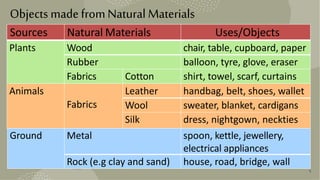
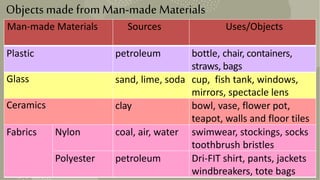
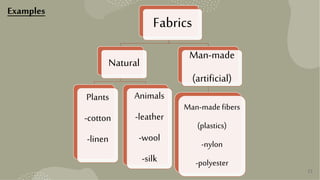
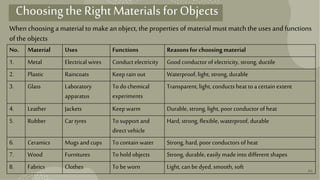
This document provides information about different types of materials used to make objects. It discusses natural materials like wood, metals, fabrics from plants and animals. It also discusses man-made materials like plastics, glass and ceramics. For each material, it describes the source, properties, examples of uses and disadvantages. The document aims to educate about classifying and choosing appropriate materials for different purposes.