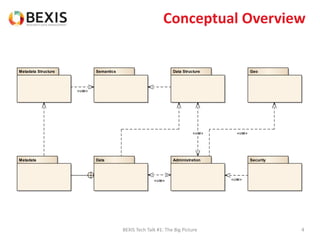
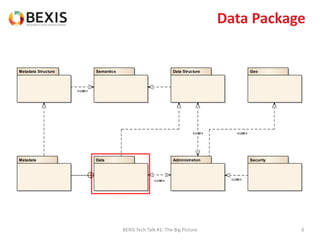
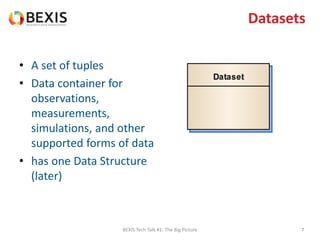
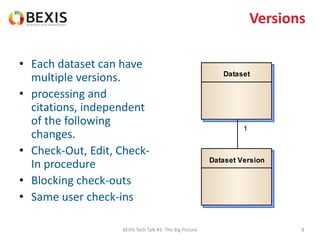
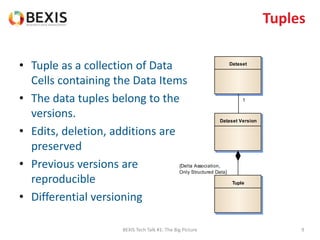
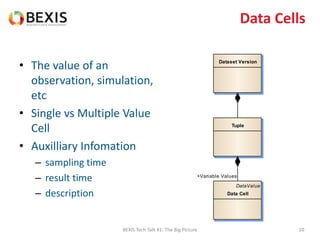
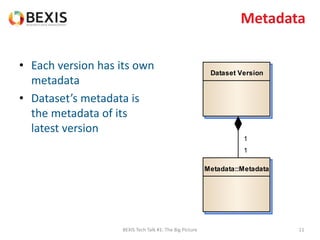
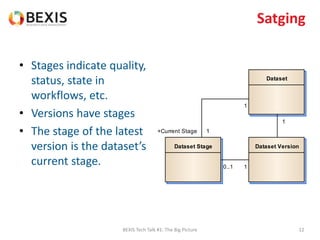
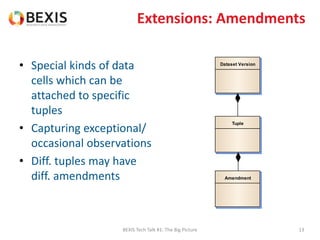
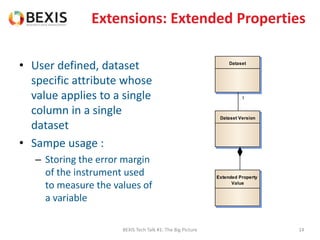
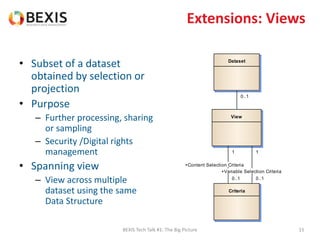
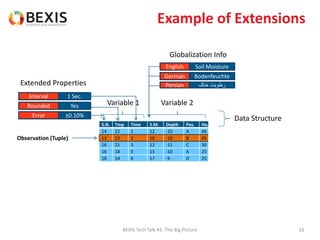
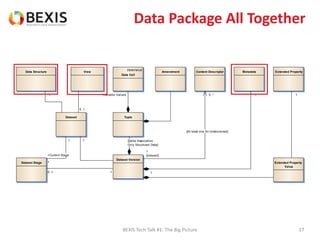
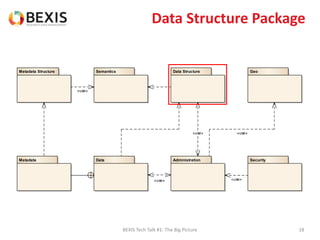
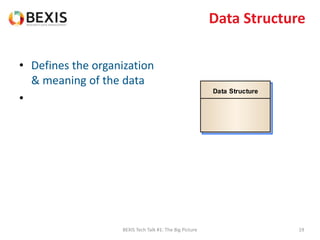
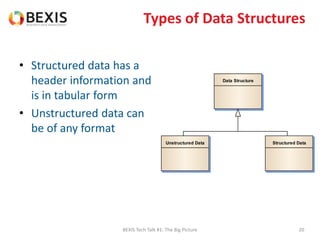
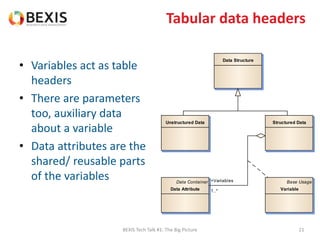
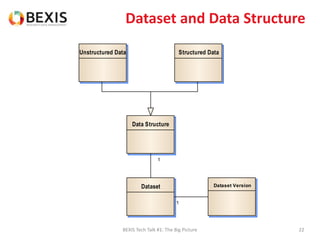
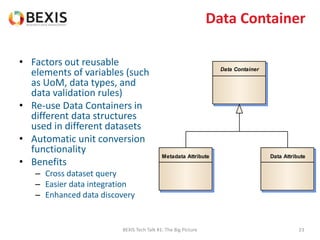
