Embed presentation
Download to read offline


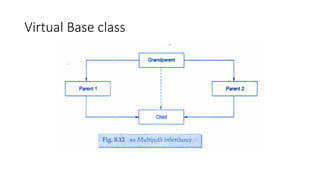

Virtual base classes in C++ prevent multiple instances of a given class in an inheritance hierarchy, particularly during multiple inheritance. By declaring a common base class as a virtual base class, duplication of inherited members is avoided, ensuring only one copy exists for any derived class. The document includes an illustrative C++ code example demonstrating the use of virtual base classes.



