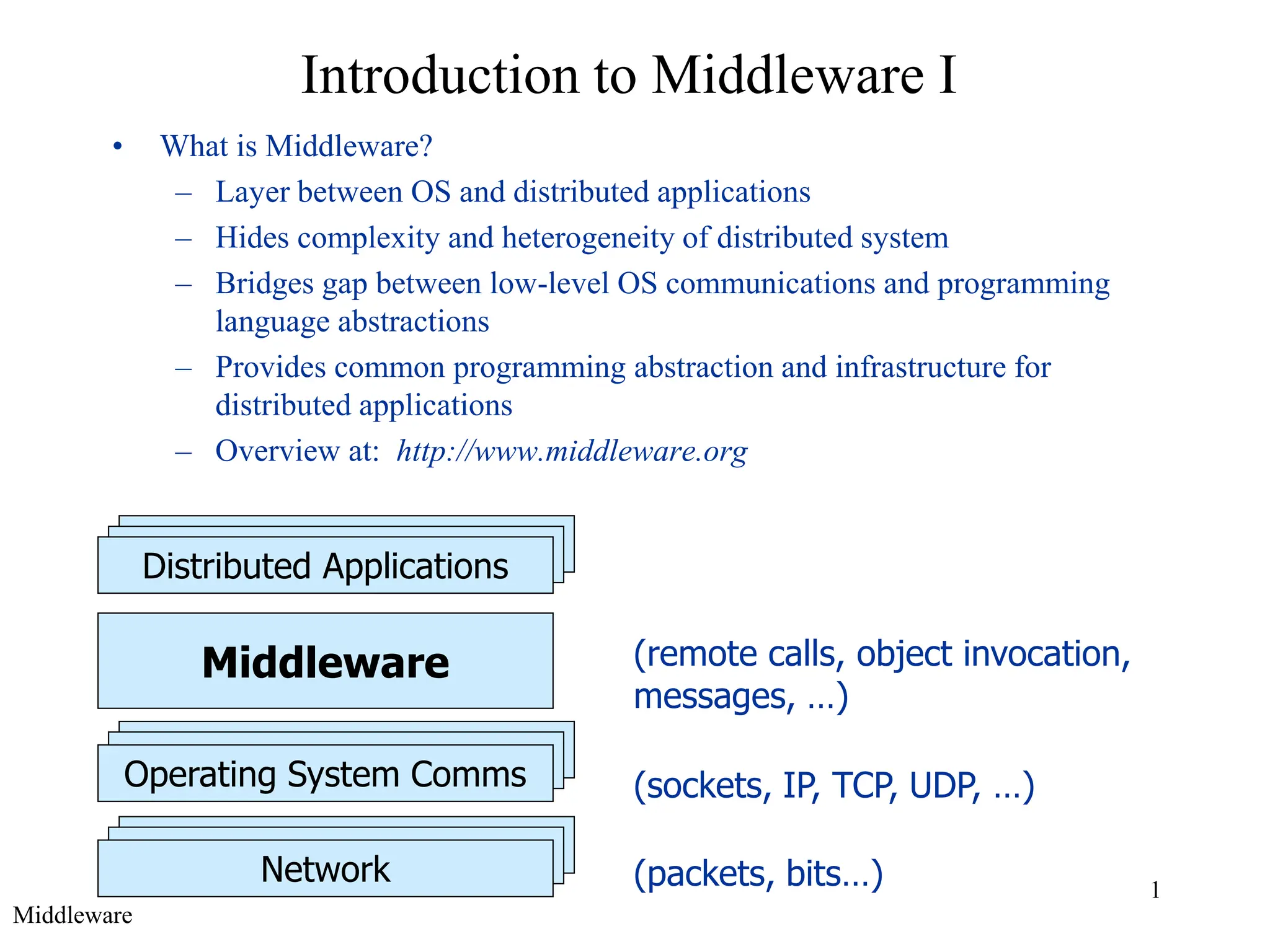
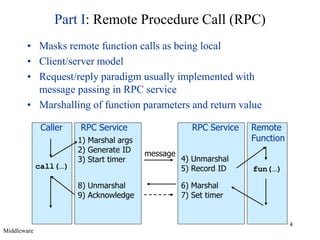
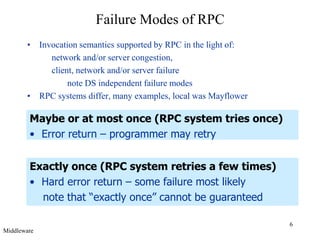
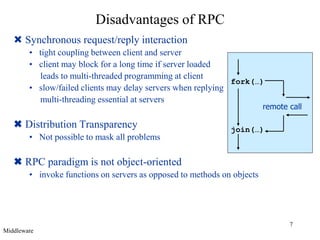
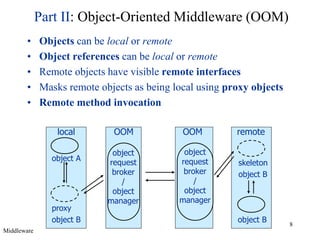
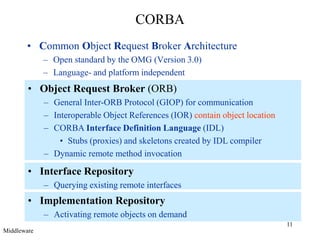
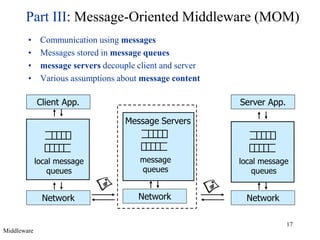
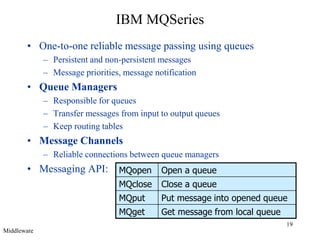
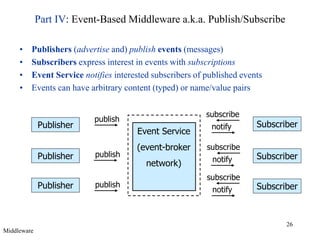
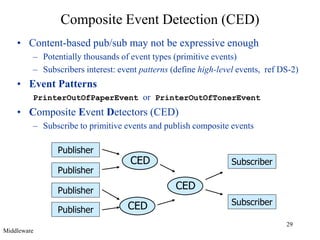
Middleware provides an abstraction layer between distributed applications and operating system communication mechanisms. It hides the complexity of distributed systems and enables different styles of communication including remote procedure calls, object-oriented remote method invocation, message-oriented asynchronous messaging, and event-based publish-subscribe interactions. Common examples of middleware technologies discussed are RPC, CORBA, Java RMI, message-oriented middleware like JMS, and event-based systems using content-based routing of published events to subscribed interests. Middleware aims to support scalable many-to-many communication patterns while providing programming models suited to distributed applications.