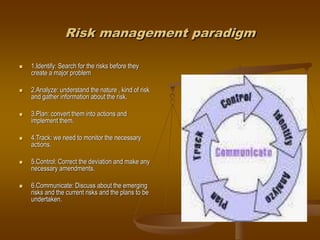
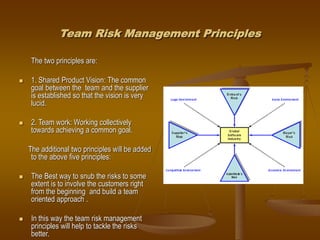
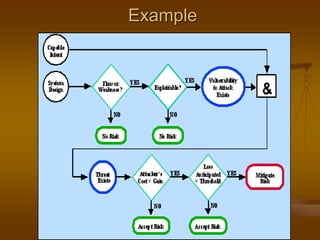
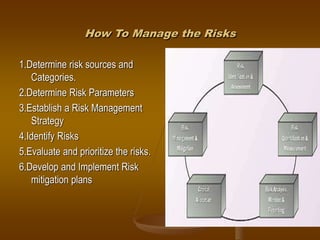
This document discusses risk management in software engineering projects. It defines risk as an uncertainty that could negatively impact a project. Risk management is the process of identifying risks, analyzing them, planning mitigation actions, tracking risks, controlling deviations, and communicating about risks. The key principles of risk management are taking a global perspective, having a forward-looking view, open communication, and integrating it into the overall project management process. Risk management should be continuous throughout the project life cycle using the main steps of identify, analyze, plan, track, control, and communicate.