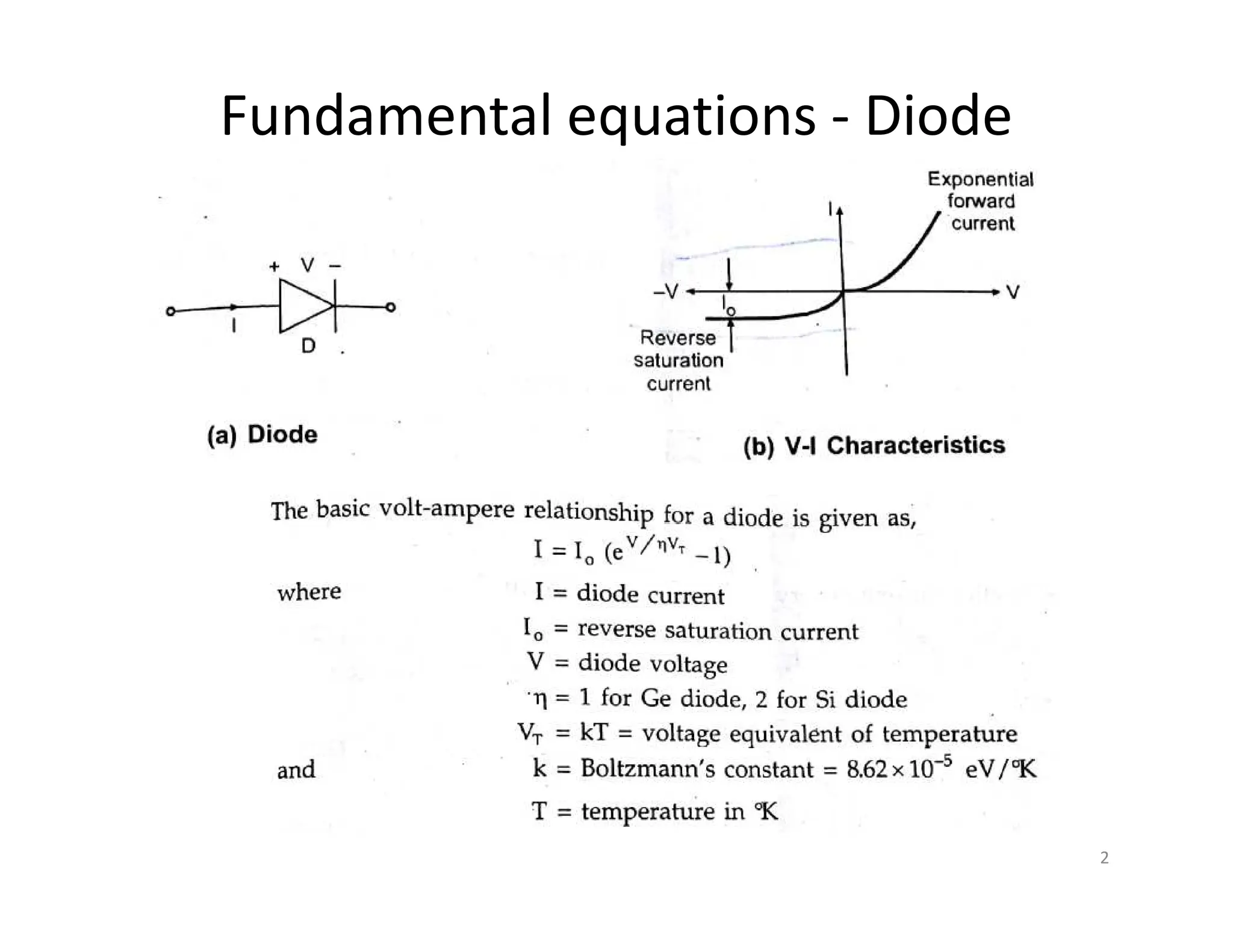
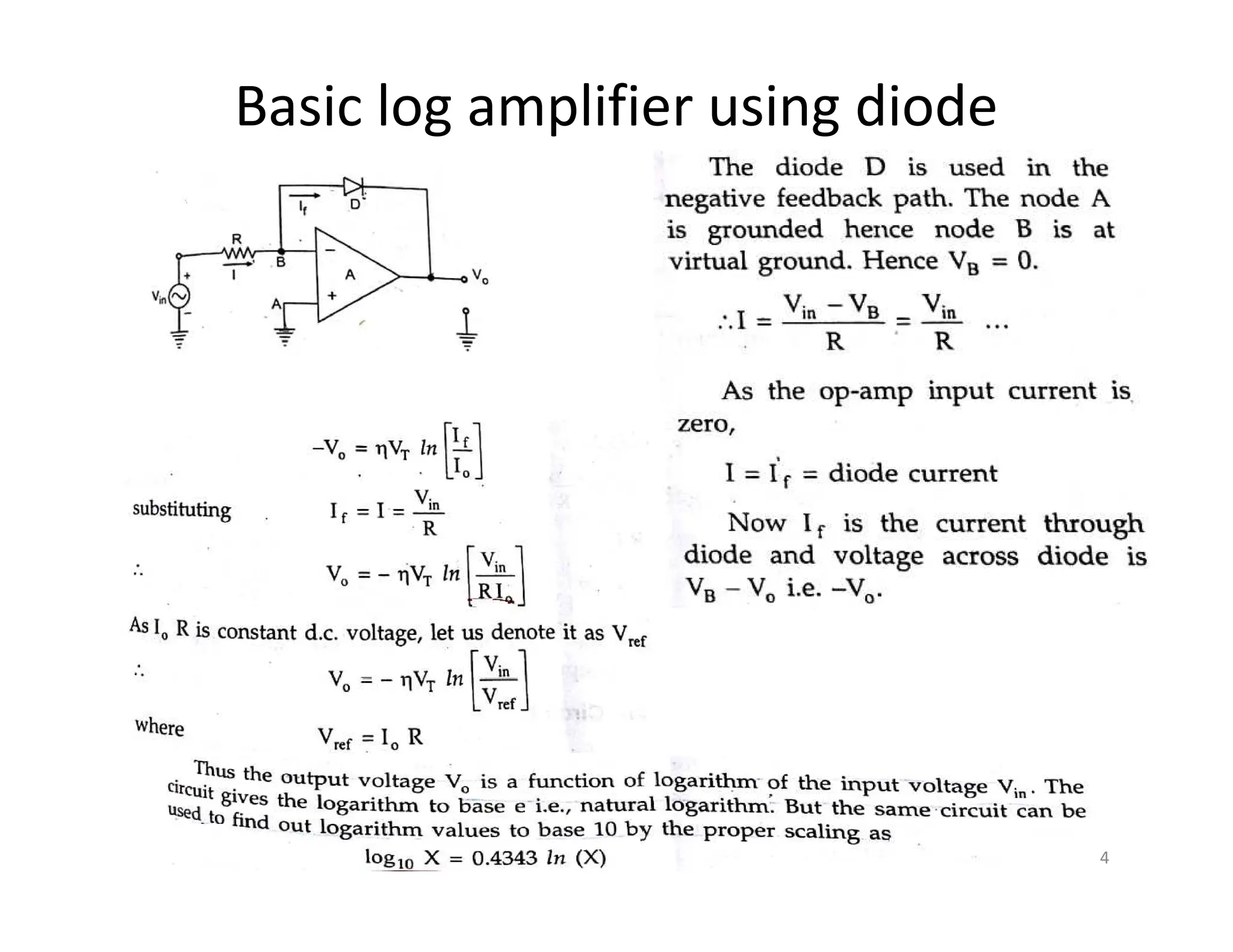
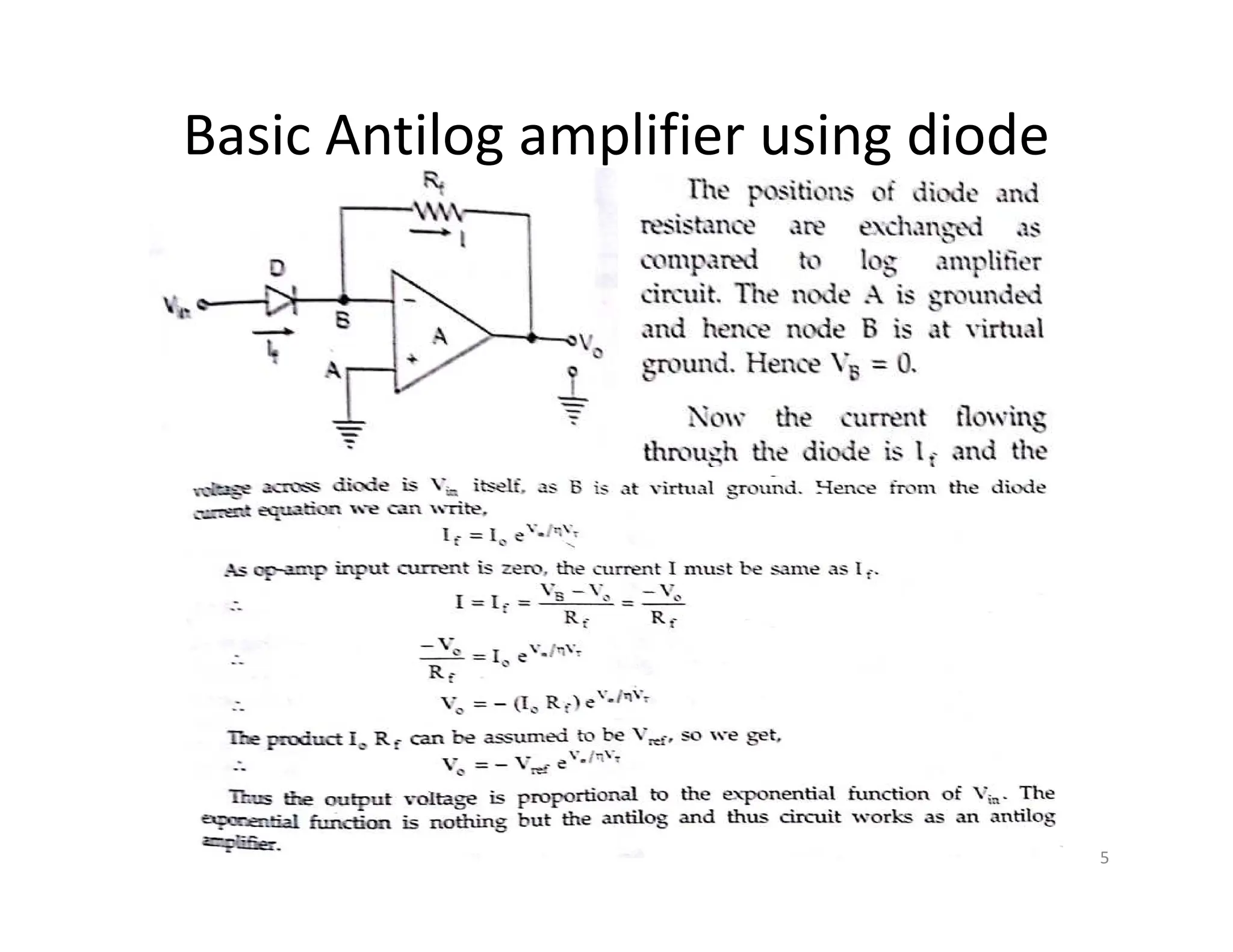
