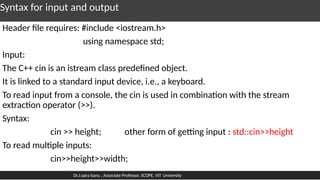
The document outlines fundamental concepts of classes and objects in C++ with detailed syntax for defining classes, creating objects, and accessing class members. It explains access specifiers (private, public, protected), methods for input and output using cin and cout, and provides examples of programs that calculate area and total marks using classes. Additionally, it covers the use of arrays in classes and the implementation of getter and setter functions for private members.















![Array of Elements in a class
Arrays can be declared as the members of a class. The arrays can be declared
as private, public or protected members of the class.
Example:
class student {
int roll_no;
int marks[size];
public:
void getdata ();
void tot_marks ();
} ;
Dr.J.saira banu , Associate Professor, SCOPE, VIT University](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250210092625-d2791fd0/85/3-Syntax-pptx-for-oops-programing-language-17-320.jpg)
![Array of objects
In C++, an array of objects is a collection of objects of the same class type that
are stored in contiguous memory locations.
Since each item in the array is an instance of the class, each one's member
variables can have a unique value.
This makes it possible to manage and handle numerous objects by storing
them in a single data structure and giving them similar properties and
behaviours.
className arrayName[arraySize];
• arrayName is the name of the array of objects.
• arraySize is the number of objects in the array or the size of array, specified
as a constant expression.
Dr.J.saira banu , Associate Professor, SCOPE, VIT University](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-250210092625-d2791fd0/85/3-Syntax-pptx-for-oops-programing-language-18-320.jpg)


