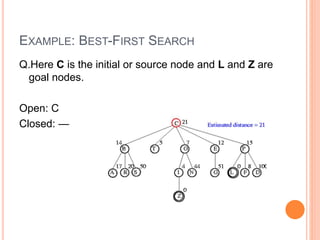
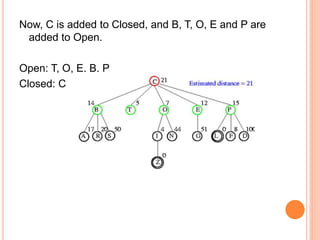
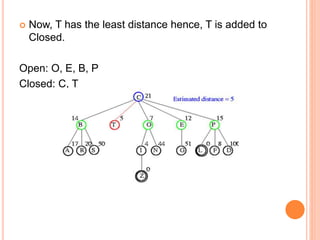
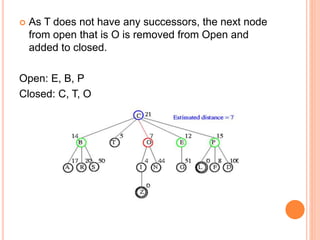
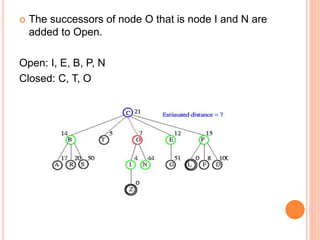
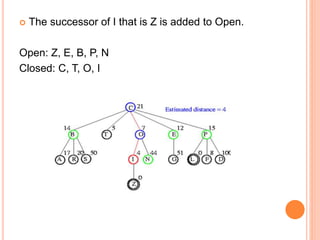
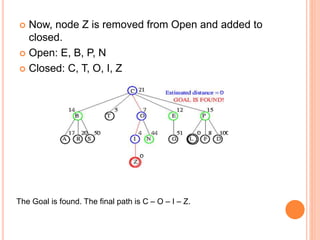
Best first search is an informed search algorithm that traverses the search tree by choosing the most promising node first. It uses an evaluation function to determine which node to expand next based on estimated distance to the goal. It maintains an open list of generated nodes not yet expanded, sorted by estimated cost. At each step, it removes the node with lowest estimated cost from the open list and expands it, adding any generated successors to the open list. This allows it to combine benefits of breadth-first and depth-first search by prioritizing promising paths over less promising ones. An example is provided tracing the steps of best first search to find the goal nodes L and Z from the starting node C in a search tree.