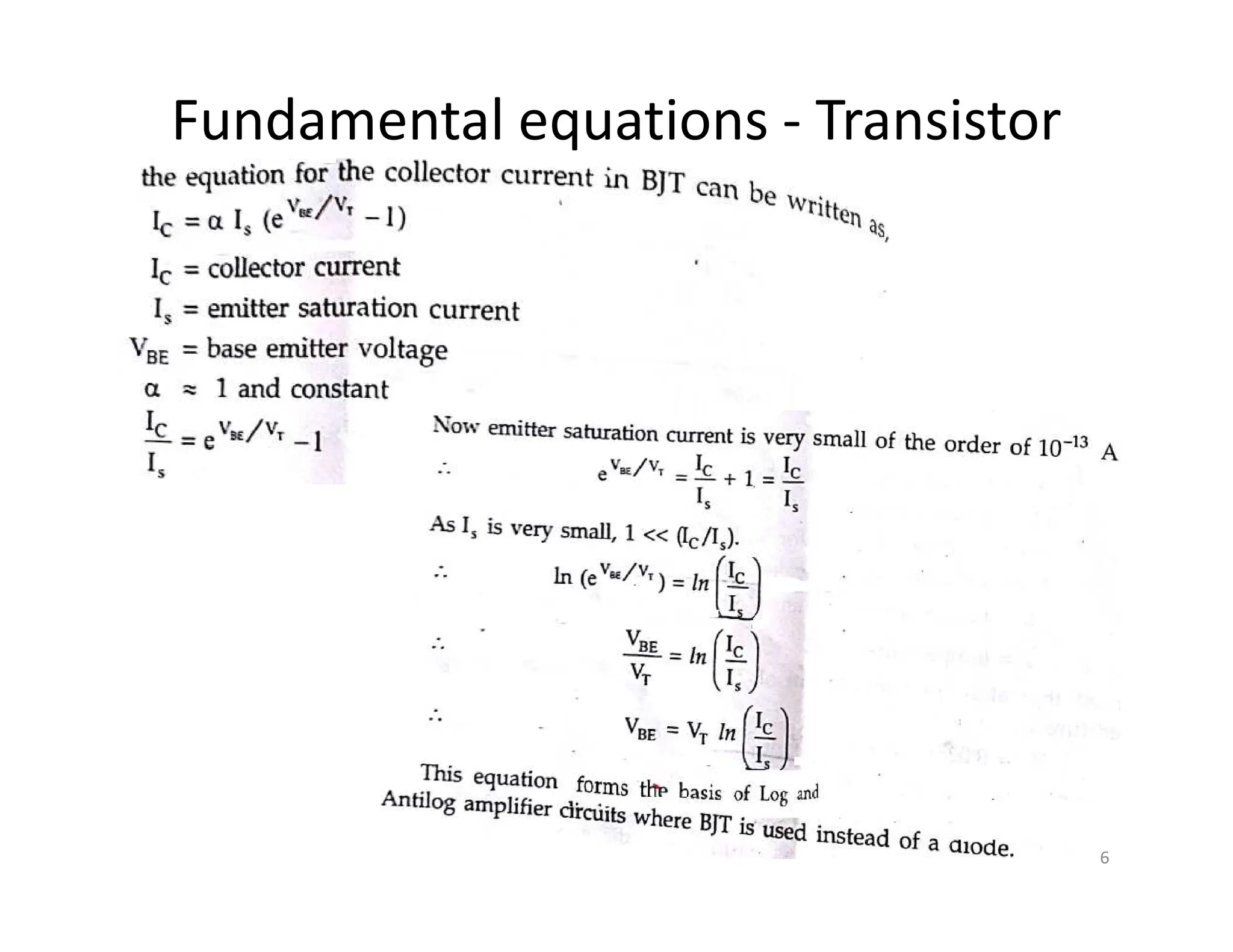
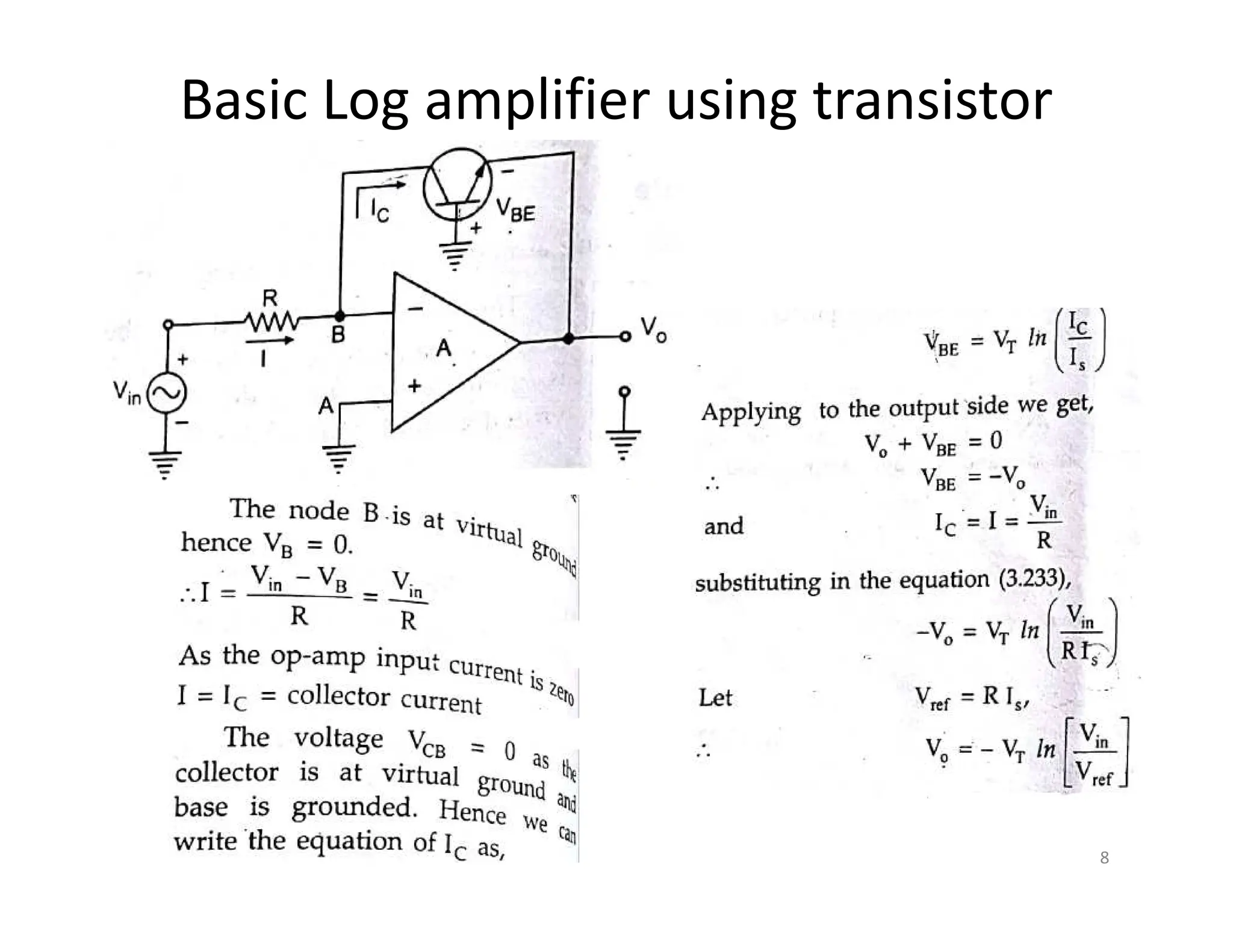
