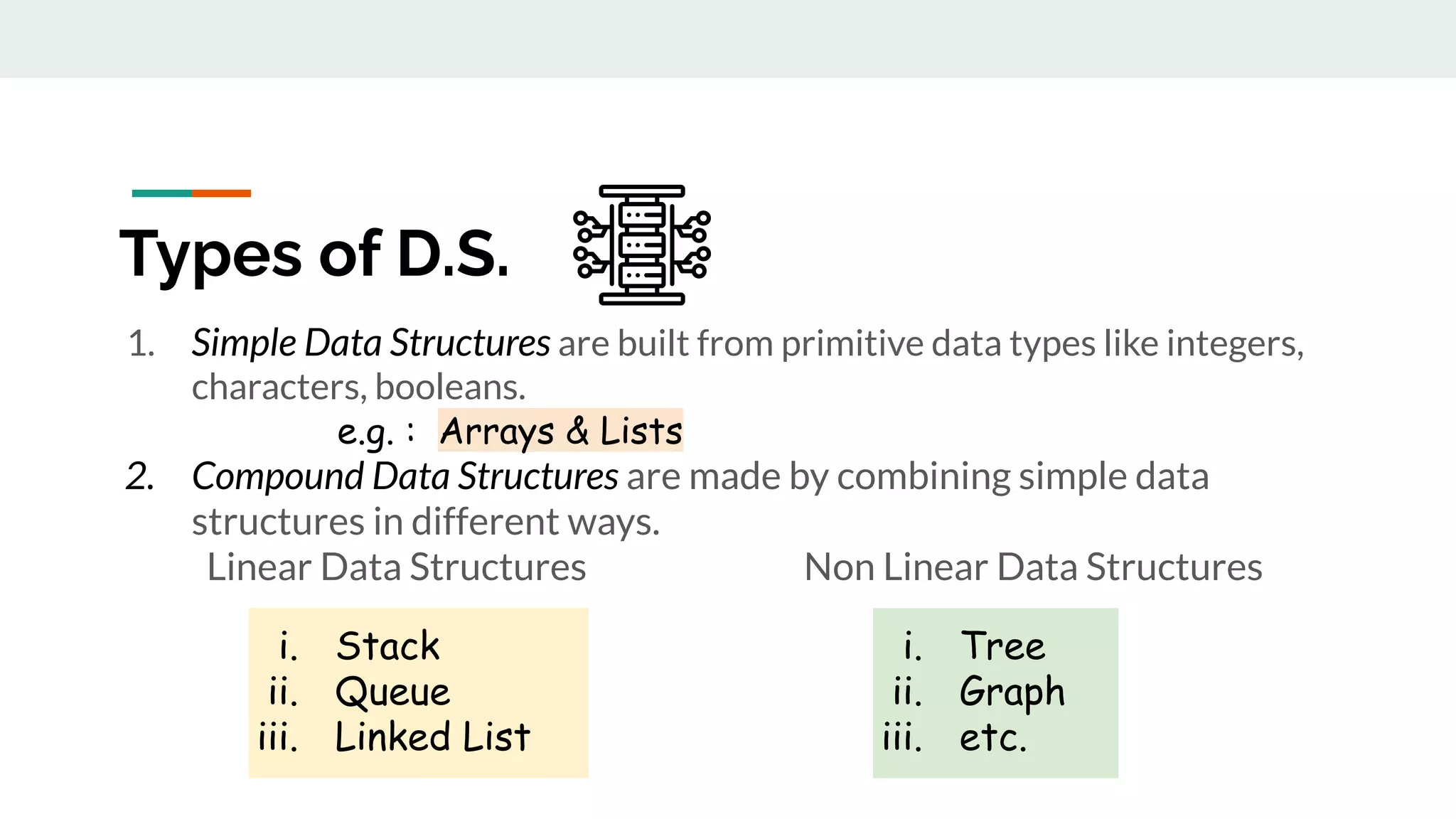
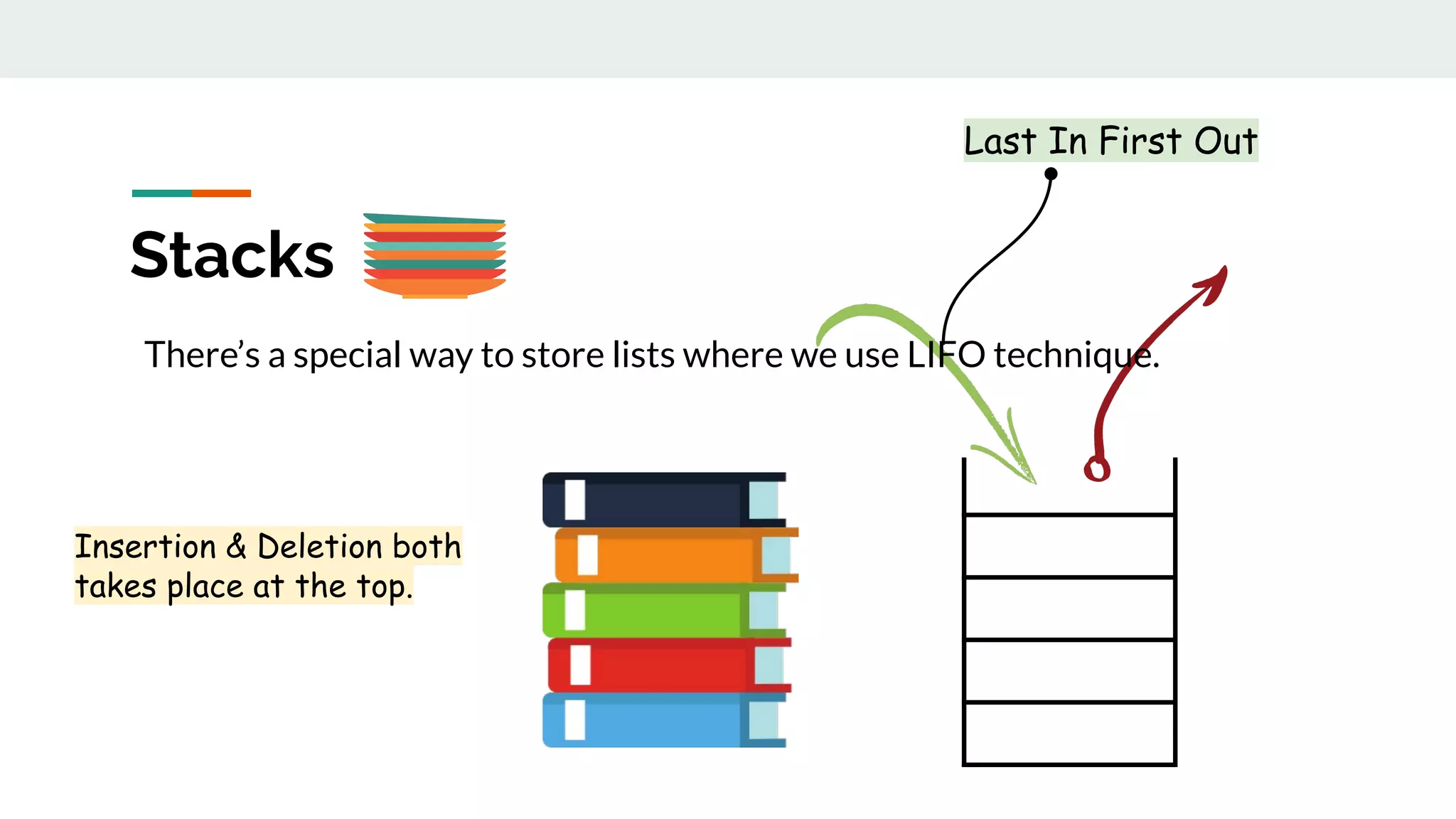
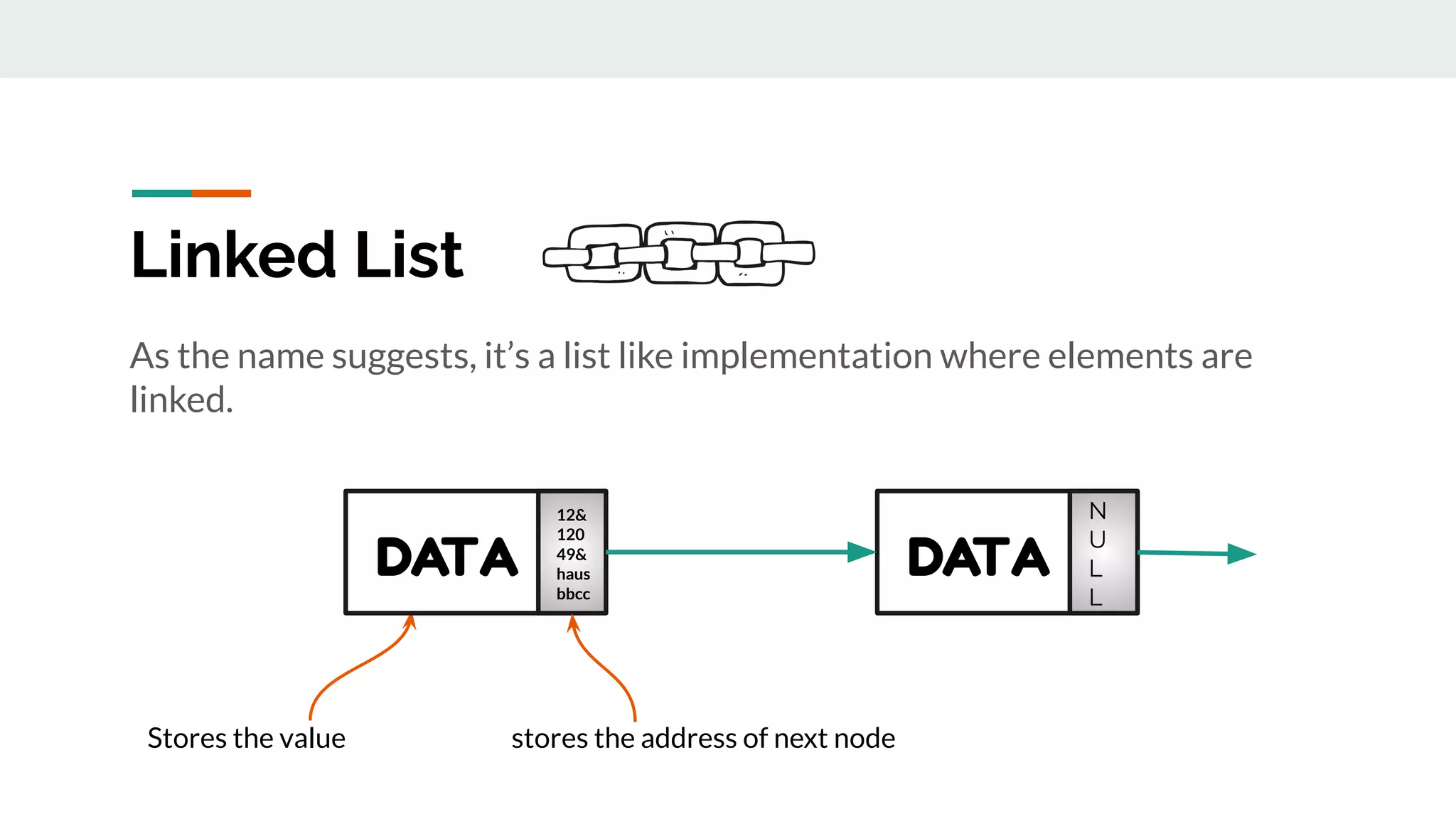
