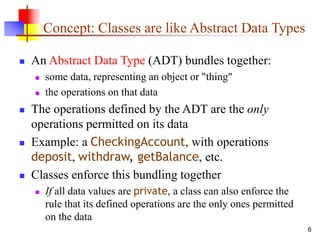
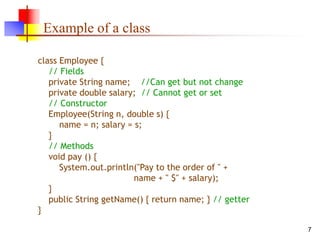
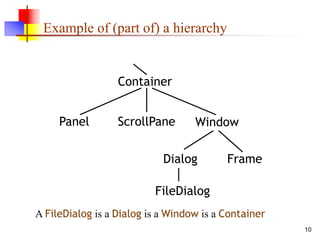
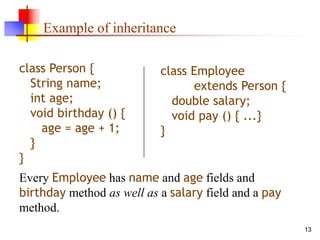
An object contains both data and methods that manipulate that data. The data represents the state of the object. Classes describe objects by defining their fields and methods. Objects inherit fields and methods from their superclass. To create an object, the appropriate constructor must be called using the new keyword. Access control determines which fields and methods are accessible to other classes.





























![36
Kinds of access
Java provides four levels of access:
public: available everywhere
protected: available within the package (in the same
subdirectory) and to all subclasses
[default]: available within the package
private: only available within the class itself
The default is called package visibility
In small programs this isn't important...right?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/38-object-concepts1-211007165043/85/38-object-concepts-1-36-320.jpg)
