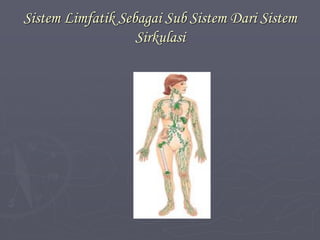
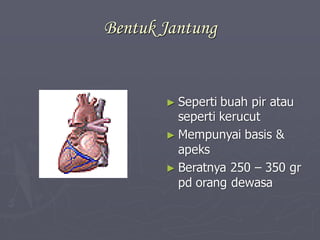
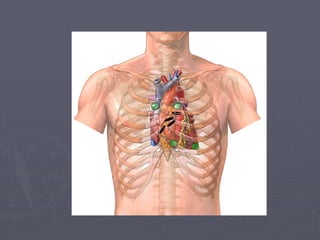
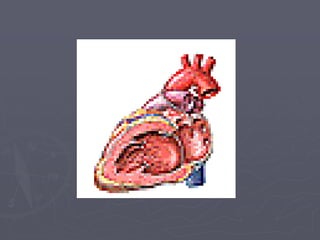
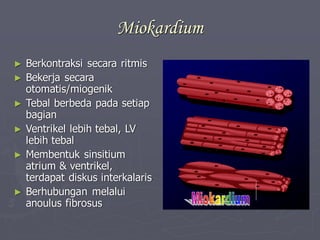
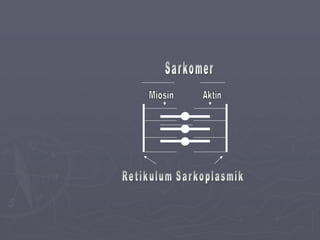
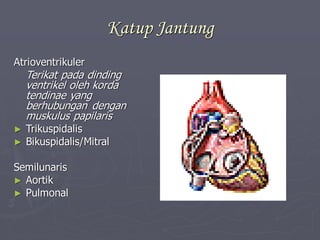
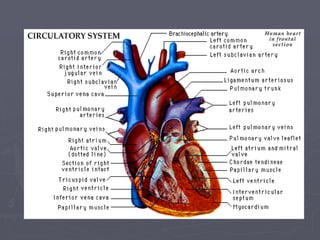
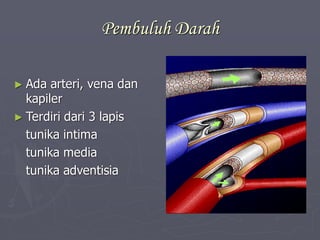
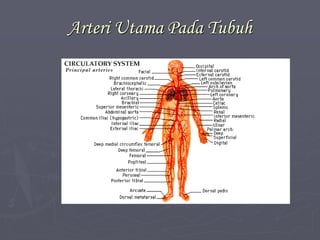
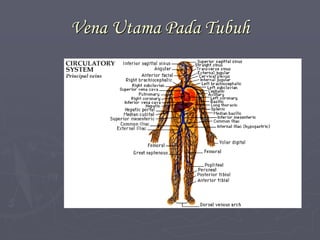
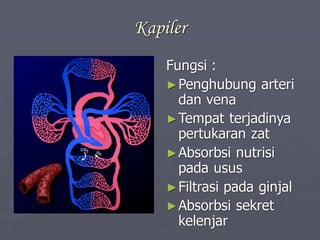
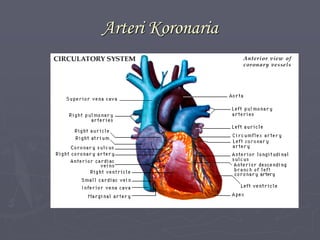
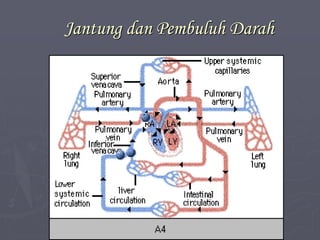
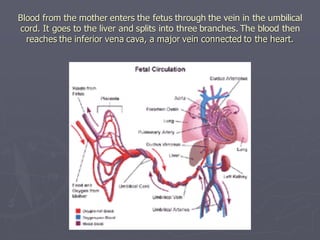
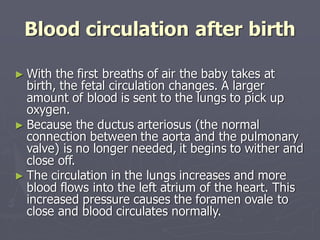
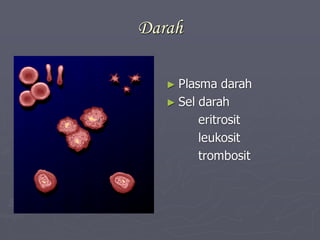
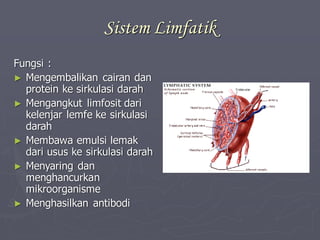
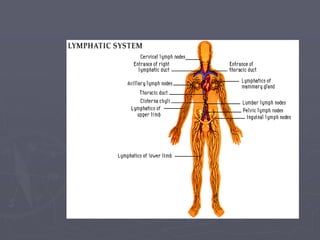
Sistem kardiovaskuler merupakan bagian dari sistem sirkulasi yang mengalirkan darah ke seluruh tubuh melalui jantung dan pembuluh darah. Jantung berfungsi memompa darah ke paru-paru dan seluruh tubuh, sedangkan sistem pembuluh darah mengangkut darah ke jaringan dan organ tubuh. Sistem ini sangat penting untuk mensuplai oksigen dan nutrisi serta mengangkut produk samping metabolisme di seluruh tubuh.