The document outlines an Australian history course that evaluates how historians produce history and how students can independently conduct historical inquiry. It includes the following key elements:
- Students will examine how history has been recorded and approaches to history have changed over time through case studies and source materials.
- They will independently develop and carry out a semester-long historical investigation project on a topic like the arrival of the British in Australia.
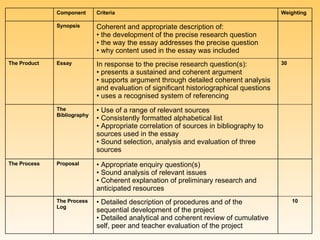
- The project will be assessed based on the process, proposal, bibliography, essay, and synopsis demonstrating their historical argument and analysis of sources.