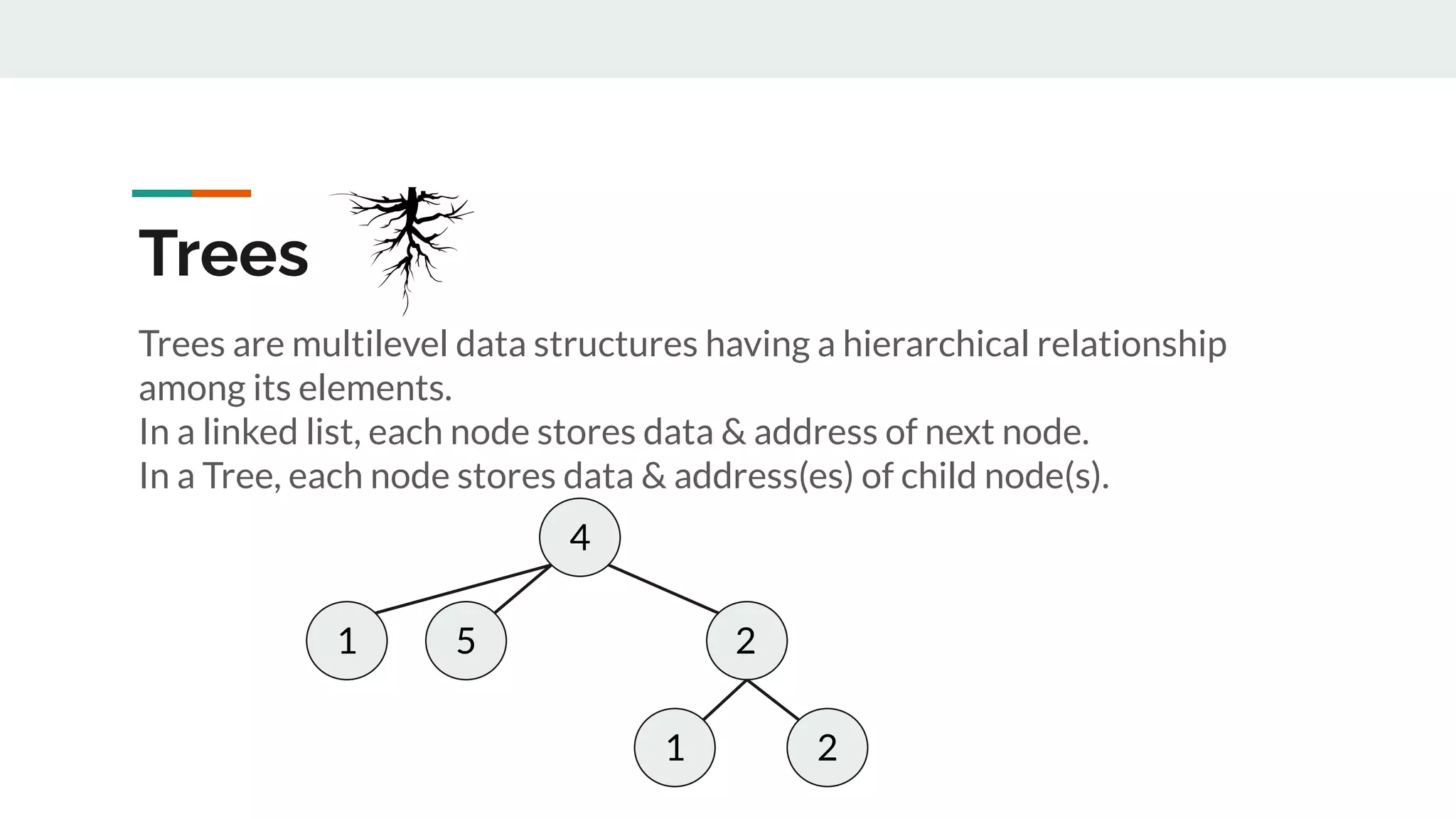
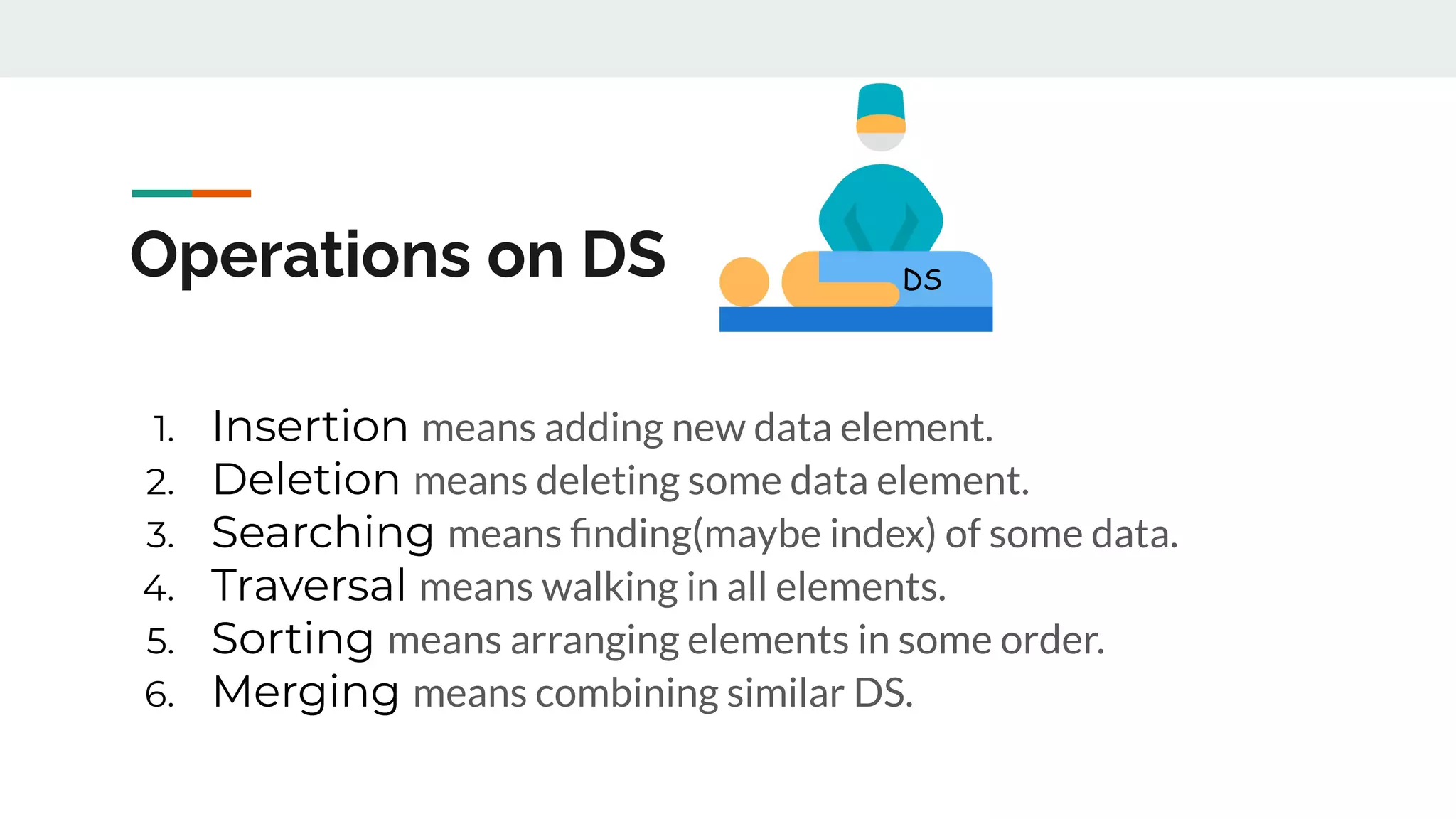
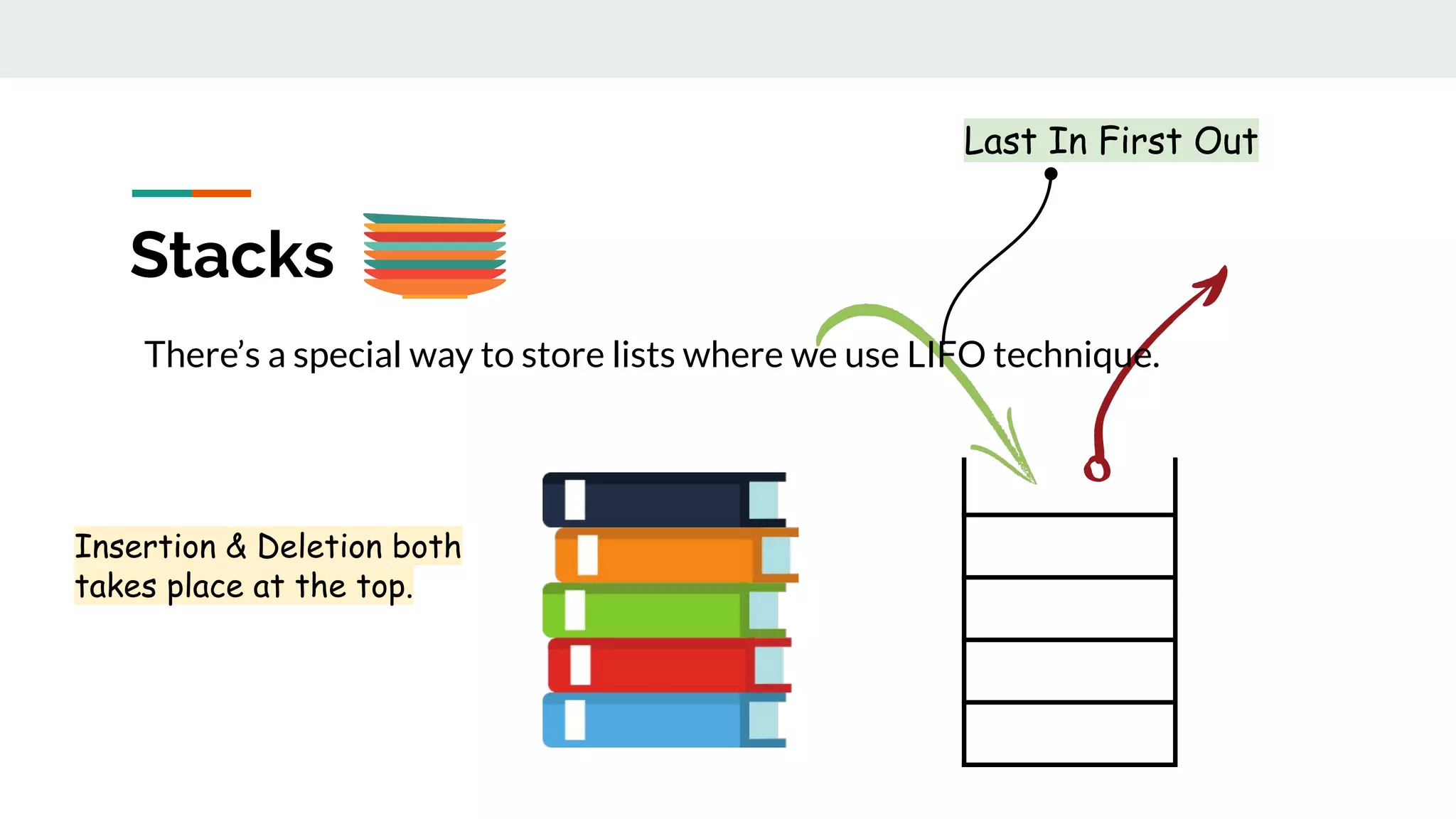