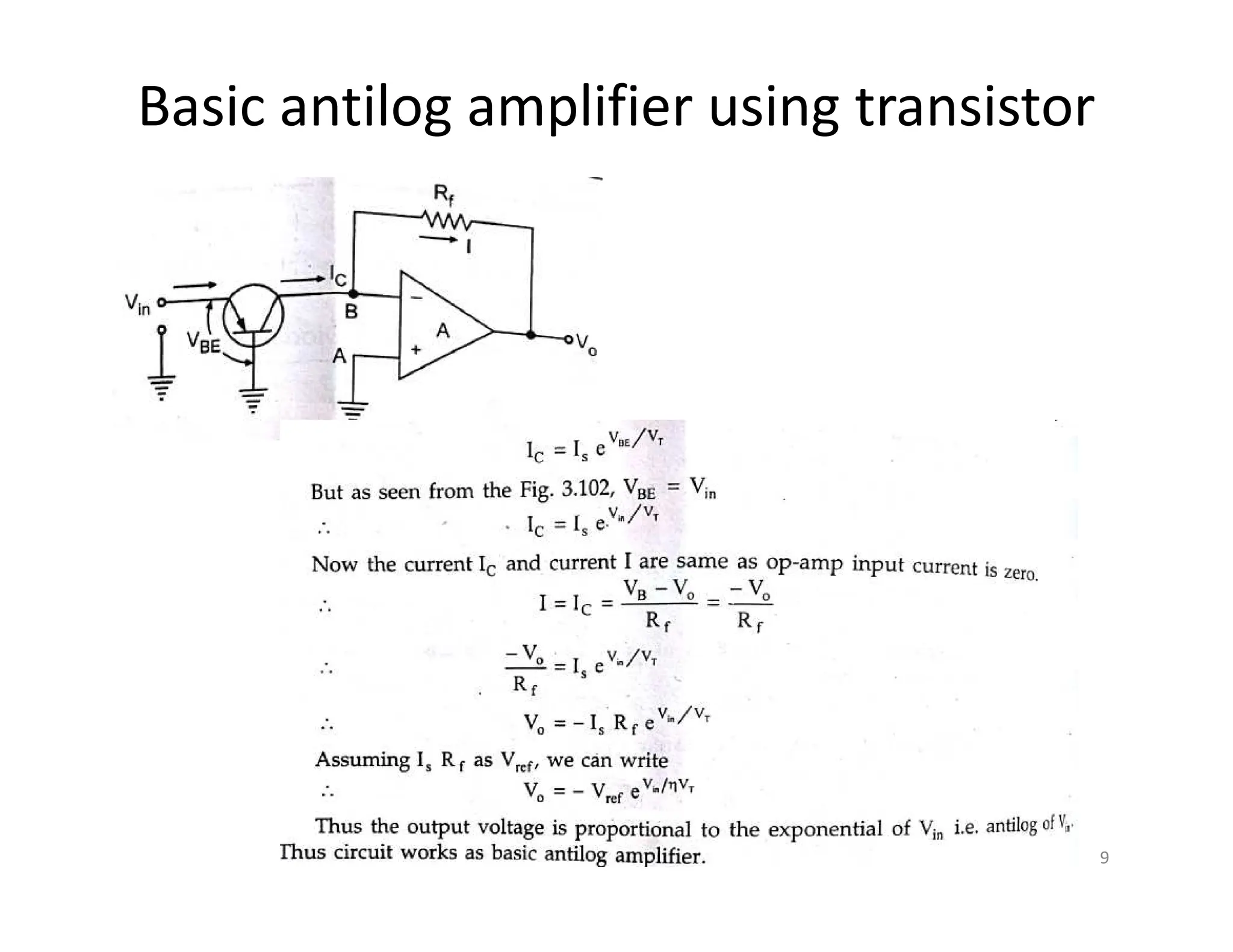
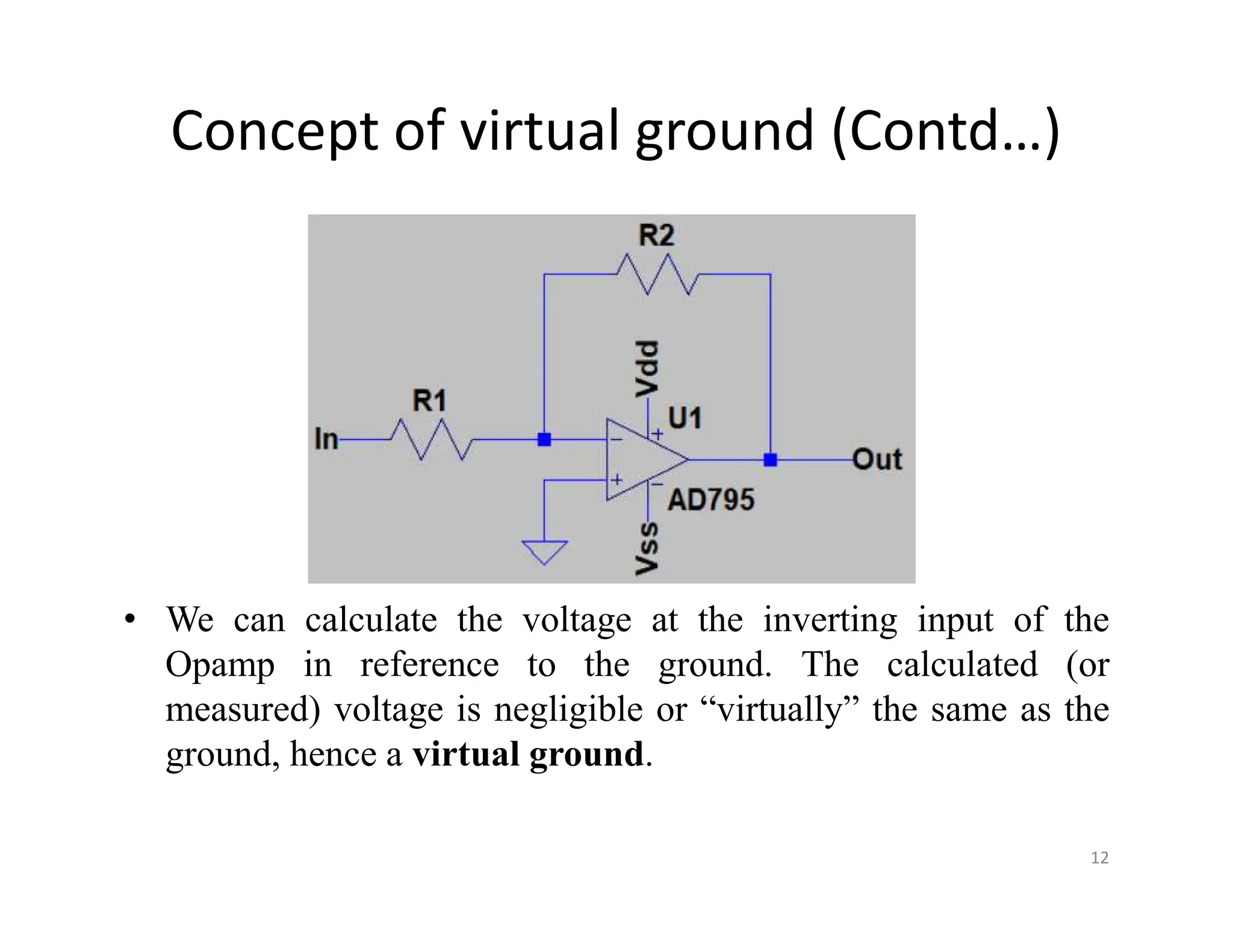
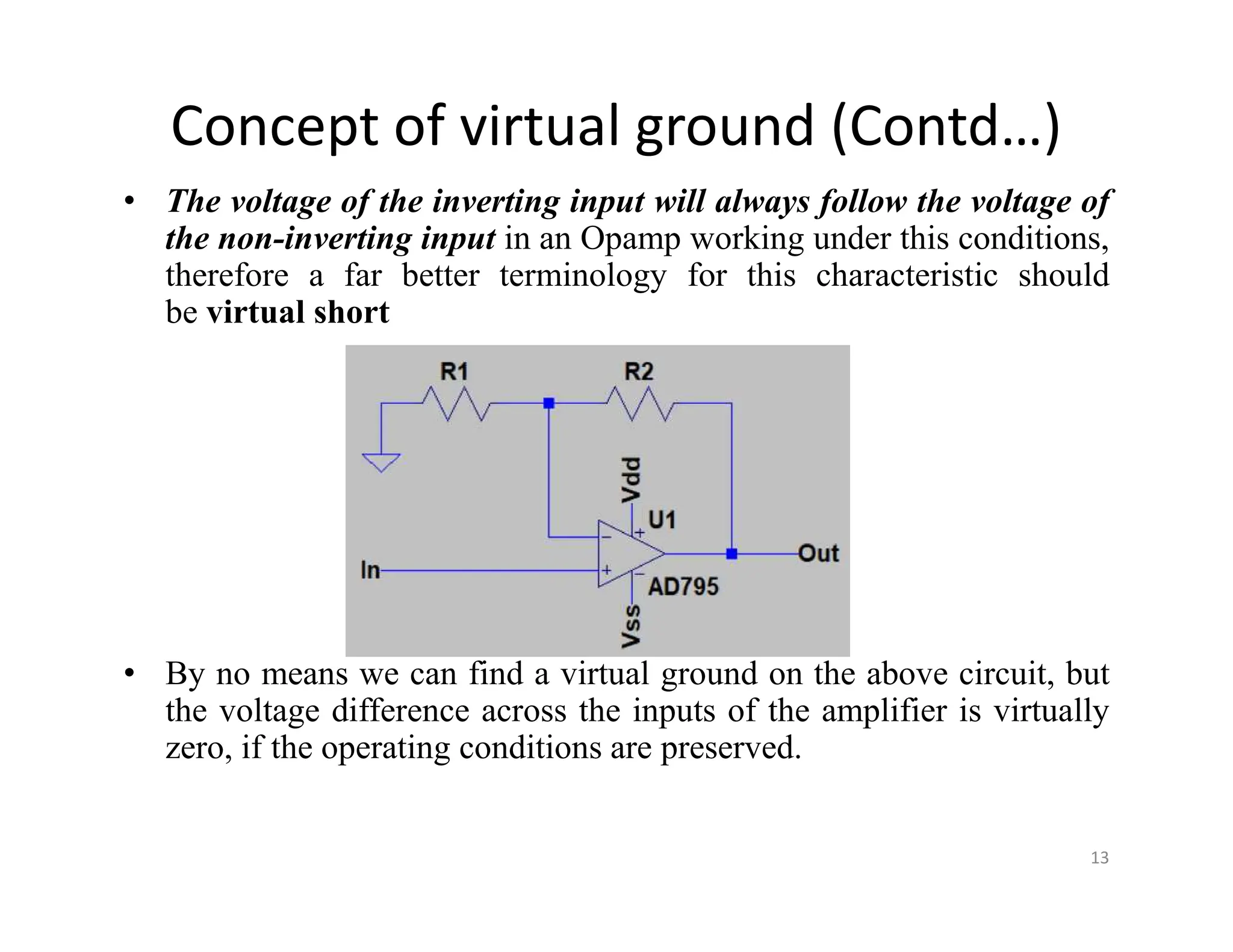
The document discusses log and antilog amplifiers using diodes and transistors, as well as the concept of virtual ground in electronics. A virtual ground is defined as a circuit node maintained at a steady reference potential that aids in circuit analysis, especially in operational amplifiers. The document also emphasizes the relationship between the voltage at the inverting and non-inverting inputs of an op-amp under specific conditions, referring to this characteristic as a virtual short.