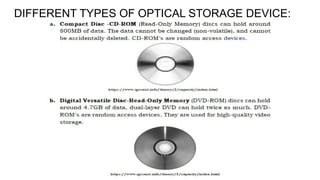
The document discusses the objectives of computer system servicing, including measuring components and their impact on performance. It highlights various types of memory, storage, and processing units in computers, elaborating on their functions and measurement units. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding these components for effective computer system assembly and performance evaluation.