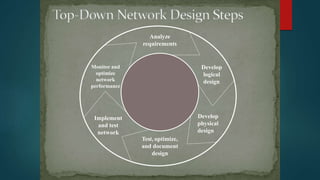
The document discusses network design approaches and processes. It emphasizes understanding business needs and goals, and using a top-down approach to network design that begins with logical design before physical design. Key phases discussed include analyzing requirements, logical design, physical design, testing and optimization, and ongoing network management. The document stresses the importance of understanding the business, applications, users and technical constraints to develop a network design that meets organizational objectives.