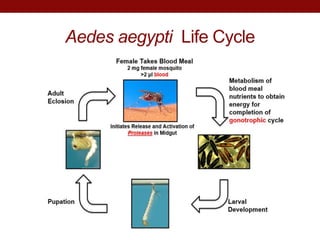
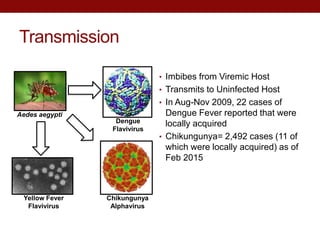
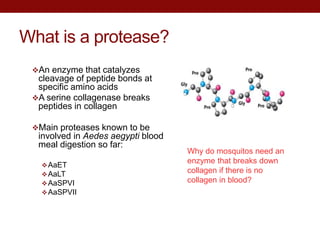
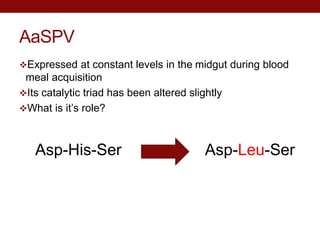
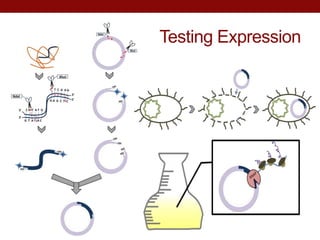
This document summarizes research on expressing and purifying serine collagenases from the Aedes aegypti mosquito in order to better understand their roles in blood meal digestion. Key findings include:
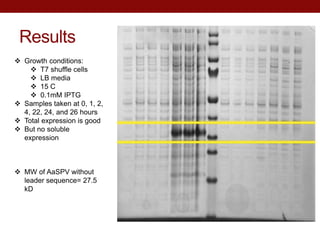
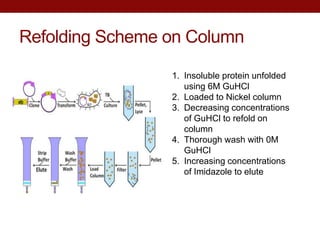
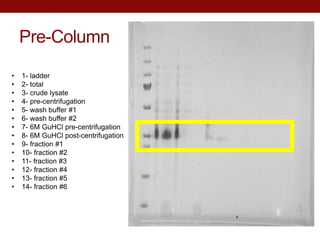
- AeSPV was successfully expressed in E. coli but not in soluble form, requiring refolding techniques for purification.
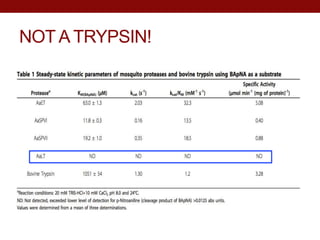
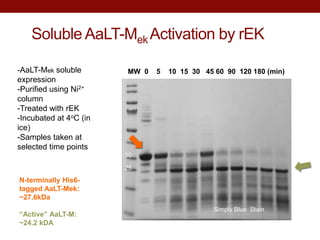
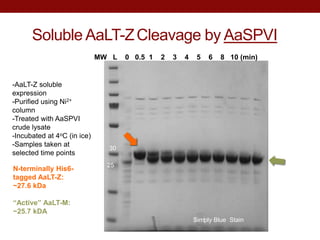
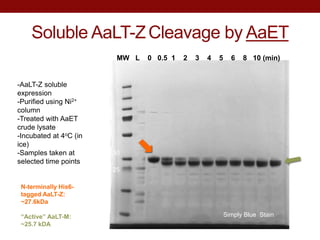
- AaLT was expressed both as a zymogen (AaLT-Z) and with an enterokinase cleavage site (AaLT-Mek) to activate it. Both forms were activated by different mosquito proteases.
- Future work will test the protease activities against specific substrates and elucidate their roles in blood meal digestion. This research could inform new mosquito-