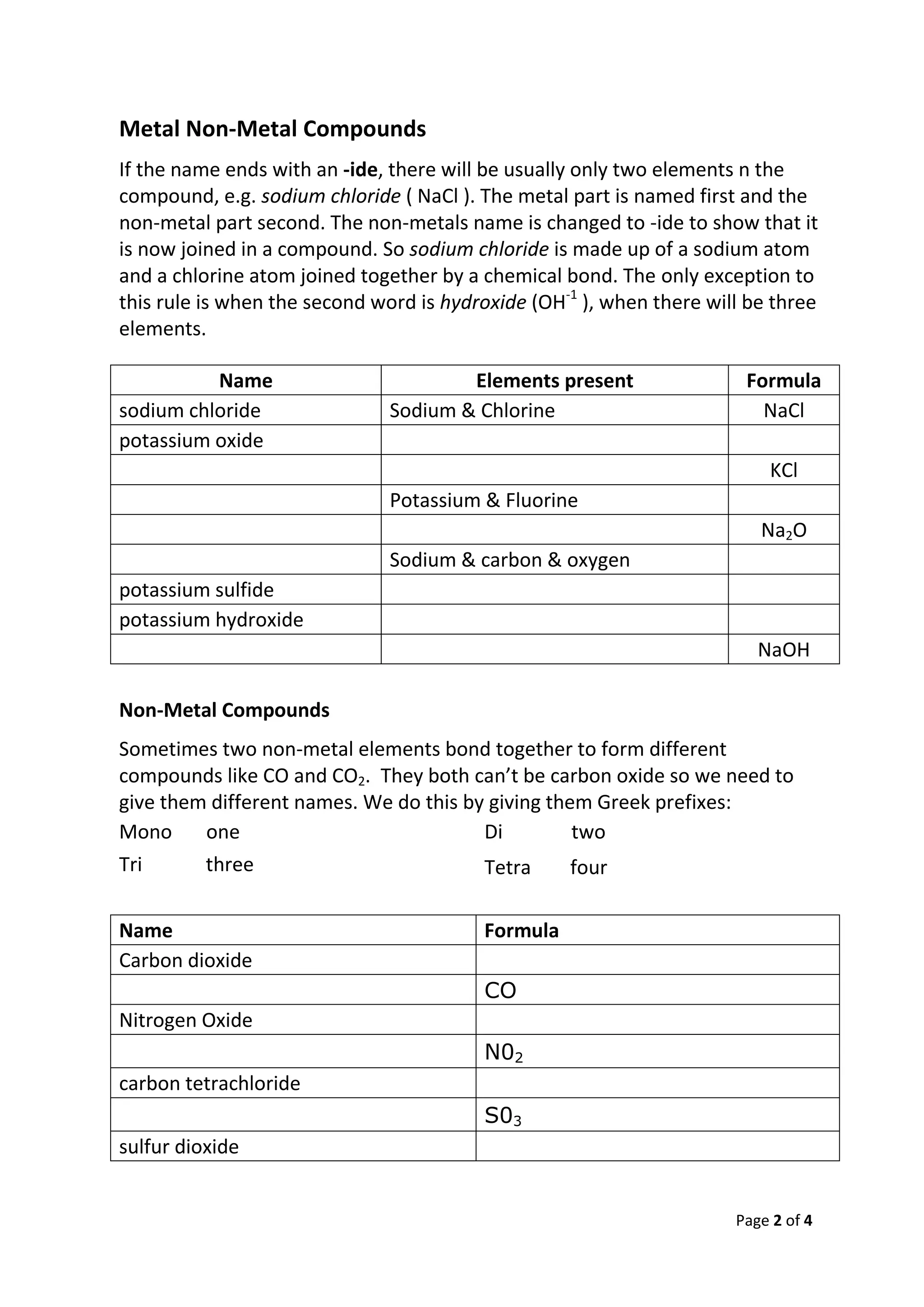
The document provides information about naming chemical compounds, including:
- Compounds consisting of a metal and nonmetal take the name of the metal followed by the nonmetal with an "-ide" suffix (e.g. sodium chloride).
- Nonmetal compounds are distinguished by Greek prefixes like "mono", "di", etc (e.g. carbon dioxide vs carbon monoxide).
- Compounds ending in "-ite" or "-ate" contain oxygen, with "-ate" indicating more oxygen ("-ite" less).
- Some compounds contain hydrogen, indicated by "hydrogen" in the name or the prefix "bi-".
- Metals forming multiple compounds are distinguished by Roman numerals indicating the metal's charge