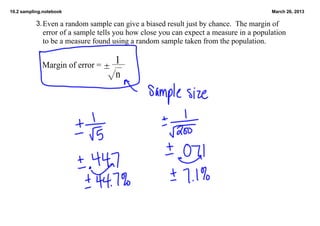
This document discusses different types of sampling methods used in surveys: convenience samples are those easily accessible to researchers; self-selected samples involve volunteers; systematic samples select every nth participant; and random samples give all participants an equal chance of selection. It provides examples of each type, noting whether samples are likely biased, and how margin of error relates to sample size and population estimates.