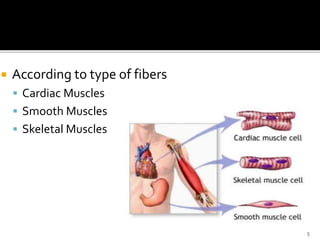
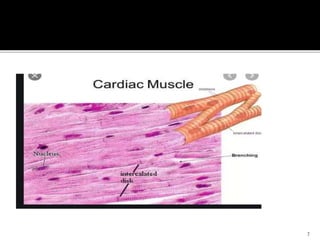
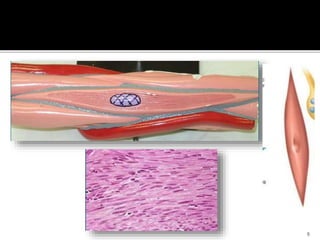
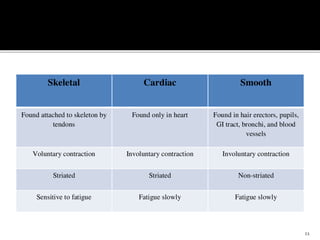
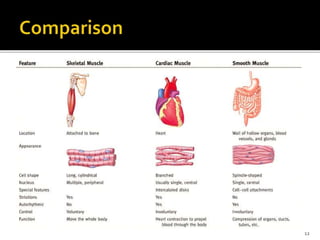
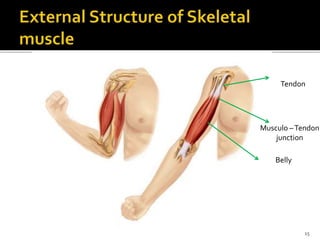
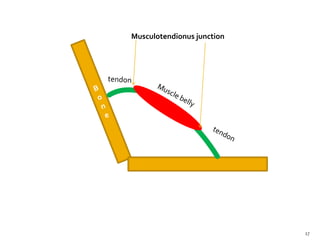
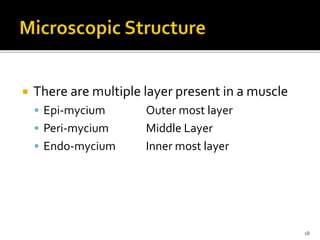
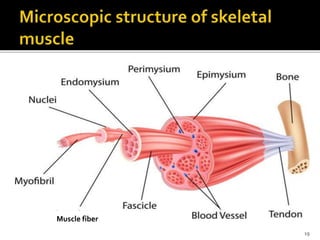
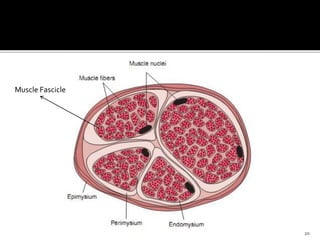
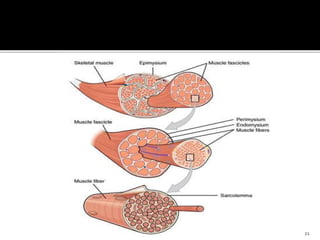
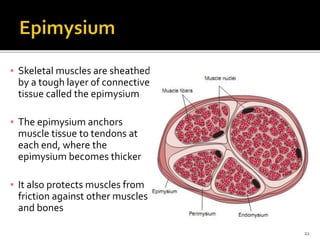
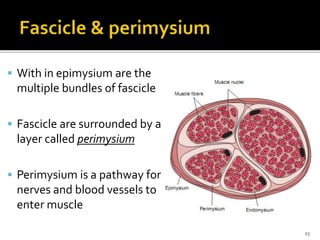
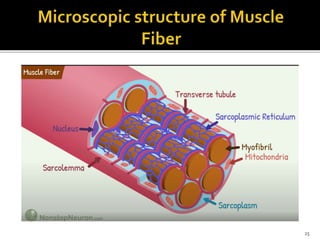
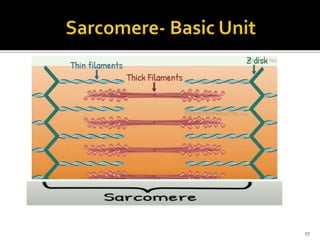
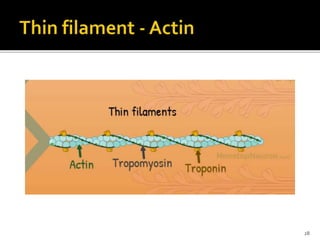
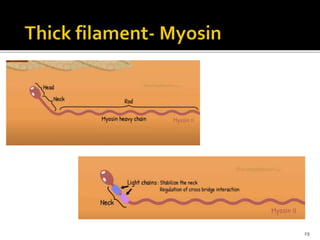
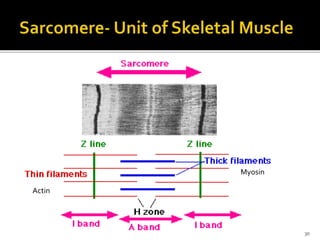
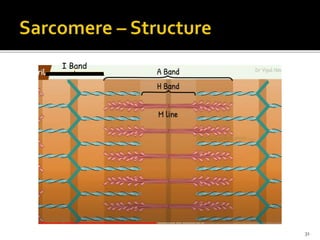
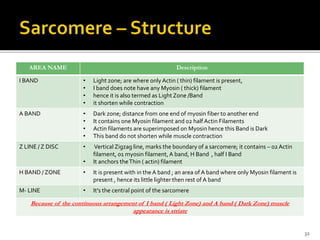
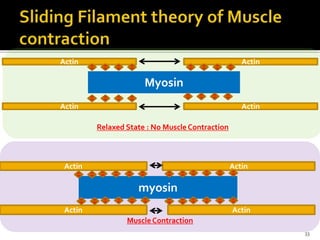
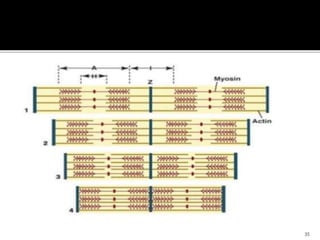
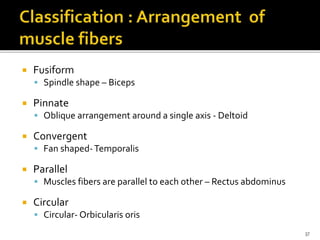
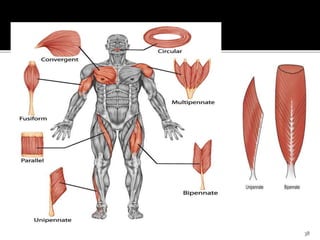
This document discusses the anatomy and physiology of muscles. It defines myology as the study of muscles and describes the main functions of muscles as contraction to produce movement, maintenance of posture, and assisting blood circulation. It then discusses the different types of muscles based on control (voluntary vs involuntary) and fiber type (cardiac, smooth, skeletal). The majority of the document focuses on describing the structure and function of skeletal muscles in more detail.