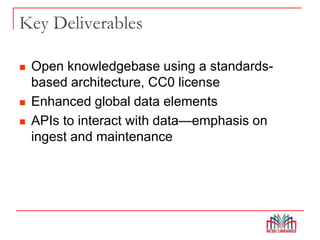
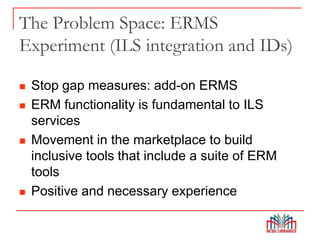
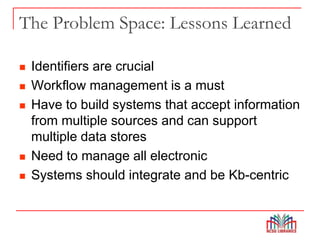
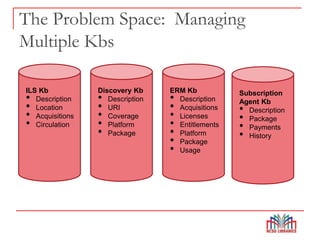
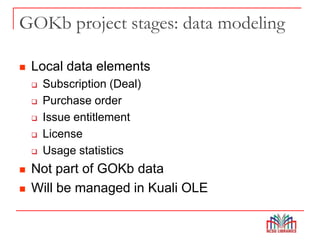
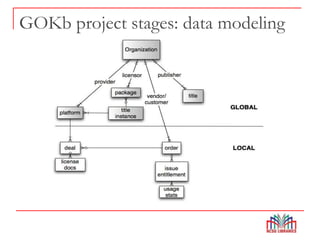
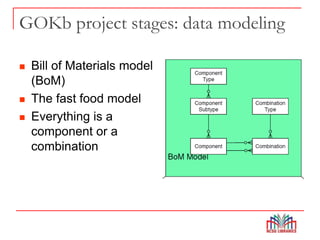
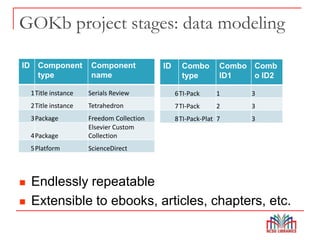
The Global Open Knowledgebase (GOKb) is a community-maintained knowledgebase being developed with funding from the Mellon Foundation to integrate with the open source library system Kuali OLE. GOKb will contain standardized global data elements for managing electronic resources and will use APIs to allow interaction with and maintenance of the data. Its goals include enhancing data sharing between libraries and improving the management of electronic resources through tight integration with library systems.