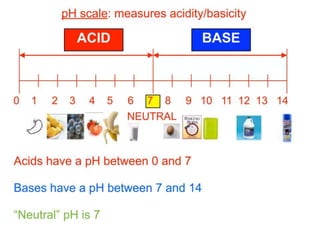
The document discusses naming rules for binary acids, oxyacids, and hydrated ionic compounds. It explains that binary acids contain hydrogen and a nonmetal and their names start with "hydro-", while oxyacids contain hydrogen and an oxyanion with the acid name based on the polyatomic ion. The document also outlines naming conventions for hydrated ionic compounds, which contain water molecules as part of their crystal structure.