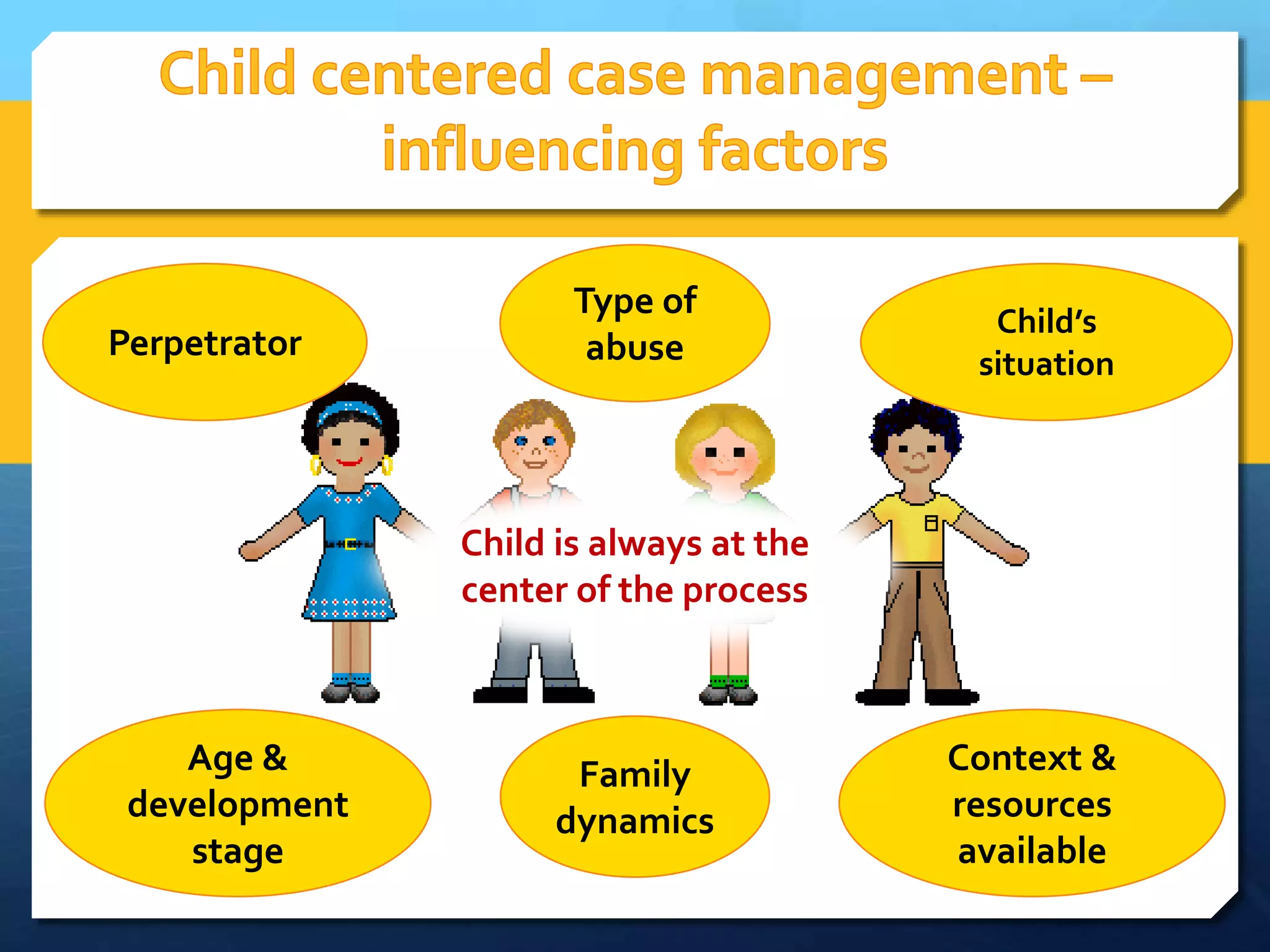
The document discusses the case management process for child survivors of sexual abuse. It describes the stages of the process, including intake and assessment, developing an action plan, implementation, follow up, and case closure. Key points are empowering children and caregivers through information sharing, ensuring the child is at the center, and balancing confidentiality and the child's best interests. Case management requires communication between the child, caregivers, and service providers and is not a linear process. Documentation is important throughout.