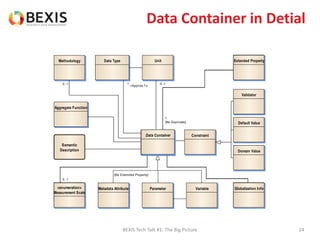
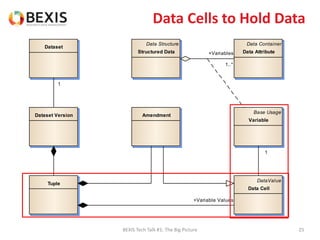
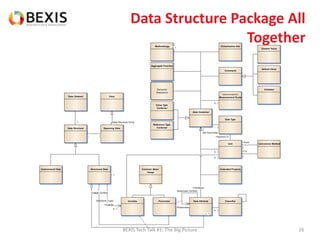
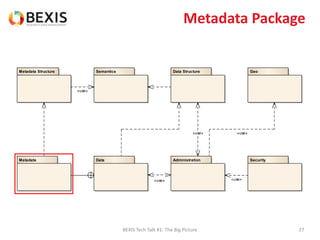
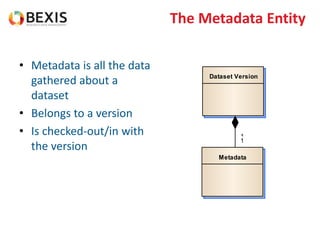
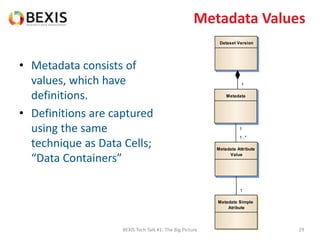
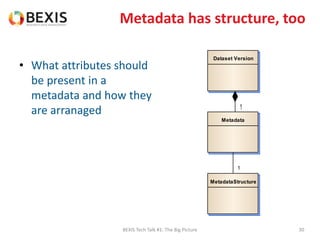
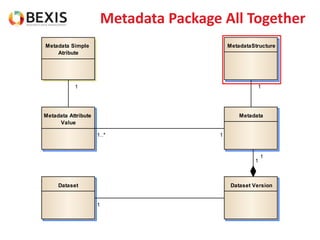
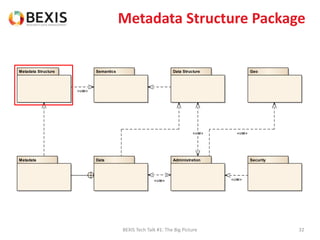
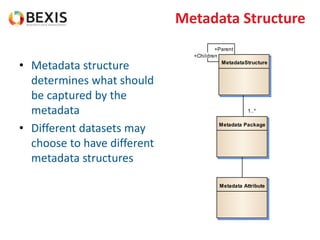
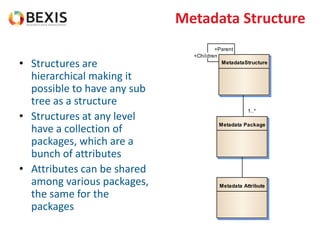
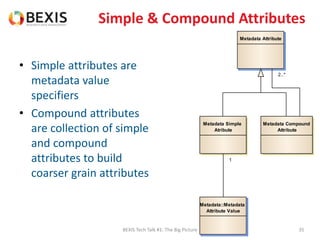
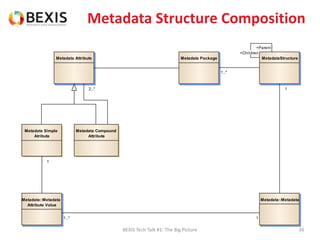
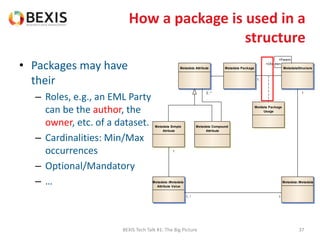
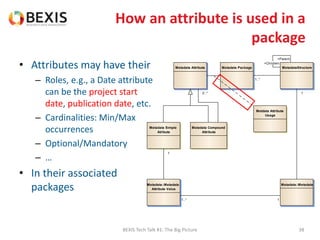
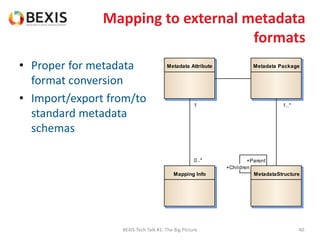
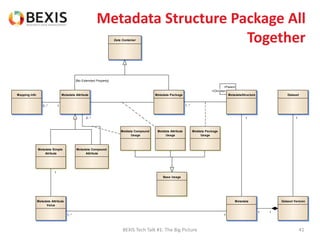
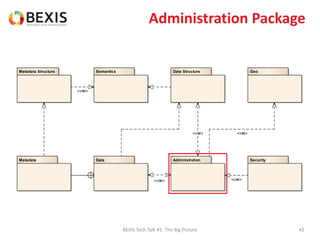
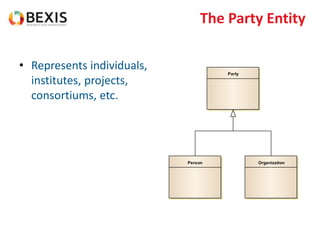
