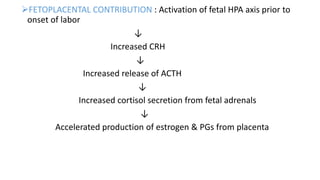
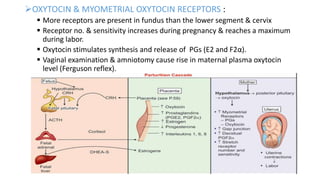
The document discusses the process of labor and delivery. It defines labor as the series of events that lead to the expulsion of the fetus, placenta, and membranes from the uterus through the vagina. Normal labor is spontaneous in onset, involves a vertex presentation, and does not prolong unduly without complications. Abnormal labor is referred to as dystocia. The document then examines the various hormonal and physical changes involved in initiating and progressing labor, including uterine distension, fetal contributions, estrogen, progesterone, prostaglandins, and oxytocin. It describes the stages of labor and how contractions become more frequent, intense, and prolonged over time.