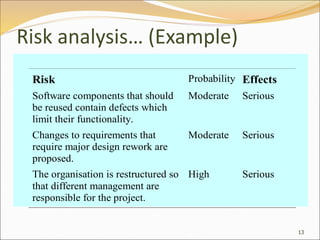
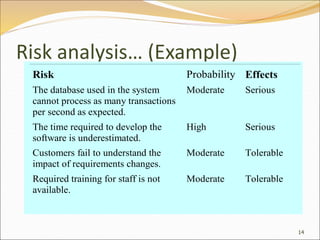
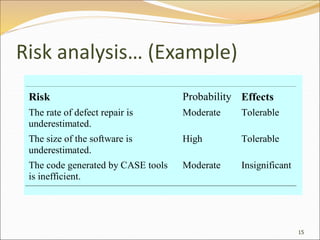
Risk management involves identifying risks that could affect a project, analyzing the probability and impact of those risks, developing strategies to manage the risks, and monitoring the risks over the course of the project. The document provides examples of common risk types for software projects, how to analyze risks based on probability and impact, strategies for avoiding, minimizing, or mitigating risks, and indicators that can show risks developing over time.