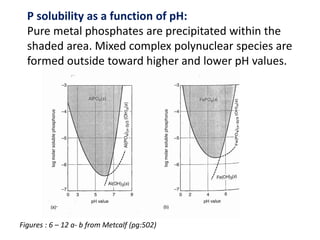
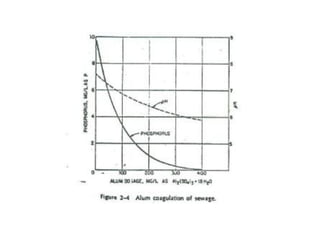
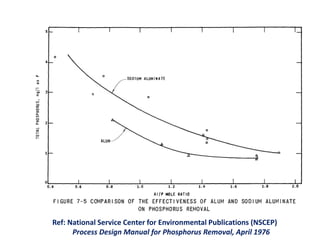
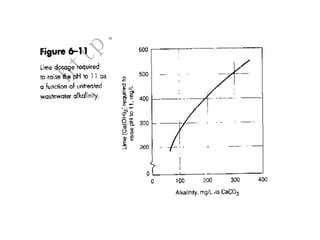
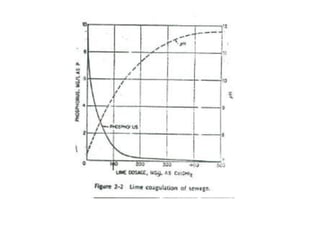
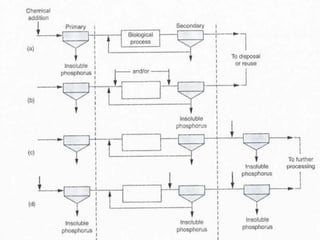
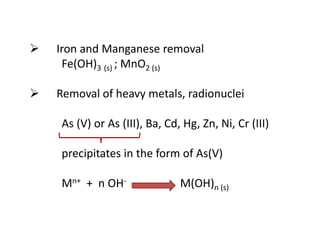
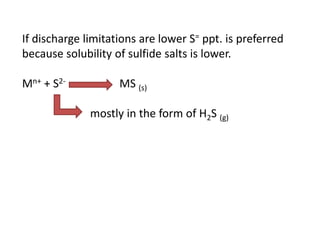
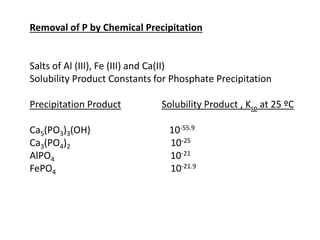
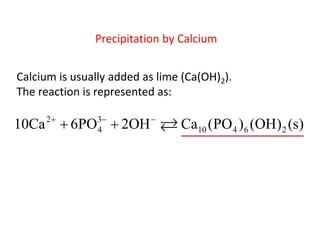
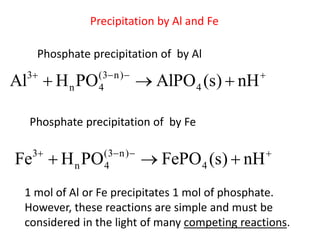
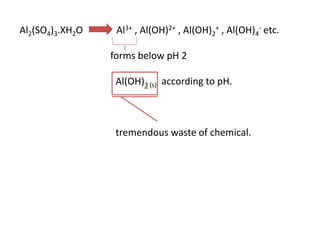
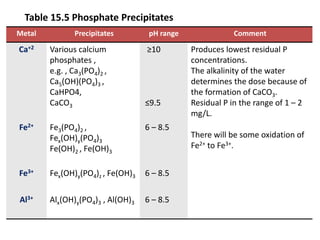
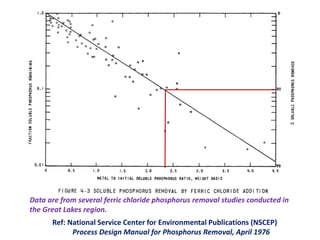
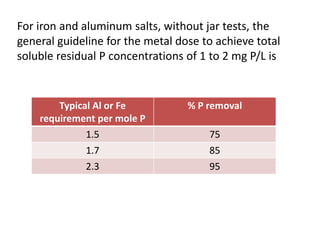
This document discusses chemical precipitation for phosphorus removal from water and wastewater. It describes how calcium, aluminum, and iron are commonly used to chemically precipitate phosphorus in the forms of orthophosphate, condensed phosphates, and organic phosphates. Optimal pH ranges and solubility products for various phosphate precipitates are provided. Factors affecting chemical dosing requirements like pH, alkalinity, and initial phosphorus concentration are also summarized.














![Al3+ + PO43-
AlPO4
Ksp = [Al3+][PO43-]
Ksp = [Al3+](α3.Ptotal)
[PO43- ]
α3 =
[H3PO4 ] + [H 2 PO4- ] + [HPO4 = ] + [PO 43- ]
α3 = fraction of PO43- in total P species.
PT =
K sp
α3 . [Al3+ ]
[Al3+]
as pH
and
α3 as pH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-131220020542-phpapp01/85/13-phosphorus-removal-by-chem-ppt-27-320.jpg)