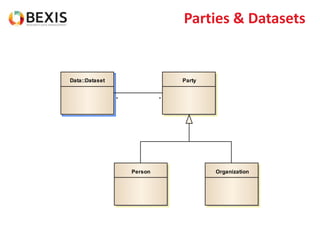
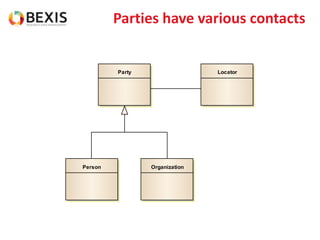
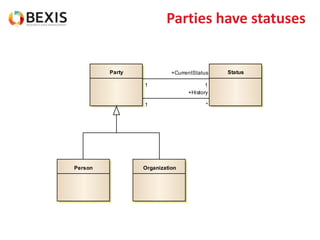
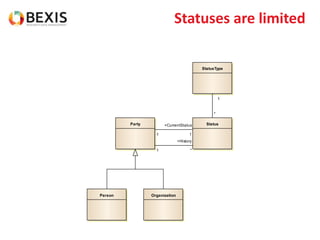
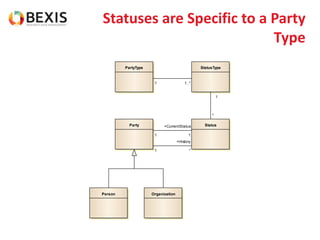
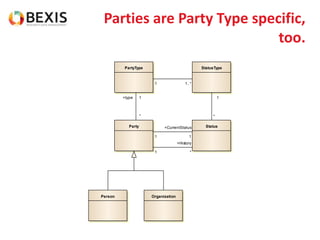
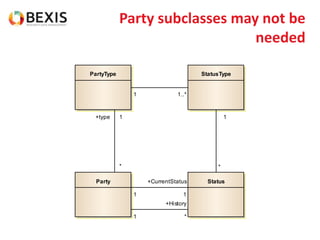
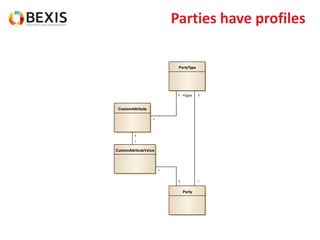
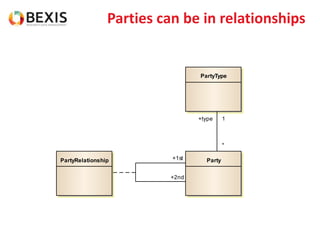
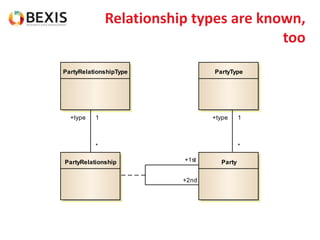
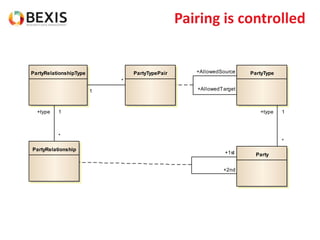
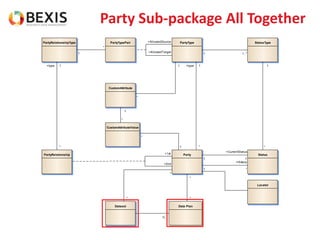
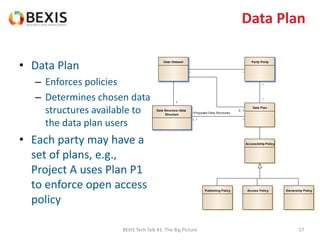
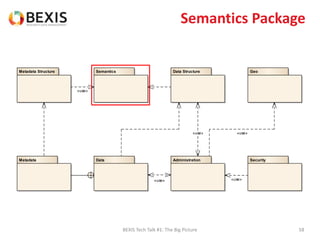
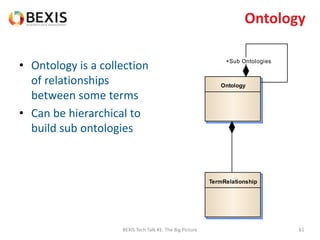
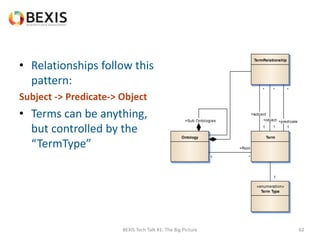
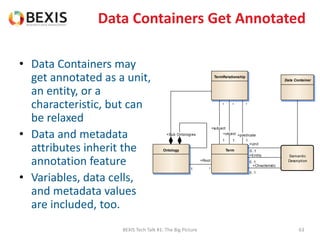
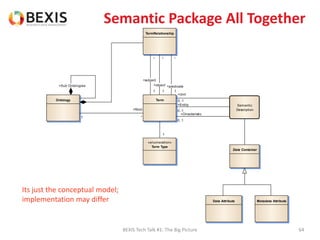
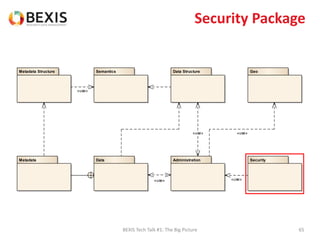
