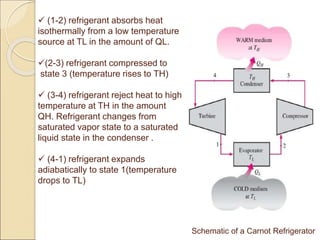
The document explains the reversed Carnot cycle, which involves the reversal of heat and work interactions to create a highly efficient refrigeration cycle. It describes the cycle's four main processes: adiabatic compression, isothermal compression, adiabatic expansion, and isothermal expansion, along with related thermodynamic properties and behaviors. However, it notes that practical implementation is limited due to the contrasting operational speed requirements of the adiabatic and isothermal processes.