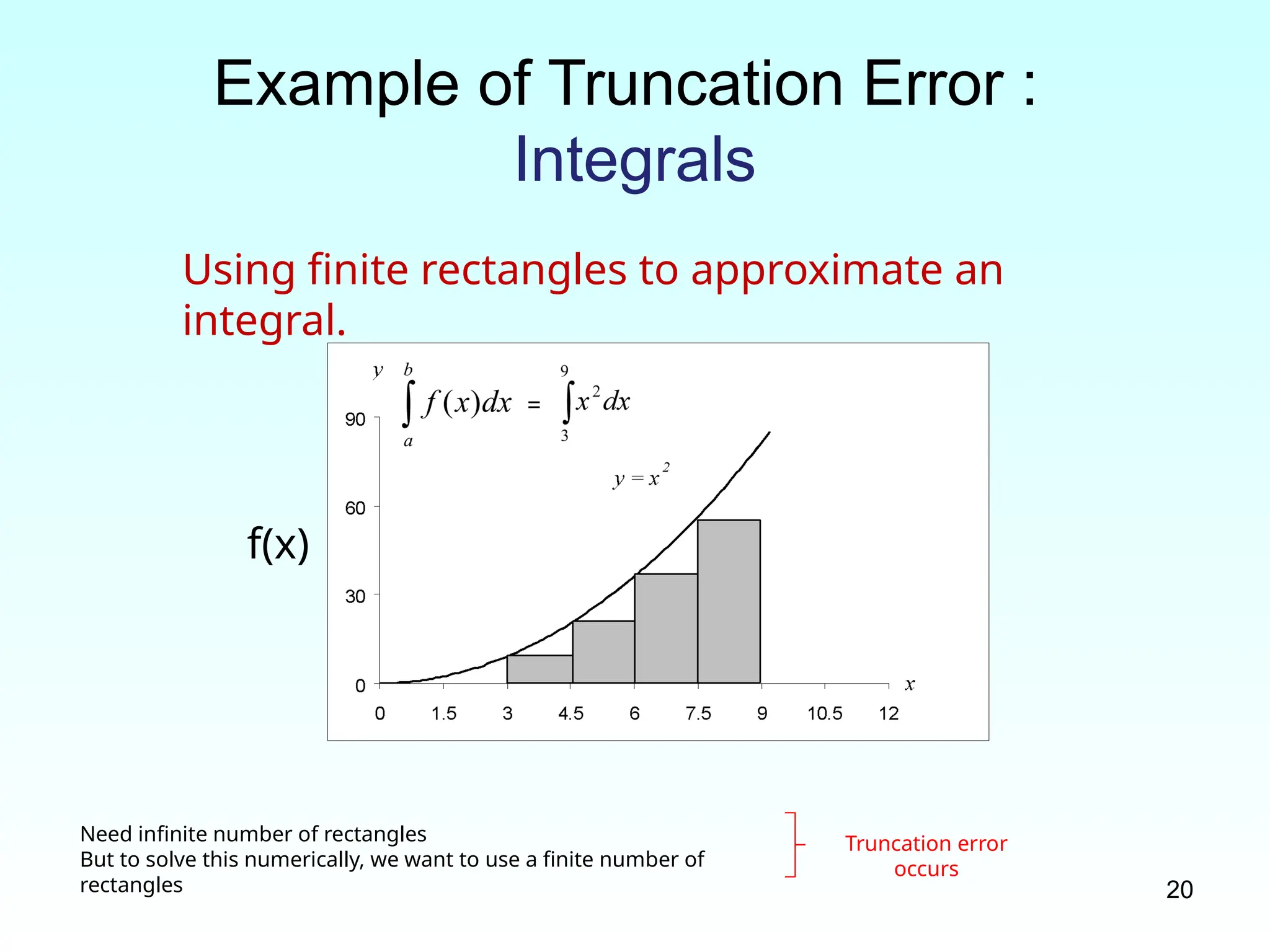
Example of Truncation Error :
Integrals
Using finite rectangles to approximate an
integral.
f(x)
Need infinite number of rectangles
But to solve this numerically, we want to use a finite number of
rectangles
Truncation error
occurs
=
21. 22. Additional Resources
• Numerical Methods with Applications: Abridged (2nd
Edition) – Autar Kaw, Egwu Kalu
http://mathforcollege.com/nm/topics/textbook_index.html
• Introductory Methods of Numerocal Analysis – S. S.
Sastry
23.