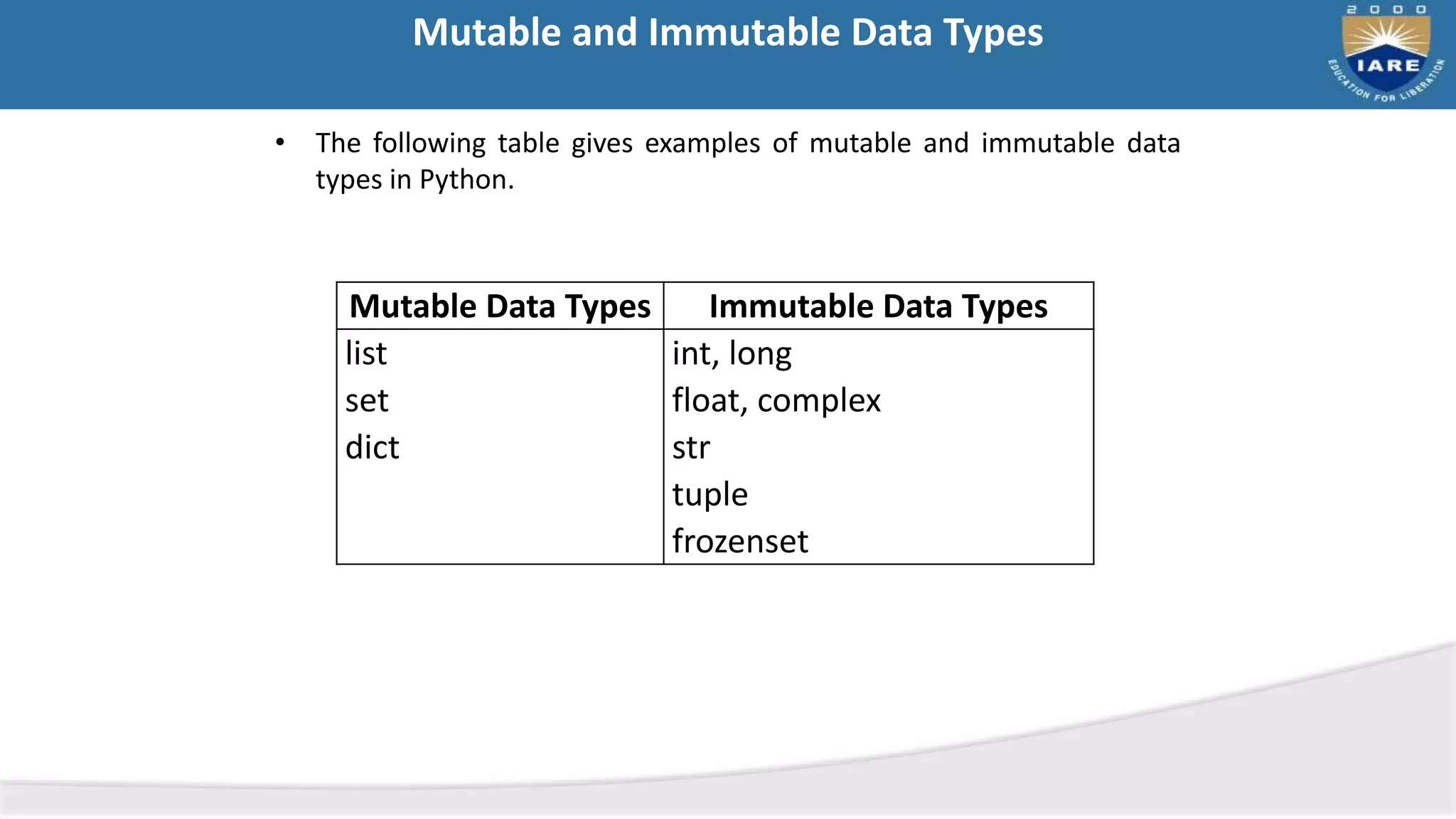
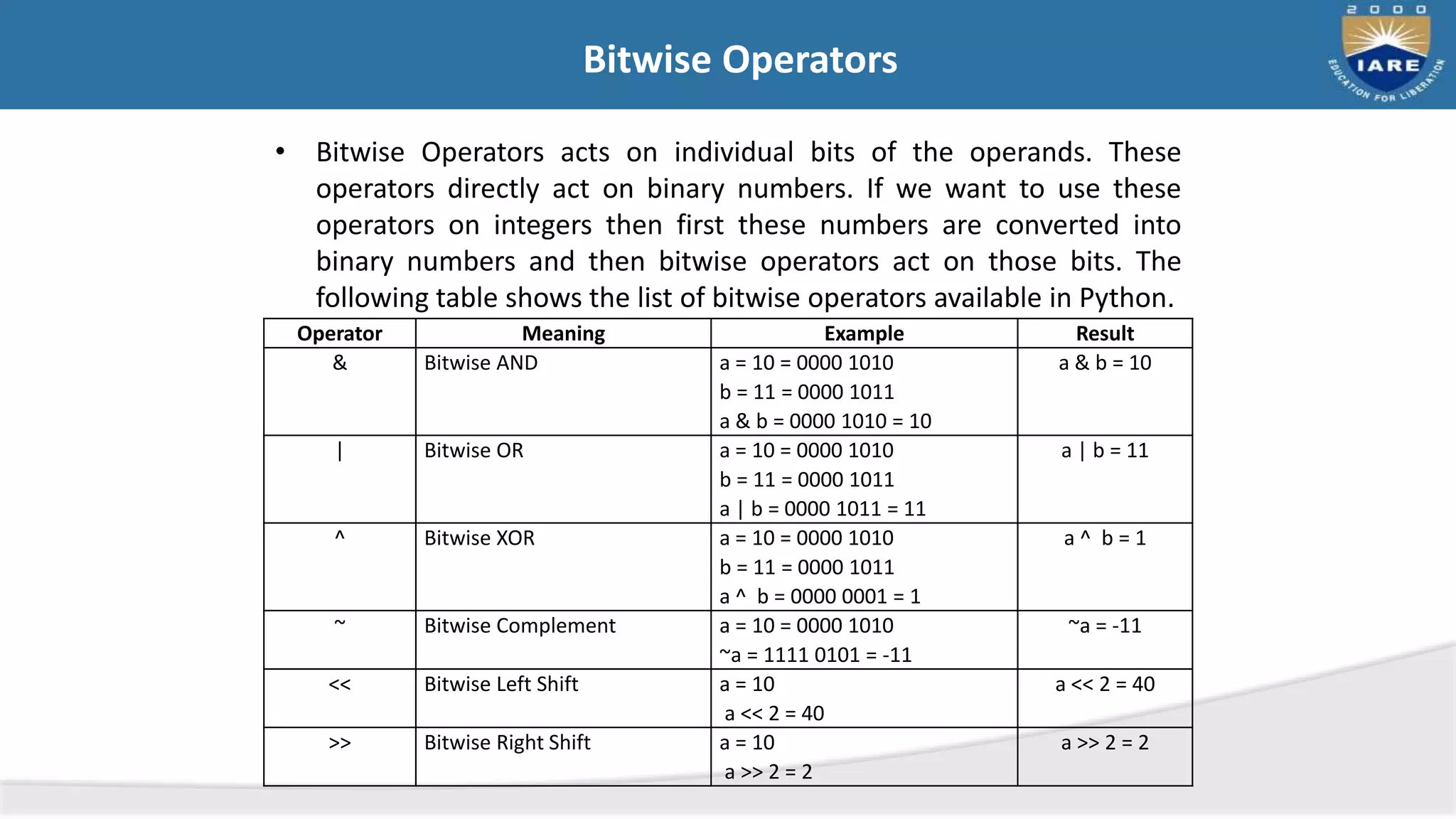
This document discusses Python data types and operators. It describes mutable and immutable data types in Python and provides examples. It then defines and provides examples of different types of operators in Python including arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, bitwise, boolean, and membership operators. Finally, it discusses operator precedence and provides a table showing operator precedence from highest to lowest.