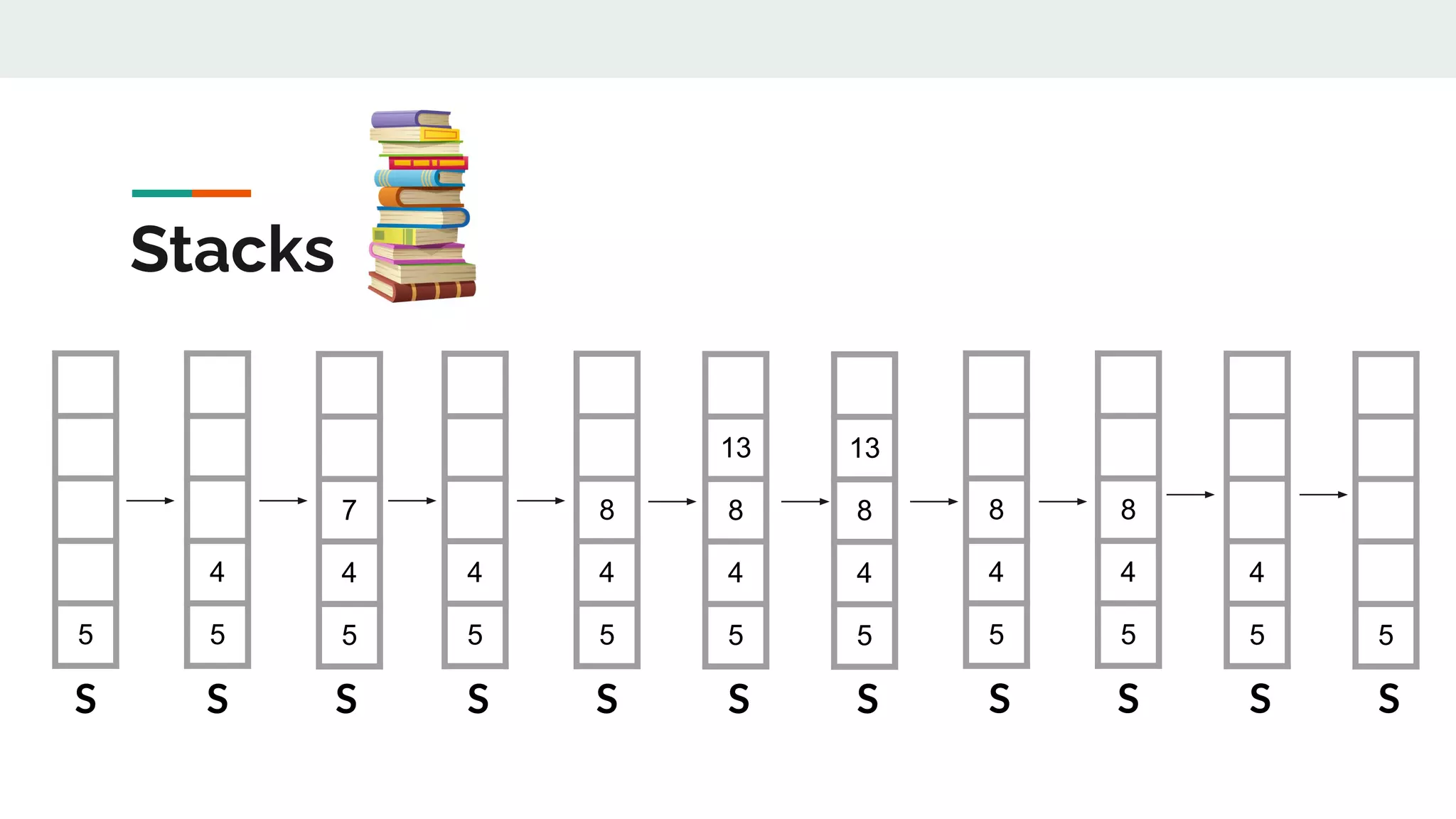
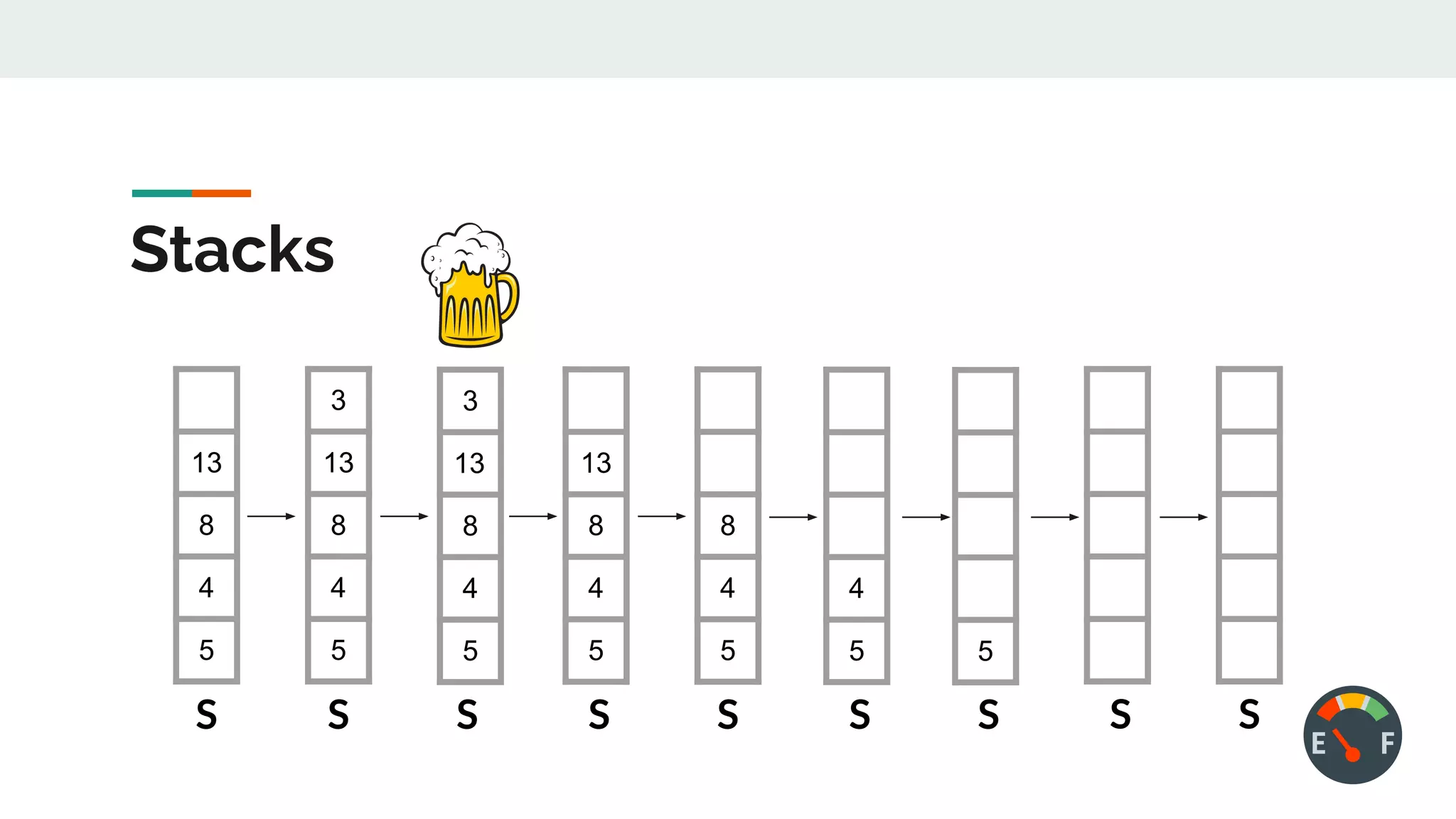
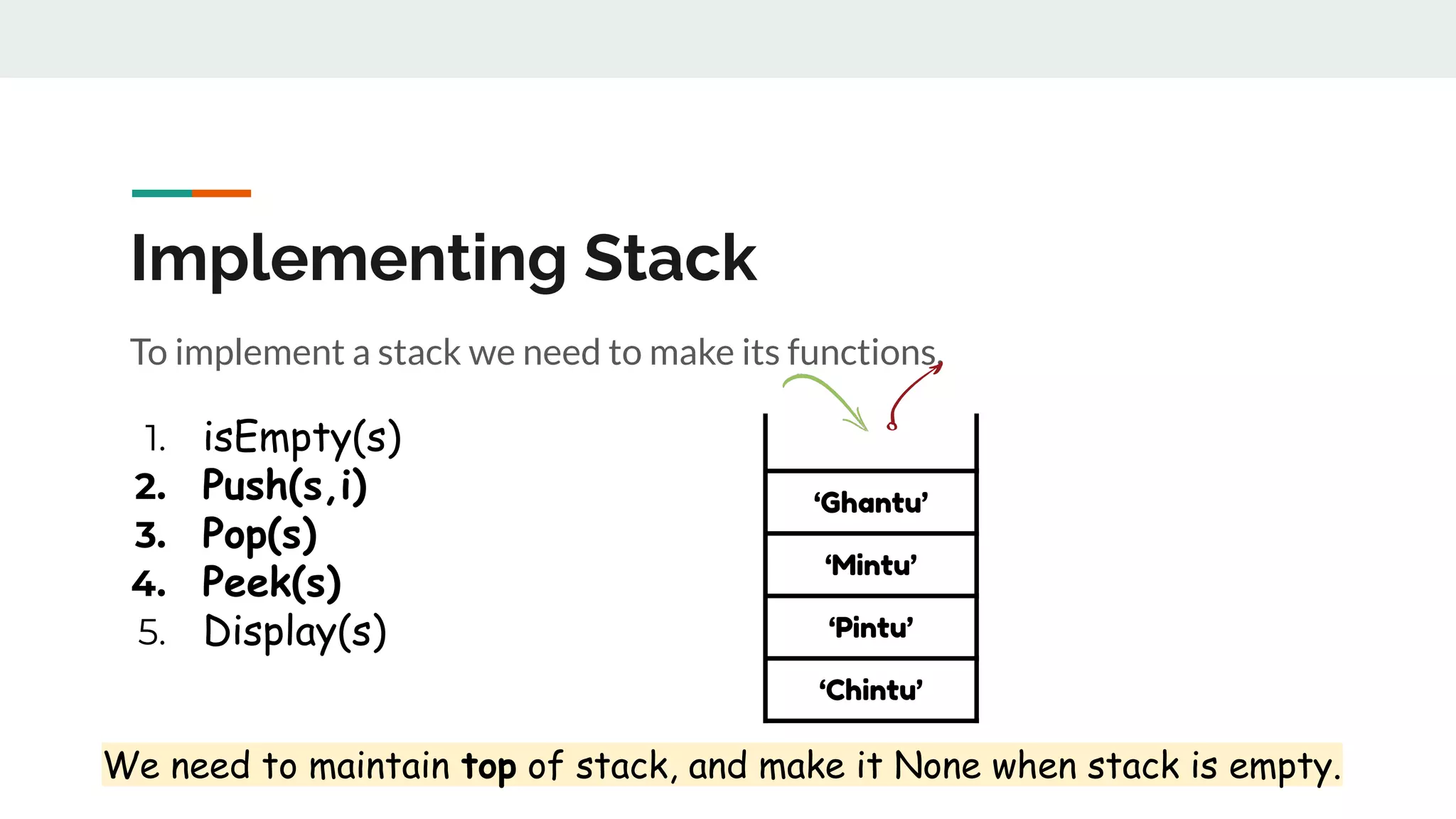
This document discusses data structures and provides examples of common linear data structures like arrays, stacks, queues, and linked lists. It explains that data structures can be simple, using primitive types, or compound, combining simple structures. Linear data structures store elements in a linear order and support insertion and deletion at one or both ends. Examples provided include stacks, which use a last-in first-out approach, and linked lists, where each node stores data and a link to the next node. Code is presented for implementing a stack data structure with functions like push, pop, peek and isEmpty.