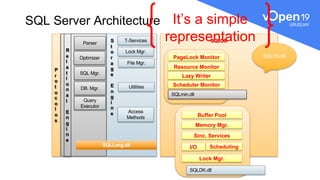
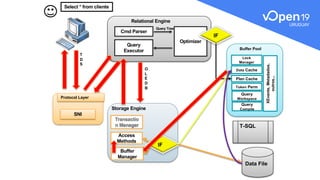
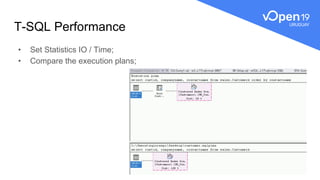
This document discusses various query tuning techniques that SQL Server programmers should know. It covers understanding how queries work and set theory, testing queries, formatting T-SQL for readability, using appropriate predicates and set theory operations, avoiding implicit conversions, and using locks appropriately. The document also includes diagrams of the SQL Server architecture and physical query tree to illustrate how queries are processed.