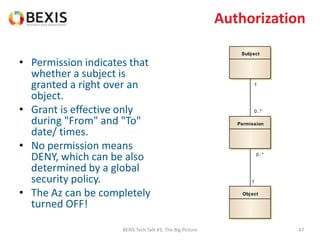
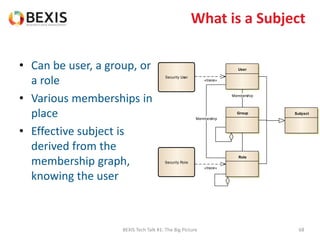
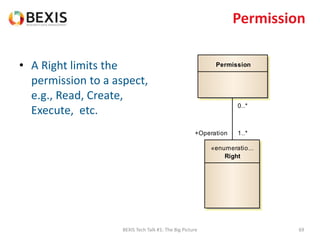
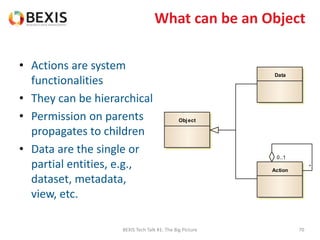
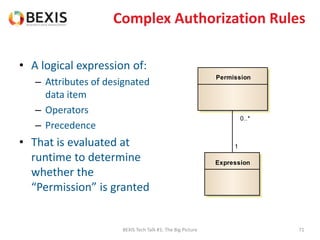
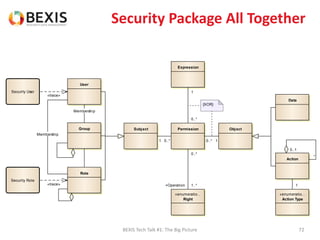
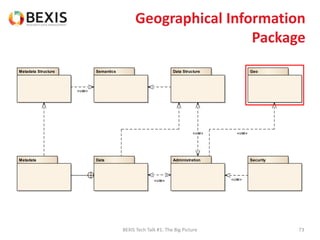
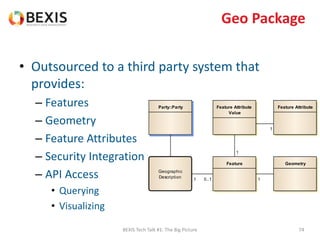
The document outlines the conceptual model for data lifecycle management discussed in the BEXIS Tech Talk series. It covers the requirements for flexible data structures, versioning, metadata management, and the organization of datasets, including data containers and attributes. Additionally, it highlights the importance of semantic annotation, security measures, and the framework for managing parties and relationships within the data management ecosystem.